-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Colorectal Cancer/ Colon Cancer
Colorectal Cancer/ Colon Cancer
Best Colorectal/Colon Cancer Treatment in Hyderabad, India
Colorectal cancer, also known as colon cancer, is a type of cancer that begins in the large intestine (colon) or the rectum of the body. The colon and the rectum make up the lower part of the human digestive system.
Colon Cancer generally occurs in older adults. However, it can even occur at any other age as well. Colon cancer generally begins with noncancerous clumps of cells known as polyps. These cells are formed inside the colon. Eventually, these polyps can turn into cancerous cells.
The symptoms and outlook of colon cancer generally depend on the size and stage of cancer during diagnosis. This is a common type of cancer.
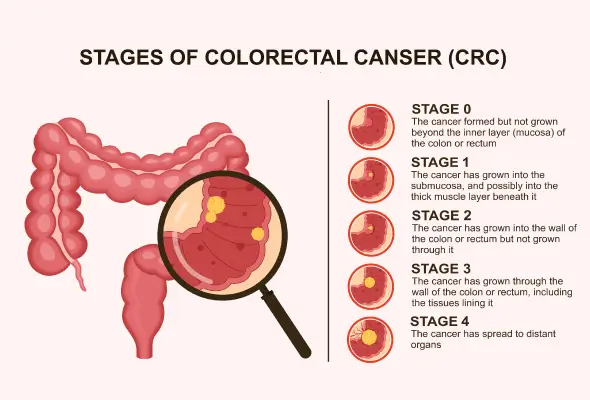
Stages of Colorectal Cancer
The stages of colorectal cancer can be determined through the process of staging. This will help doctors to understand the stage of cancer. Accordingly, the doctor will suggest the necessary treatments. There are various stages of colorectal cancer such as:
- Stage 0: This stage is also known as carcinoma in situ where the abnormal cells are situated only in the lining of either the colon or rectum.
- Stage 1: In this stage, the abnormal cells grow from the lining of the colon or rectum into the muscle layer. Till now, the tumor will not spread to other parts of the body.
- Stage 2: In this stage, cancer begins to spread to the walls of the rectum or colon or the nearby tissue. However, at this stage, cancer still doesn't affect the lymph nodes.
- Stage 3: In this stage, cancer eventually moves on to the lymph nodes while still not affecting the other organs/parts of the body.
- Stage 4: This is the last stage of colorectal cancer. In this stage, cancer begins to move to other parts of the body including the lungs and liver.
Types of Colorectal Cancer
There are many types of colorectal cancer. One of the most common types of cancer is adenocarcinoma. Adenocarcinoma refers to the tumor that begins in the lining of the internal organs. This type of cancer can even form in different organs like the breast or the lungs. A few other types of colorectal cancer can include:
- Gastrointestinal Stromal Tumors (GIST): This refers to the tumor that begins in the muscle tissue of the digestive tract. However, this tumor rarely occurs in the colon. They start a noncancerous tumor but can become cancerous over time which is known as sarcomas.
- Lymphoma: This refers to the type of cancer which generally begins in the lymph node of the immune system and moves on to the colon or rectum. However, this cancer can even develop in the colon or rectum initially.
- Carcinoids: Carcinoids refer to a tumor that begins in the special hormone-producing cells in the intestine. This type of cancer generally has no symptoms and can only be treated through surgery.
- Turcot Syndrome: Turcot syndrome is a rare disorder that can create colon cancer, colorectal polyposis, and brain tumors. Individuals with this syndrome have been found with the mutations MLH1, APC, and MSH2 in different genes.
Symptoms of Colorectal Cancer
Symptoms related to colorectal cancer can be rare and vague. Colon cancers and polyps that are detected at an early stage generally have no symptoms. However, if they are detected at a later stage there are a few common symptoms and signs such as:
-
Diarrhea, Constipation, or narrowing of the stool that can last for a while
-
Dark stools, rectal bleeding, or blood in the stool
-
Gnawing or cramping stomach ache
-
Decreased appetite
-
Vomiting
-
Weight Loss
-
Fatigue and Weakness
-
Jaundice
Though the above-mentioned symptoms are referred to as common, these may vary for each individual. Some of the symptoms mentioned above can even be due to other infections or diseases such as hemorrhoids and inflammatory bowel disease. If you have any of the above-given signs or symptoms make an appointment with your doctor immediately to rule out all the possibilities.
Causes of Colon Cancer
Most cases of colon cancer occur without a clear understanding of their exact cause. The development of colon cancer is attributed to alterations in the DNA of colon cells. DNA serves as the instructional guide for cell behavior, and these alterations prompt abnormal cell multiplication and prolonged survival, disrupting the natural life cycle where healthy cells would normally die. This excessive cell growth may lead to the formation of a tumor, and the invasive nature of these cells can result in the destruction of surrounding healthy tissues. Over time, these aberrant cells may detach, spreading to other parts of the body, a stage referred to as metastatic cancer.
Risk Factors for Colorectal Cancer
There is no guaranteed way to know if you’re going to get colorectal cancer or not. However, certain risk factors can make it more likely to be detected with colorectal cancer. These include:
- Age: People who are over the age of 50 are more likely to develop colorectal cancer. The average age for detection of colorectal cancer is generally 72.
- Weight: Obesity is also a contributing factor to colorectal cancer.
- Family History: People who have immediate family members or any blood relatives who were detected with colorectal cancer are at a high risk of being diagnosed with colorectal cancer.
- Type 2 Diabetes: People who have type 2 diabetes are more likely to develop colorectal cancer.
- Diet: Eating a lot of red meat such as pork, beef, veal, and lamb can increase the risk of developing colorectal cancer. People need to follow a healthy diet to lower the risk of any diseases or conditions. Eating lots of fruits and vegetables will help individuals to lead a healthy life.
- Already been detected with colorectal cancer: Those who have been diagnosed with colorectal cancer, especially before the age of 60, are more likely to develop cancer in another part of the colon or rectum. They should seek Colorectal Cancer Treatment in Hyderabad for further assistance.
- Polyps in the colon or rectum: Polyps refer to certain growths that can occur in the rectum or colon. These growths are generally benign and are common for people aged above 50. However, over time, some of these polyps can become cancerous. Hence, this increases the risk of developing colorectal cancer. Polyps can be detected and removed before they turn cancerous.
- Smoking: Smoking can increase an individual’s risk of developing colorectal cancer. Cigarette smoke consists of various cancer-causing agents known as carcinogens. When swallowed, this can cause cancer in certain parts of the digestive system. Sometimes, the agents can enter the blood vessels and travel through the body to the intestines.
- FAP (Familial Adenomatous Polyposis): FAP is a genetically inherited condition. Under this, many polyps are formed from the age of 16, and by the age of 20, these polyps could become cancerous. Therefore, those who have FAP are at a high risk of developing colorectal cancer before the age of 40.
- HNPCC (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colon Cancer): There are very few cases where colorectal cancer is caused because of HNPCC. However, people with HNPCC are still at risk of developing colorectal cancer. This condition can even cause other types of cancers as well. Some of the other risk factors can include:
-
Excessive usage of alcohol
-
Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD)
-
Diagnosis of Colorectal Cancer
Colorectal Cancer can be diagnosed in the following ways:
- Colonoscopy: This refers to a diagnostic process where doctors examine the entire length of the large intestine of the body.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): This refers to an exam of the rectum.
- Fecal Occult Blood Test (FOBT): This is a blood test that is done to check the stool for any blood that can only be seen with the help of a microscope.
- Biopsy: This refers to a process where the tissue samples are removed with the help of a needle or during surgery. These tissues are later examined under a microscope to check for any abnormal or cancer cells.
- Sigmoidoscopy: A process that will examine the lower one-third of the large intestine.
- Barium Enema: A process that will examine the large intestine, the lower part of the small intestine, and the rectum using a contrast dye that contains barium.
Other types of diagnosis can include a blood count and imaging tests. These tests can include ultrasound, CT Scan, or MRI of the abdomen.
Treatment For Colorectal Cancer
During a colonoscopy, small polyps are generally removed without the need for an incision on the body. At CARE Hospitals, larger or more complex polyps are removed through surgery. There are different types of colorectal cancer treatment in Hyderabad done for different stages of colorectal cancer. These can include:
- Polypectomy: This refers to the process of removing polyps during a colonoscopy.
- Endoscopic Mucosal Resection: Larger polyps are removed during this treatment process. A colonoscopy is done using a special tool that helps to remove the polyps.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This is a minimally invasive surgery. In this process, small incisions are made to remove the abnormal cells.
- Chemotherapy: This is a normal treatment that uses certain drugs to remove any type of cancer including colorectal cancer.
- Radiation Therapy: This treatment uses powerful energy sources like X-rays to kill cancer cells.
How can CARE Hospitals help?
Cancer treatment can be difficult, time-consuming, and stressful for both the doctor and the patient. CARE Hospitals ensures that the entire process, including the colorectal cancer surgery in Hyderabad, runs smoothly to receive the best possible results. CARE Hospitals provide the most advanced diagnostic services in oncology. We use state-of-the-art equipment and technology. Our highly qualified team of doctors provides appropriate treatment to all of our patients. We ensure that we are always available to you and ensure that you live a quality life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Still Have a Question?

