-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

White Tongue
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
White Tongue
The term "white tongue" refers to any part of the tongue that has a grayish-white coating. One may have a coating that covers the entire tongue or patches of coating. Various factors can cause a white tongue, and each one requires a different treatment. In most cases, a white tongue is a harmless symptom, but in rare instances, it may indicate a serious condition.
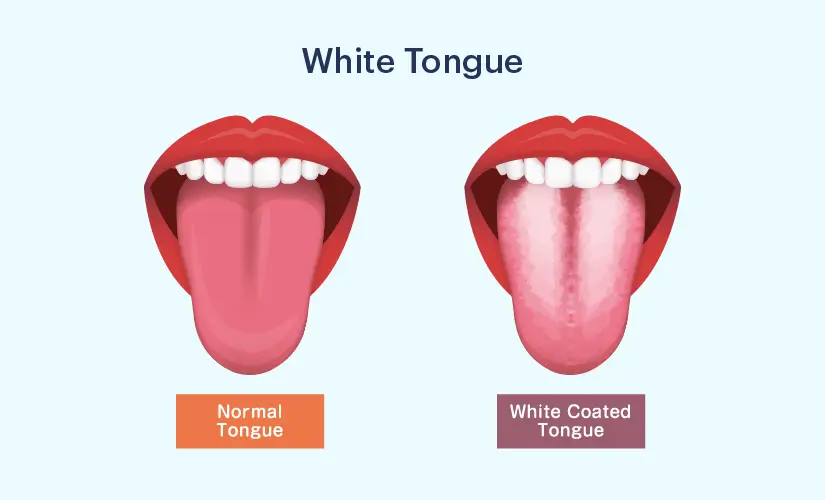
What is White Tongue?
A white tongue refers to the presence of a thick layer of white film that covers the surface of the tongue. This coating can appear in patches, cover the entire tongue, or be limited to the back part. While a white tongue may initially seem concerning, it is usually a symptom of trapped bacteria, debris (such as food and sugar), or dead cells on the tongue. If the condition persists for more than a few weeks or if the person experiences pain or difficulty speaking or eating, it is advisable to seek medical advice from a doctor.
White Tongue Symptoms
The surface of the tongue can become coated with germs and debris due to factors such as:
- Dehydration: Moderate dehydration can cause a white coating to develop on the tongue. When the body lacks sufficient fluids, it can affect the mouth's natural cleaning processes, allowing germs and debris to accumulate on the tongue's surface.
- Illness: Infections and illnesses, especially those accompanied by fever, can contribute to a whitish appearance on the tongue. This is often due to the body's response to the illness, which can affect the normal shedding of dead cells from the tongue's surface.
- Dry Mouth (Xerostomia): A dry mouth can lead to a buildup of bacteria and debris on the tongue. Saliva plays a crucial role in maintaining oral health by washing away particles and preventing the growth of harmful microorganisms.
- Infection: In cases of infection, irritation, or chronic inflammation of the tongue's surface, one may observe a whitening of the top layer or the presence of white spots or patches on the tongue. This can be a sign of various underlying issues.
- Oral Thrush (Candidiasis): One of the most common conditions associated with a white-coated or patchy tongue is oral thrush, which is caused by Candida yeast overgrowth. This infection can manifest as white, creamy plaques on the tongue and other parts of the mouth. It is often seen in individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those undergoing cancer treatment, living with HIV/AIDS, or taking certain medications like antibiotics that disrupt the normal balance of oral flora.
- Weakened Immune System: People with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to oral yeast infections, including oral thrush. This is because their bodies may struggle to keep Candida under control, leading to its overgrowth and the characteristic white patches on the tongue and mouth.
- Scarlet Fever: Some illnesses, such as scarlet fever, can cause red spots or a strawberry-like appearance on the tongue. This condition results from a streptococcal infection and is typically accompanied by a red rash on the skin. The tongue's appearance can serve as a diagnostic clue in such cases.
Causes of White Tongue
A white tongue can result from various medical conditions:
- Leukoplakia - A common disorder known as leukoplakia is caused by an overgrowth of cells in the lining of the mouth. These cells fuse with the keratin protein, which is also found in hair, creating a raised white patch on the tongue. In many cases, alcohol consumption or smoking tobacco can irritate the mouth and tongue, leading to the development of this condition. Sometimes the cause is unknown. Leukoplakia is often not a dangerous condition, although it can occasionally progress to oral cancer years or even decades after its initial appearance.
- Oral Lichen Planus - Oral lichen planus is a chronic inflammatory condition of the mouth. It can be triggered by an immune system dysfunction, which affects the body's ability to fight against microbes and other threats. This medical condition is not contagious.
- Geographic tongue - Geographic tongue may develop as the skin of our tongue regenerates. The top layer of the tongue's skin can peel off in patches too quickly, leaving behind sore, red, and painful areas that are often prone to infection. Other areas of the tongue become more stationary during this process and turn white.
- Dental thrush - Oral thrush, a mouth infection caused by the yeast Candida (fungus), can lead to a white tongue. While a person usually has candida in their mouth, it only causes problems when it multiplies uncontrollably.
- Syphilis - Syphilis is a bacterial infection and a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that is transmitted through sexual contact. A white tongue is one of the many symptoms of this dangerous condition.
Other causes of a white tongue can include:
- Poor oral hygiene
- Chewing, dipping, smoking, or vaping tobacco
- Breathing through the mouth
- Use of antibiotics
- Wearing dentures or injuring the tongue with a sharp object.
Why is my tongue white?
A white tongue can be caused by several factors. Here are some common reasons:
- Oral Hygiene Issues: Poor brushing and flossing can lead to a buildup of bacteria, dead cells, and food particles on your tongue, which can cause it to appear white.
- Dehydration: Not drinking enough water can cause your tongue to become dry and coated with a white layer.
- Thrush: A yeast infection in the mouth, known as oral thrush or candidiasis, can cause a white, creamy coating on the tongue.
- Leukoplakia: This condition causes white patches on the tongue that can be caused by irritation from tobacco use or other factors. It’s important to have it checked by a healthcare provider as it can sometimes be a precursor to more serious conditions.
- Geographic Tongue: This condition causes patches on the tongue that can appear white and map-like. It’s usually harmless and doesn’t require treatment.
- Stomach or Digestive Issues: Sometimes, gastrointestinal problems or imbalances can lead to a white coating on the tongue.
- Infections: Certain infections, including bacterial infections, can cause a white appearance on the tongue.
How is the White Tongue treated?
White tongue often disappears on its own within a few weeks. However, if it persists for a long time, it is better to seek treatment. The causes and treatments for white tongue differ depending on the symptoms.
- Tongue Rash - Most of the time, rashes go away on their own. In order to treat symptoms like burning or aching gums, the doctor may prescribe steroid mouthwashes and steroid sprays if the patient has an oral lichen planus rash that doesn't go away.
- Hairy Tongue - Most likely, the doctor won't specifically mention hairy tongue. Instead, they'll focus on restoring a compromised immune system. In exceptional circumstances, they may recommend antiviral medications like valacyclovir or famciclovir. Alternatively, they might immediately treat white spots with a substance (such as retinoic acid or podophyllin resin).
- Infection - The doctor will prescribe antifungal medications like nystatin or fluconazole for fungal infections like oral thrush. Antibiotics (such as penicillin) are necessary to eradicate the bacteria if syphilis is the cause of the white tongue.
- White Patches - There is no chance that the white spots related to the geographic tongue may develop into cancer. The main goal of treatment is to control uncomfortable symptoms. For instance, one can avoid consuming painful foods and beverages. Doctors may remove the patches if there is a chance that they might develop into cancer, as is occasionally the case with leukoplakia. Scalpels, lasers, and even cryotherapy (freezing with liquid nitrogen) are some of the tools they may use.
Complications
Complications of a white tongue can include:
- Gum Disease: Bacteria and debris on your tongue can contribute to gum disease, which can cause tooth loss and affect overall oral health.
- Infections: The bacteria or yeast causing the white coating can spread, leading to infections in other parts of your mouth or body.
- Oral Cancer: White patches from conditions like leukoplakia, if left untreated, can sometimes develop into oral cancer.
- Bad Breath: A white coating on the tongue can contribute to persistent bad breath due to bacteria and dead cells.
- Difficulty Eating or Swallowing: If the white coating is due to a thick buildup or infection, it might make eating or swallowing uncomfortable.
Home remedies for White Tongue
Most people can eliminate white tongue by maintaining good dental hygiene and staying hydrated by consuming enough water. Here are some home remedies that can be helpful:
- Drink at least eight glasses of water every day.
- Use a gentle toothbrush to clean the teeth.
- To remove the white coating, brush the tongue or use a tongue scraper.
- Use mouthwash and mild fluoride toothpaste.
- Avoid using products such as cigarettes and vape pens, as they can expose the tongue to pollutants.
- Avoid consuming meals that can irritate the mouth, such as those that are salty, sour, acidic, or extremely hot.
- Probiotics are another technique that can help with oral symptoms like a white tongue. Certain bacterial strains known as probiotics are beneficial for the digestive system.
- To reduce the bacteria that cause a white tongue, mix food-grade baking soda with a toothbrush and gently massage the tongue, teeth, and gums together.
- Baking Soda Scrub: Use a toothbrush with food-grade baking soda to scrub your tongue, teeth, and gums. This can help reduce bacteria that cause a white tongue.
- Raw Garlic: Eating garlic can help fight infections because it has antibacterial and antifungal properties, which may help against Candida.
Tongue Scraping: Gently scrape your tongue from back to front to remove bacteria and debris.
How to Prevent a White Tongue?
Sometimes we have no control over developing a white tongue. However, the likelihood can be lowered by maintaining adequate dental hygiene. Visit the dentist for a checkup every six months. Brushing teeth twice a day is always beneficial. Daily flossing and a balanced diet rich in fresh fruits and vegetables are recommended.
Consider stopping drinking or reducing cigarette usage if the symptoms of the white tongue are severe. Make routine follow-up appointments with a dentist or healthcare professional. Regular maintenance can help prevent the development of cancer in the white patch.
When to call a doctor
You should call a doctor if you have a white tongue and experience any of the following:
- Persistent White Coating: If the white coating on your tongue doesn’t go away with improved oral hygiene or home remedies.
- Pain or Discomfort: If you feel pain, soreness, or a burning sensation on your tongue.
- Difficulty Eating or Swallowing: If the white coating makes it hard to eat or swallow.
- Visible White Patches: If you have white patches on your tongue that look unusual, especially if they don’t scrape off.
- Other Symptoms: If you have additional symptoms such as persistent bad breath, fever, or unexplained weight loss.
- Change in Oral Health: If you notice any new or worsening symptoms in your mouth or throat.
FAQs
1. Is White Tongue serious?
Even though a white tongue might be unsettling, the condition is often transient and harmless. However, a white tongue can also be a sign of various serious medical conditions, ranging from an infection to a precancerous condition.
2. Does a White Tongue mean you are sick?
No, not always. A white tongue usually indicates that you need to focus on your general health and oral hygiene. For instance, it can imply that you should brush and floss more regularly, as well as abstain from alcohol and cigarettes
3. What deficiency causes a White Tongue?
A lack of iron or vitamin B12 might result in a white tongue.
4. How long does it take to get rid of a White Tongue?
Although there are several reasons for a white tongue, it normally fades away in a few weeks. If it persists longer than that or if an individual experiences difficulty speaking or eating, it is important to consult a healthcare professional.
5. Can stomach problems cause a white tongue?
Yes, stomach issues, like acid reflux or digestive problems, can sometimes cause a white coating on the tongue.
6. Is a white tongue bad?
A white tongue is not usually serious and can often be harmless. However, if it doesn’t go away or is accompanied by other symptoms, it’s a good idea to see a doctor.
7. Does a white tongue mean you're sick?
Not necessarily. A white tongue can be a sign of various things, including poor oral hygiene or minor infections. However, if you have other symptoms or it persists, it might be a sign of an underlying health issue.
8. What does a white tongue indicate?
A white tongue can indicate a buildup of bacteria, dead cells, or debris. It can also be a sign of oral thrush, dehydration, or other conditions. If it doesn’t improve or is linked with other symptoms, consult a healthcare provider.
References:
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/17654-white-tongue

Still Have a Question?



