-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Bladder Cancer
Bladder Cancer
Best Bladder Cancer Treatment in Hyderabad
Bladder Cancer refers to cancer that arises in the cells of the bladder. The bladder is a hollow muscular organ situated in the lower abdomen and stores urine. Bladder cancer is one of the most common types of cancer seen in men.
Bladder Cancer generally begins in the urothelial cells. These cells are lined inside the bladder. The Urothelial Cells can even be found in the Kidneys and Ureters (the tube that connects the bladder and the kidneys). There is a chance for urothelial cancer to occur in the kidneys and ureters, however, this type of cancer is more common in the bladder.
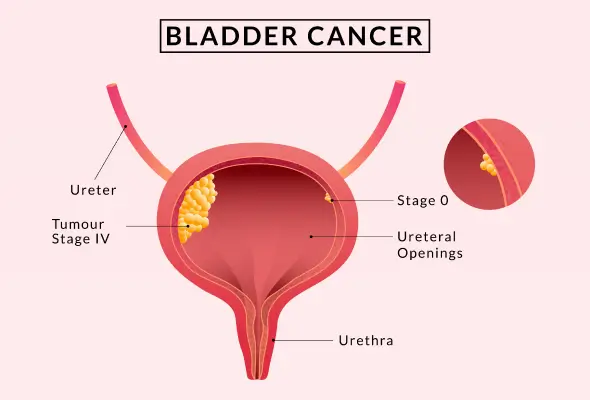
Most bladder cancers are diagnosed during the stage when the cancer is completely treatable. However, there have been certain instances where early-stage bladder cancer relapsed even after successful treatment. Therefore, people need to go for regular follow-up tests for years after their treatment for the prevention of a relapse. CARE Hospitals provide bladder cancer treatment in Hyderabad with the top medical professionals.
Symptoms of Bladder Cancer
People diagnosed with bladder cancer usually experience any discomfort or abnormality associated with urination. However, some patients may not have these symptoms and some may have these symptoms that could even lead to a separate medical condition which is not cancer.
Common signs and symptoms of bladder cancer are:
-
Blood in the Urine (Hematuria) or blood clot in the urine
-
Burning or painful sensation during urination
-
Having the constant need to urinate frequently
-
Having the urge to urinate but being unable to do so
-
Back pain on 1 side of the lower body
A few other symptoms of advanced bladder cancer can include pain in the pelvic region, loss of appetite, and weight loss. Sometimes, when the first symptoms of bladder cancer are seen, this could mean that the cancer has already spread to other parts of the body. In this case, the symptoms of cancer depend on where it has spread.
Types of Bladder Cancer
There are many different types of cells available in the bladder that can become cancerous. Hence, the type of bladder cancer depends on what the tumour's cells look like. There are mainly three types of bladder cancer:
-
Urothelial Carcinoma:
Previously known as transitional cell carcinoma, Urothelial Carcinoma (UCC) begins in the cells that line the inside of the bladder. UCC is one of the most common bladder cancers that is diagnosed. It even accounts for 10-15% of kidney cancer that occurs in adults.
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma is generally associated with chronic irritation in the bladder. This could be a result of either an infection or a urinary catheter that has been used for a long term. This type of cancer is rare and accounts for only 4% of the population being diagnosed with it. It is most common in areas where a certain parasitic infection (schistosomiasis) causes bladder cancer.
-
Adenocarcinoma
Adenocarcinoma is a type of bladder cancer that is very rare and accounts for only 2% of the population being diagnosed with it. This type of cancer begins in the cells that create a mucus-secreting gland in the bladder.
Risk Factors of Bladder Cancer
Some of the risk factors of bladder cancer include:
Smoking: Smoking is known to be injurious to health. People who smoke regularly have a high risk of being diagnosed with bladder cancer which is 4-6 times more than someone who does not smoke.
Age: People who are above the age of 65-70 tend to be diagnosed with bladder cancer as compared to a younger population.
Gender: According to research, men are more likely to develop bladder cancer as compared to women.
Chemical Exposure: People who are exposed to certain chemicals used in dye, textile, rubber, paint, leather, and printing industries have a higher risk of being diagnosed with bladder cancer. These chemicals include aromatic amines which can be harmful.
Chemotherapy or Radiation: Those who were exposed to chemotherapy or radiation earlier have a long-term risk of being diagnosed with bladder cancer.
Family History: Those who have a family history of bladder cancer are twice as likely to be diagnosed with bladder cancer. This can happen because of certain genetic factors that can lead to the inability to remove dangerous chemicals after exposure. Apart from this, an inherited disease, known as Lynch Syndrome is linked to colorectal cancer, and can even increase the risk of bladder cancer.
Chronic Bladder Issues and Infections related to Urinary Tract: People who have long-term bladder inflammation and irritation are more likely to develop bladder cancer.
Diabetes Medicine: Those who take Pioglitazone, which is a drug taken for type 2 diabetes to reduce lower sugar, have a high risk of developing bladder cancer.
Diagnosis of Bladder Cancer
Doctors can use various tests, scans, and procedures to find the correct diagnosis of bladder cancer. Some of the diagnoses can include:
-
Urine Tests
If there is any blood found in the urine, the doctor would ask you to do a urine test.
-
Cystoscopy
Cystoscopy is the main diagnostic procedure that is used to identify bladder cancer.
-
Biopsy
Biopsy or Transurethral resection of bladder tumour (TURBT) will be conducted if there are abnormal tissues found during a cystoscopy. A TURBT can even be used to find out the type of tumour, and how deeply it is in the layers of the bladder.
-
CT Scan
CT scan can be used to measure the size of the tumour.
-
MRI
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) uses magnetic fields to produce a detailed image of the body. An MRI can even be used to measure the size of the tumour.
-
PET Scan
Positron Emission Tomography (PET) or PET-CT Scan helps to find bladder cancer that may have spread to other parts of the body.
-
Ultrasound
Ultrasound uses sound waves to get a better picture of the internal organs. This can help doctors to find out if the patient's ureters and kidneys are blocked.
Treatments for Bladder Cancer
During the early stage of cancer, when the cancer tumour exists only in the bladder, bladder cancer surgery is conducted where the doctors remove the entire bladder from the body. However, this procedure will be conducted only as a last resort. At CARE Hospitals, which is the best hospital for bladder cancer treatment, our well-experienced doctors will help you through the treatment of bladder cancer. Other bladder cancer treatments are available at CARE Hospitals that our doctors prefer to use.
The treatments for bladder cancer are dependent on the stage of cancer. There are mainly two types of surgeries that our doctors perform to treat bladder cancer. These include:
Transurethral Resection
Transurethral Resection is a procedure that is performed during the early stage of bladder cancer. This process includes passing an instrument through the urethra which is used to remove the tumour and other abnormal tissues.
Cystectomy
Cystectomy is a procedure where either part of the bladder or the entire bladder is completely removed. To remove the part of the bladder or the entire bladder, it can be accessed by an incision in the stomach.
Hence, surgery along with other treatments can be used to treat bladder cancer. Our cancer specialities are experienced surgeons that will ensure that all the patients will not endure any bladder cancer surgery side effects.
How can CARE Hospitals help?
Cancer care at the bladder cancer centre can be intense, complex, and prolonged for both the physician and the patient. It requires coordinated, concerted, and precise planning to ensure that the procedure goes smoothly and that only the best outcomes are received. At CARE Hospitals, we provide the best diagnostic services in the field of Oncology. We use state-of-the-art equipment and technologies. We offer world-class and cost-effective clinical care. Our well-trained staff support will provide assistance and proper care during the recovery period. Our staff is always available to support you and answer all your queries. CARE Hospitals is the best hospitals for bladder cancer treatment in Hyderabad with modern and advanced surgical procedures that will help you to improve your quality of life.
Frequently Asked Questions
Still Have a Question?

