-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Cervical Cancer
Cervical Cancer
Best Hospital for Cervical Cancer Treatment
Cervical Cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the Cervix which is the lowest part of the uterus. It refers to a malignant tumour of the cervix. Most cervical cancer cases are linked to a virus that has a high risk, this is known as human papillomavirus (HPV) which is generally transmitted through sexual contact.
Although, in most cases, women who have HPV are known to have no symptoms and the infection generally resolves spontaneously. This happens because when a woman is exposed to HPV, the immune system of the body helps to prevent the virus from attacking any further. However, for a few people, the virus sometimes survives for years leading to some cervical cells becoming cancer cells.
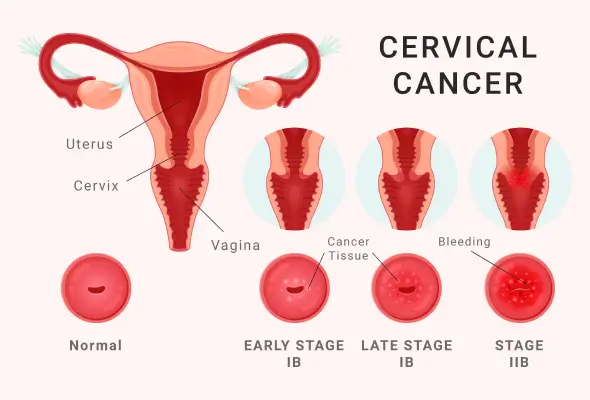
Types of Cervical Cancer
The type of cervical cancer will help to determine the treatment and prognosis. There are two types of cervical cancer. These include:
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Squamous cells refer to thin and flat cells that line the outer layer of their cervix which extends into the vagina. The Squamous Cell Carcinoma generally begins in these cells. This is the most common cervical cancer that occurs in most women.
- Adenocarcinoma: This is the type of cancer that begins in column-like shaped glandular cells. These cells line the cervical canal.
However, you need to keep in mind that there have been very rare cases where both types of cells are involved in cervical cancer. Very rarely does cancer occur in other cells of the cervix.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
Cervical Cancer when diagnosed at an early stage generally has no symptoms or signs. Whereas, some symptoms of advanced cervical cancer that are observed in patients can include:
-
Bleeding of the vagina in between periods, during intercourse, or after menopause.
-
Bloody and watery vaginal discharge can be heavy as well as have a foul odour.
-
Pain in the pelvic region.
-
Pain during intercourse.
-
Heavier or longer menstrual bleeding.
-
Increased vaginal discharge
If you have any of the above symptoms that concern you make sure you immediately make a call to contact your doctor.
Causes of Cervical Cancer
Cervical Cancer in a body begins when the healthy cells of the cervix undergo mutations in their DNA. A cell's DNA consists of certain instructions that help the cell to function.
Healthy cells tend to multiply and grow at a certain rate, and they end up dying together. Hence, during cervical cancer because of the mutations the cells multiply, grow out of control, and don't end up dying. These cells start to accumulate and form a tumour. Cancer cells can break off from a tumour and spread to other parts of the body.
It is known that one of the main causes of cervical cancer is HPV. It is a common type of virus. However, most people with this virus don't develop cancer. This means that there are other factors involved in the development of cervical cancer. This can include your lifestyle choices and the environment in which you're living.
Risk Factors of Cervical Cancer
Certain risk factors involving cervical cancer include:
-
Multiple Sexual Partners - The more sexual partners a person has - and the more sexual partners that your partner may have - the higher the risk for acquiring HPV.
-
Early Sexual Activity - Those who start to have sexual intercourse at an early age tends to increase the risk of getting HPV.
-
STIs - Having other Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STIs) like syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhoea, and HIV/AIDS increases the possibility of receiving HPV.
-
Smoking - People who smoke, or have people who smoke around them are exposed to many types of cancers that can affect the lungs and other parts of the organs. These harmful chemicals are absorbed by the lungs and are then spread to the rest of the body through the bloodstream. Squamous cell cervical cancer can be linked to smoking. It is known that women who smoke have a higher chance to get cervical cancer as compared to those women who don’t smoke.
-
Weak Immune System - Having a weak immune system puts the human body at high risk. The immune system needs to be strong to destroy the cancer cells and slow their spread and growth. Hence, people who have a weak immune system due to other health conditions and have HPV are more likely to develop cervical cancer.
Prevention of Cervical Cancer
Although rare, certain prevention steps can be taken care of. These include:
-
HPV Vaccine
You can ask your doctor about receiving the HPV vaccine which can help to reduce the risk of cervical cancer and another type of cancers related to HPV.
-
Routine Pap Tests
Pap tests will help to detect any precancerous conditions in the cervix. Once detected, it can be monitored or treated accordingly to prevent cervical cancer. The ideal age to begin routine pap tests would be 21 which can then be repeated every few years.
-
Sex Education
You need to have proper knowledge of sex education. This means that you need to practice safe sexual intercourse to prevent cervical cancer. It includes being safe from any sexually transmitted diseases and using a condom while having any type of sexual intercourse. It would also be good to limit the number of sexual partners.
-
Quit Smoking
For those of you who don't smoke, it is better that you don't start. If you smoke, then try to talk to your doctor about certain strategies that will help you to quit.
Diagnosis of Cervical Cancer
CARE Hospitals, the best hospital for Cervical Cancer Treatment, ensure that our well-trained staff will help you through the entire process of diagnosis. If there is cervical cancer suspected, then the doctor will start through a thorough examination of the cervix using a colposcope. A colposcope refers to a special kind of magnifying instrument that is used to check for abnormal cells. During this time, the doctor will collect samples of tissues using:
-
Punch biopsy: This involves using sharp tools to take tiny samples of the cervical tissue.
-
Endocervical Curettage: This refers to using a tiny, spoon-like shape instrument (curet) or a slim/thin brush that can be used to scrape off the cervical tissue.
These tissues will then be further examined for malignancy. If the tissues are malignant, then our experienced doctors may suggest imaging tests to stage cancer.
Treatment of Cervical Cancer
Treatments offered by CARE Hospitals for cervical cancer include surgery, tracheostomy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy. The treatment of cervical cancer depends on many factors such as the stage of cancer, personal preferences, and other health conditions that you may be going through.
Surgery
Those who are diagnosed with an early stage of cervical cancer can be treated through surgery. The type of surgery will completely depend on the size of the tumour and the stage of cancer. Some of the options can include:
- Surgery to cut and remove the cancer: For those who have small cervical cancer, it can be possible to remove cancer completely with a cone biopsy. This process includes cutting a piece of cervical tissue that is shaped like a cone and leaving the rest of the tissue intact with the cervix. During this process, the uterus remains in the body making it possible to become pregnant if you choose.
- Hysterectomy: This refers to the process of removing the cervix and the uterus. A hysterectomy can cure cervical cancer and prevent any recurrence. However, this procedure will make it impossible for you to become pregnant if you choose.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted Therapy refers to targeted drug treatments that focus on certain weaknesses which are present in the cancer cell. Targeted drug treatments block these weaknesses and cause cancer cells to die. This therapy is generally combined with chemotherapy and can be an option for advanced cervical cancer.
Immunotherapy
This is a drug treatment that will strengthen the immune system to fight cancer cells. The immune system may not be able to fight cancer cells, since these cells produce proteins that are undetectable by the cancer cells. Therefore, immunotherapy interferes with this process.
How CARE Hospitals Can Help?
At CARE Hospitals, which is the best hospital for cervical cancer treatment in Hyderabad, we offer comprehensive diagnostic services in the field of Oncology. Our well-trained multidisciplinary staff will support you and assist you in the entire process. We even provide out-of-hospital support for all our patients. Our staff will always be available at your service and will answer any query that you may have. CARE Hospitals uses state-of-the-art equipment and technology. Our advanced and modern surgery procedures will ensure that you live a quality life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Still Have a Question?

