-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Treatment in Hyderabad
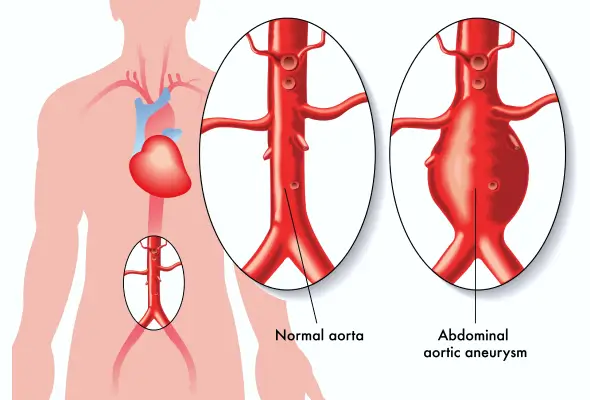
When the lower part of the major vessel, the aorta gets enlarged, it is known as an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Aorta is the main vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the body and runs through the heart to the chest and abdomen area.
Aorta holds a major function inside the body and hence a condition like an abdominal aortic aneurysm can cause life-threatening situations. The aneurysm may rupture and cause excessive internal bleeding, which can be life-threatening.
The abdominal aneurysm treatments can vary according to the degree of damage done. Sometimes, the aneurysms may even require emergency surgeries.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms may not be prominent and also be difficult to get detected. The aneurysm may never rupture and doesn't cause symptoms unless it becomes large. It usually grows slowly over time. It may cause symptoms while growing and when it becomes large.
An enlarged abdominal aortic aneurysm may show the following symptoms:
-
Deep and constant pain in the belly area (often near the belly button)
-
Pulsating abdomen
Risk Factors
There are a lot of risk factors associated with abdominal aortic aneurysms:
-
Tobacco use- Smoking is the leading cause of the conditions like abdominal aortic aneurysms as these can weaken the aorta walls and rupture them. People who chew and smoke tobacco are at a higher risk of developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Heavy and chronic smokers should get an ultrasound of the abdomen regularly, especially at the age of 65-75 years.
-
Age- People over the age of 65 are more prone to conditions like abdominal aortic aneurysms as their aorta walls may weaken with age.
-
Being male- Men are more prone to abdominal aortic aneurysms than women.
-
Family history- If one of your family members (blood-related) has an abdominal aortic aneurysm, you are more likely to get it.
-
Other aneurysms- If you have a medical history of aneurysms in other large vessels than the aorta like in the thoracic aortic aneurysm; you’ll be at a high risk of developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Diagnosis
The doctor performs a physical examination to assess your symptoms and evaluates the medical and family history to identify the cause of the aneurysm. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT, and MRI can be performed to confirm the diagnosis.
-
Abdominal ultrasound- the sound waves are used to diagnose and screen the blood flows through the belly area along with the aorta. It is a painless test and the transducer is placed on the abdomen slowly to create the image on the computer. It travels back and forth and the device sends signals to the screen.
-
CT scan of the abdomen- the cross-sectional images are created with the help of X-rays of the abdomen where the doctors can see a clear picture of the aorta. It is a painless test that can also detect the size and shape of the abdominal aortic aneurysm. A dye may also be given along with the CT to mark the veins clearly.
-
Abdominal MRI- the computer-generated radio waves along with the magnetic field are used to create detailed images of the abdominal structures and aorta. The blood vessels can also be clearly seen with the help of a dye employed in the veins.
Screening of the abdominal aortic aneurysm
Smokers, especially men are at increased risk of developing an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Screening recommendations are:
-
One-time screening for an abdominal ultrasound for men aged in the range of 65-75 years and who have smoked before.
-
If they have never smoked, a family history will be analysed for the condition of abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Treatment
The doctor’s main aim is to stop the rupturing of the aneurysm for the abdominal aortic aneurysm. Hence, the abdominal aortic aneurysm treatment might take proper surgery or monitoring depending upon the size of the abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Medical monitoring
-
Medical monitoring involves the treatment as mindful watching if the abdominal aortic aneurysm isn’t rapid or big.
-
It is done to see the minor symptoms and requires regular assistance and check-ups by the doctors.
-
The imaging tests are required to determine the aneurysm size and manage conditions like blood pressure.
-
People would be asked for an abdominal ultrasound every six months and later for daily follow-ups.
Surgery
If the abdominal aortic aneurysm is about the size of 1.9 to 2.2 inches (4.8 to 5.6 centimetres) or more than that, surgery is recommended as these may rupture and cause life-threatening issues. The other symptoms include stomach pain, or you have a leaking, tender or painful aneurysm.
Surgery will depend on age, condition, type of aneurysm, and size. It includes:
-
Endovascular repair- a catheter is inserted through the leg’s artery and is guided towards the aorta to repair the abdominal aortic aneurysm. A graft is also inserted to provide strength to the weak aorta section.
-
Open abdominal surgery will be the removal surgery of the damaged part of the aorta. The graft replaces the damaged part, and the recovery might take a month or more.
Post-operation care and recovery for Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
Recovery from abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair, whether through open surgery or endovascular repair (EVAR), involves careful post-operative care to promote healing and reduce complications.
- Hospital Stay: After surgery, you'll usually spend a few days in the hospital for monitoring and initial recovery. The duration of stay depends on the type of surgery and your overall health.
- Pain Management: You'll receive pain medications to manage discomfort during the recovery period. Take them as prescribed and communicate with your healthcare team if you experience severe or persistent pain.
- Activity Restrictions: Initially, you'll need to limit physical activity to allow your body to heal. Avoid lifting heavy objects, strenuous exercise, and driving until cleared by your doctor. Gradually increase activity levels as advised.
- Wound Care: Follow your doctor's instructions for wound care, including keeping the surgical incision clean and dry. Report any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or drainage, to your healthcare provider.
- Diet: Your doctor may recommend dietary modifications, such as a low-sodium diet, to promote healing and manage blood pressure. Stay hydrated and eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains.
- Medications: You may need to take medications to manage blood pressure, prevent blood clots, and control other medical conditions. Take medications as prescribed and attend follow-up appointments for monitoring.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider. These appointments allow your doctor to monitor your recovery, assess the success of the surgery, and make any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a healthy lifestyle can help prevent future complications and promote overall well-being. Quit smoking, maintain a healthy weight, exercise regularly, and manage stress.
Why Choose CARE Hospitals?
Through integrated clinical and medical practice, teaching, and research, we at CARE Hospitals strive to inspire optimism and promote health and provide accurate Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm treatment in Hyderabad and our other facilities. We aim to deliver the best results and the highest quality service through every team member's focused effort.
Frequently Asked Questions
Still Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly

