Anemia Treatment in Hyderabad
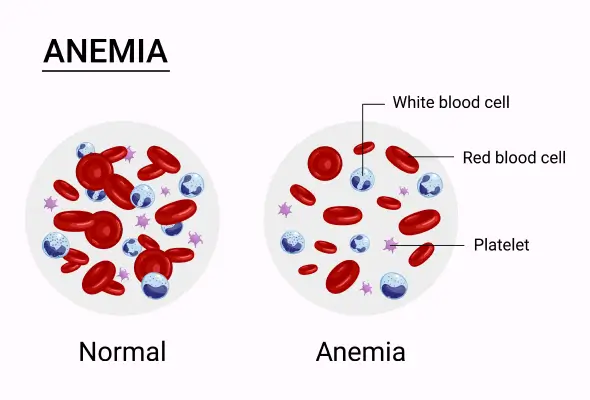
Anaemia is a disease where you lack proper healthy red blood cells (RBC). Red blood cells help carry oxygen to the tissues of your body. Anemia is also referred to as low haemoglobin treatment. If you have anaemia, it makes you feel very weak and tired.
Anaemia can either be temporary or long-term. Anaemia can also range from mild to severe. Most cases of anaemia are due to more than one cause. You should definitely visit your doctor if you suspect anaemia. Anaemia could be a warning sign of a serious illness. By eating a healthy, balanced diet, you will be able to prevent getting anaemia.
The treatments for anaemia can be as simple as taking supplements or can be as serious as some medical procedures. At CARE Hospitals, we have specialists who can provide accurate anaemia treatment in Hyderabad for Iron Deficiency.
Types of Anaemia
There are several types of anaemia based on the cause.
-
Aplastic anaemia - When your body halts producing enough red blood cells, then the condition is known as Aplastic anaemia. A common symptom, as well as a side effect of this type of anaemia, is that it leaves you very fatigued. This fatigue makes you more prone to uncontrolled bleeding and other infections.
-
Iron deficiency anaemia - This is quite a common type of anaemia. The blood lacks enough red blood cells in this condition and hence oxygen is not carried properly throughout the body.
-
Sickle cell anaemia - Sickle cell disease is the name given to this group of disorders. This is an inherited disorder of red blood cells. This disease is characterized by red blood cells with shapes like sickles (crescent moon-shaped). This makes it difficult for the cells to move smoothly through the blood vessels.
-
The other two types of anaemia include Thalassemia and Vitamin deficiency Anaemia.
-
Anemias linked to bone marrow diseases: Conditions like leukemia and myelofibrosis can disrupt the bone marrow's ability to produce blood, leading to anemia. These cancerous or similar disorders can range in severity from mild to life-threatening.
-
Hemolytic anemias: This type of anemia occurs when red blood cells are destroyed more quickly than the bone marrow can produce them. Some blood disorders accelerate the destruction of red blood cells. Hemolytic anemia may be inherited or develop later in life.
Symptoms of Anaemia
As we have discussed previously, anaemia can have several causes. The signs and symptoms of anaemia depend upon these various causes and the severity of the anaemia. Sometimes, if your anaemia is mild, you might show no symptoms at all.
A few signs and symptoms that might indicate anaemia:
-
Mild to severe weakness
-
Constant fatigue
-
Pale skin or yellow-tinted skin
-
Irregularity of heartbeats
-
Shortness of breath
-
Feelings of dizziness or lightheadedness
-
Pain in the chest
-
Cold feeling in the hands and feet
-
Headaches
In the beginning, the anaemia could be so mild that it is totally unnoticeable. Gradually, the symptoms of anaemia worsen with the condition.
Causes of Anaemia
Anemia happens when your blood lacks sufficient red blood cells.
This can occur if:
- Your body doesn't produce enough red blood cells
- Bleeding causes a loss of red blood cells faster than they can be replenished
- Your body breaks down red blood cells.
Risk Factors Associated with Anaemia
There are a few factors that can be considered risk factors for anaemia. They are as follows:-
-
You should always have a balanced diet. A diet lacking in certain vitamins and minerals might push you towards anaemia. If your diet is consistently low in vitamin b 12, copper, iron, and folate, the risk of developing anaemia increases.
-
The intestine is the organ that helps with the absorption of nutrients. If you have a disorder in the intestine, the absorption of nutrients in your small intestine gets affected. Intestinal disorders. This leads to diseases such as small Crohn’s disease and Celiac disease. This increases your risk of having anaemia.
-
As we know, menstruations in women cause the loss of a lot of red blood cells. This puts them at a greater risk of anaemia. Men are also at a lesser risk of developing anaemia due to this very reason.
-
During pregnancy, the intake of multivitamins is very necessary including folic acid and iron. If you do not take these during your pregnancy, you will be at a greater risk of developing anaemia.
-
There are some chronic conditions such as cancer, and kidney failure, and these chronic conditions can put you at a greater risk of anaemia. This is because chronic diseases like these could lead to a shortage of red blood cells.
-
Also, if you suffer from chronic blood loss due to conditions like ulcers or something else, this can contribute to depleting the iron stored in the body. This leads to iron deficiency anaemia.
-
Anaemia can be inherited. If you have a family history of anaemia, such as sickle cell anaemia, then it will put you at an increased risk of having anaemia.
-
There are also certain factors, such as certain infections, autoimmune disorders, and blood diseases that increase your risk of having anaemia. If you have a history of these, then you might have a risk of getting anaemia. Other factors also include exposure to toxic chemicals, alcoholism, and the use of certain medications. These might affect your red blood cells.
-
Last but not least, as with all diseases, old age puts people at an increased risk of getting anaemia.
Diagnosis of Anaemia
If you are about to undergo an anaemia treatment, then you would be asked several questions about your medical and family history by your doctor. Then a physical examination would be performed on you. Once done, the following tests would be run on you by the doctors:-
Complete blood count (CBC) - Anaemia is a blood disease. The count of red blood cells is really necessary. This test is performed to get a complete count on the number of red blood cells in your body. Knowing the number of red blood cells in your body is extremely essential for the doctor to determine whether you are suffering from anaemia.
A test is also done to determine the shape and size of your red blood cells and the path of iron deficiency anaemia treatment. Through this test, it is determined whether your red blood cells are of normal shapes and sizes.
Sometimes additional tests are done with bone marrow to determine if you have anaemia.
Treatment of Anaemia
Anaemia treatment depends on the underlying cause.
- Iron Supplements: If anemia is caused by iron deficiency, supplements may be prescribed to boost iron levels. This is often necessary when anemia results from insufficient iron in the diet or chronic blood loss.
- Vitamin B12 Supplements: Anemia caused by a vitamin B12 deficiency is typically treated with B12 supplements, either orally or through injections. This is common in individuals with pernicious anemia or absorption issues.
- Folic Acid Supplements: Folic acid supplements are used to treat anemia due to folic acid deficiency, which may occur from poor dietary intake or absorption problems.
- Treatment of Underlying Conditions: Anemia can be a symptom of other medical conditions such as chronic kidney disease, inflammation, or bone marrow disorders. Addressing these underlying causes may help resolve the anemia.
- Blood Transfusions: In severe cases, particularly when anemia causes symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain, blood transfusions may be necessary to rapidly restore red blood cells and improve oxygen levels.
- Dietary Changes: Mild anemia or supportive treatment may involve adjusting the diet to include more iron-rich foods, such as red meat, poultry, fish, beans, lentils, fortified cereals, and leafy greens.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Managing factors that contribute to anemia, like heavy menstrual bleeding or gastrointestinal bleeding, and avoiding substances that hinder iron absorption (e.g., excessive caffeine or calcium) may also be part of the treatment approach.
 HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers



