-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Arthritis
Arthritis
Best Arthritis Treatment in Hyderabad, India
Arthritis is characterized by swelling and discomfort in one or more joints. It causes joint pain and stiffness, which often increase with age. There are several forms of arthritis, like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. In Osteoarthritis, there is a breakdown of cartilage, which is the firm, slippery tissue that covers the ends of bones where they meet to create a joint. Rheumatoid arthritis is a condition in which the immune system assaults the joints, starting with the joint lining. Treatment options at an Arthritis Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad differ based on the kind of arthritis. The primary aims of arthritis therapy are to alleviate symptoms and enhance the quality of life.
Types of Arthritis
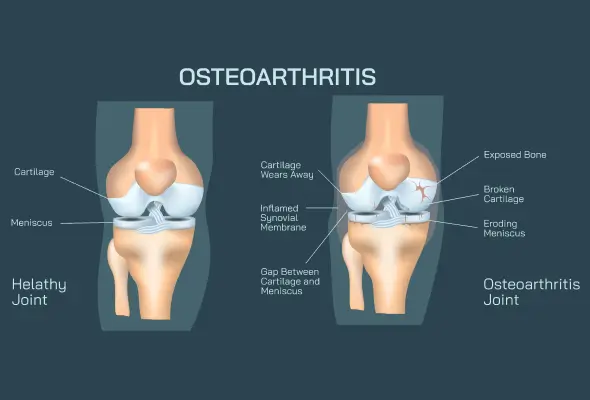
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis is the most prevalent form of arthritis that occurs when joints undergo prolonged wear and tear. Common indications include persistent pain during movement, morning stiffness, and difficulties in routine activities like bending, grooming, dressing, or climbing stairs.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis, an autoimmune disease, involves the immune system attacking various body parts, primarily joints, causing inflammation. It typically affects knuckles, elbows, or heels, with prevalent symptoms such as pain, stiffness, and swelling. Effective treatment becomes crucial for alleviating rheumatoid arthritis symptoms.
- Lupus: Lupus, another autoimmune condition, can impact joints and various organs, primarily affecting women of childbearing age. Symptoms encompass pain, fatigue, hair loss, mouth sores, chest pain, sensitivity to sunlight, and skin rashes.
- Psoriatic arthritis: Psoriatic arthritis manifests as skin and joint inflammation, often leading to swelling in fingers and toes, along with discolored and pitted fingernails. Treatment for psoriatic arthritis aims to alleviate these symptoms.
- Gout: Gout results from the accumulation of uric acid crystals in joints, typically affecting the big toe or other parts of the foot. Symptoms include stiffness, discomfort, and intense joint pain.
Symptoms
Depending on the kind of arthritis, the following signs and symptoms may occur:
-
Pain/ joint stiffness
-
Swelling/ redness
-
Reduced range of motion
Causes
The two primary kinds of arthritis, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis, have various causes and lead to distinct sorts of joint damage.
- Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis, the most common type of arthritis, is caused by wear and tear on a joint's cartilage — the hard, slippery covering on the ends of bones where they form a joint. Cartilage cushions the ends of the bones and allows for practically frictionless joint mobility; nevertheless, significant damage can result in bone grinding directly against bone, causing discomfort and limited movement. Wear and strain can develop over time and can be accelerated by a joint injury or illness. Osteoarthritis also affects the bones and the connective tissues that link muscle to bone and hold the joint together. If a joint's cartilage is significantly injured, the joint lining may become inflamed and swollen.
- Rheumatoid arthritis: The immune system of the body targets the lining of the joint capsule, a thick membrane that encloses all joint elements, in rheumatoid arthritis. The illness process can eventually damage joint cartilage and bone.
Risk factors
Arthritis risk factors include:
-
Family history: Because some kinds of arthritis run in families, you may be more prone to get the illness if your parents or siblings have it.
-
Age: Many kinds of arthritis, including osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout, become more common as people get older.
-
Gender: Women are more likely to acquire rheumatoid arthritis, but men are more likely than women to suffer from gout, another kind of arthritis.
-
Previous joint damage: People who have damaged a joint, maybe while playing sports, are more prone to develop arthritis in that joint later in life.
-
Obesity: Carrying extra pounds puts strain on your joints, especially your knees, hips, and spine.
Complications of arthritis
Weight-bearing joint arthritis can make it difficult to walk or sit up straight. Joints may progressively lose alignment and form in rare circumstances. Our patients tell us that the richness of their conversations, our meticulous attention to detail, and the quickness of their appointments provide them with health care, unlike anything they've ever had before.
Diagnosis at CARE Hospitals
Doctors examine your joints for swelling, redness, and warmth during the physical exam. They'll also want to check at our arthritis treatment hospital how well your joints can move.
Laboratory tests
Different types of bodily fluids can be analyzed to determine the type of arthritis you have. Doctors wash and numb the region before withdrawing a sample of joint fluid using a needle inserted into the joint cavity.
Imaging tests
Here are several examples:
-
X-rays: X-rays are a type of radiography that uses low doses of radiation to see bone and can reveal cartilage loss, bone deterioration, and bone spurs. X-rays may not detect early arthritic damage, although they are frequently used to monitor disease development.
-
Computed tomography (CT): CT scanners use a combination of X-rays from various angles to provide cross-sectional images of inside structures.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): MRI is a type of imaging. MRIs provide more detailed cross-sectional pictures of soft tissues such as cartilage, tendons, and ligaments by combining radio waves with a strong magnetic field.
-
Ultrasound: High-frequency sound waves are used to image soft tissues, cartilage, and fluid-containing structures around joints with this method. Ultrasound can also be used to guide the positioning of needles for extracting joint fluid or injecting drugs into the joint.
What to avoid with arthritis
Managing arthritis involves knowing what to avoid to prevent worsening symptoms and protect your joints. Here are key things to steer clear of:
- Sedentary Lifestyle: Avoid sitting or lying down for long periods. Lack of movement can increase stiffness and weaken muscles around your joints.
- High-Impact Activities: Activities like running, jumping, or heavy lifting can strain joints and worsen pain, especially in weight-bearing joints.
- Repetitive Movements: Repeated motions, such as typing or gripping tools tightly, can increase joint stress. Take frequent breaks during tasks.
- Poor Posture: Slouching or sitting awkwardly can strain your joints. Always maintain good posture to protect your spine and other joints.
- Unhealthy Diet: Avoid processed foods, sugary snacks, and trans fats, as they can increase inflammation. Limit salt and alcohol, which may contribute to swelling.
- Ignoring Pain: Pushing through pain can lead to joint damage. Listen to your body and stop activities that hurt.
- Overweight: Carrying extra weight adds pressure on joints, especially in the knees, hips, and spine. Managing your weight is crucial.
- Overusing Affected Joints: Avoid using the same joint repeatedly without rest, as this can worsen arthritis symptoms and lead to flare-ups.
- Smoking: Smoking can worsen arthritis symptoms by reducing blood flow to the joints and increasing inflammation.
- Skipping Treatment: Not taking prescribed medications or missing physical therapy sessions can lead to unnecessary pain and progression of the condition.
Managing arthritis at home
Living with arthritis can be easier with some simple lifestyle changes. Here’s how you can manage it at home:
- Stay Active
- Do gentle exercises like walking, swimming, or yoga to keep your joints flexible and muscles strong.
- Avoid activities that strain your joints too much.
- Keep a Healthy Weight
- Extra weight puts more stress on your joints. Eat healthy foods and stay active to manage your weight.
- Use Heat or Ice
- Use a heating pad or warm towel to ease stiffness and relax muscles.
- Apply an ice pack to reduce swelling and numb pain.
- Eat Healthy
- Include foods that reduce inflammation, like fish, nuts, fruits, and vegetables.
- Avoid sugary and processed foods.
- Protect Your Joints
- Use tools like jar openers or braces to avoid putting too much pressure on your joints.
- Take breaks during repetitive tasks to rest your joints.
- Manage Stress
- Practice relaxation techniques like meditation, deep breathing, or gentle stretching to reduce stress.
- Follow Your Treatment Plan
- Take your medicines as prescribed by your doctor.
- Use over-the-counter pain relief only if recommended.
- Listen to Your Body
- Rest when you feel tired, and don’t overdo activities. Balance movement with rest.
- With these small steps, you can reduce arthritis pain and improve your quality of life.
Treatment of arthritis
Arthritis treatment primarily aims to alleviate symptoms and enhance joint functionality. Finding the most effective treatment may require trying different methods or combinations.
- Medications: The type of arthritis determines the medications prescribed. Common options include:
- NSAIDs (Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs): These help relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Examples include ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB) and naproxen sodium (Aleve). Stronger versions can cause stomach irritation and may increase the risk of heart attack or stroke. NSAIDs are also available as topical creams or gels applied directly to joints.
- Counterirritants: Creams and ointments containing menthol or capsaicin (found in spicy peppers) may be applied to the skin over aching joints to disrupt pain signals.
- Steroids: Corticosteroids like prednisone reduce inflammation, relieve pain, and slow joint damage. They can be taken orally or injected directly into the affected joint. Potential side effects include bone thinning, weight gain, and diabetes.
- DMARDs (Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs): These medications slow the progression of rheumatoid arthritis and prevent permanent joint and tissue damage. Options include conventional DMARDs, biologic agents, and targeted synthetic DMARDs. Side effects, including an increased risk of infection, vary depending on the medication.
- Therapy
- Physical therapy can benefit certain types of arthritis by improving range of motion and strengthening muscles around the joints. Splints or braces may be recommended in some cases.
- Surgery: When other treatments fail, surgical options may include:
- Joint repair: This involves smoothing or realigning joint surfaces to reduce pain and improve mobility. Often done arthroscopically, it requires small incisions.
- Joint replacement: Damaged joints, such as hips or knees, are replaced with artificial ones.
- Joint fusion: Commonly used for smaller joints like those in the wrist, ankle, or fingers, this procedure removes the ends of two bones in a joint and fuses them into a single unit for stability.
The most common types of arthritis treatment are:
These drugs have a similar effect as cortisone that is made by our body; to control inflammation.
- Analgesics: Analgesics, a commonly prescribed medication in arthritis treatment, primarily serves to alleviate pain. It is specifically designed for pain relief and addresses both pain and inflammation.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) represent an additional class of pain relief medications that can be easily acquired without a prescription.
- Biologic response modifier: The most recent pharmaceutical development, finds particular application in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. These drugs intervene in the inflammatory process without impeding the overall function of the immune system.
- Osteoporosis medications: Medications for osteoporosis work to enhance the body's ability to generate new bone tissue and decelerate the loss of bone mass.
At CARE Hospitals, as one of the best Arthritis Treatment Hospital in Hyderabad, the doctors offer world-class treatment amalgamated with state-of-the-art technology to ensure you receive the best care possible.
Frequently Asked Questions
Still Have a Question?

