-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Strep Throat
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Strep Throat
Waking up with a painful, sore throat that hurts to swallow is a sign of strep throat, a common bacterial infection affecting millions yearly. Strep throat can cause severe discomfort and lead to complications if left untreated. Understanding the signs and symptoms of strep throat is crucial for early detection & proper treatment.
This comprehensive guide will explore what strep throat is, its symptoms, and how doctors diagnose it.
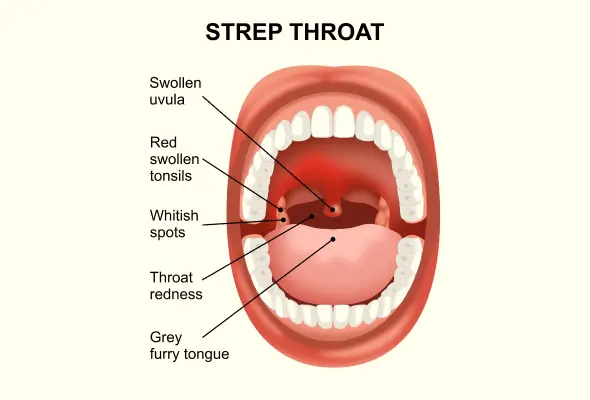
What is Strep Throat?
Strep throat is a bacterial infection. It can cause inflammation & soreness in the throat and tonsils. The infection is caused by Streptococcus pyogenes, a type of bacteria with over 120 different strains. Strep throat accounts for a significant portion of sore throat cases, making up 5-15% of adult cases and 20-30% of paediatric cases. It's most common during winter and early spring.
Symptoms of Strep Throat
Strep throat typically presents with a severe sore throat that starts suddenly. This discomfort is often accompanied by fever or chills, which can develop rapidly. The highest temperature usually occurs on the second day of infection.
Other common signs & symptoms of strep throat include:
- Painful swallowing
- Red & swollen tonsils, sometimes associated with white patches or streaks of pus.
- Tiny red spots (petechiae) on the soft or hard palate
- Swollen, tender lymph nodes in the neck
- Headache
- Loss of appetite
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea and vomiting, especially in younger children
- Body aches
In some cases, individuals with strep throat may develop a rash known as scarlet fever. This rash typically pops up first on the neck and chest but can be visible on other body parts. It may feel rough, similar to sandpaper.
Causes and Risk Factors of Strep Throat
Strep throat is due to infection by the group A Streptococcus bacteria, specifically Streptococcus pyogenes. These bacteria are highly contagious & spread through respiratory droplets. When an infected individual sneezes or coughs, they throw these droplets into the air, which others can inhale and get infected.
Direct contact with a person infected with bacteria can also lead to strep throat. This includes sharing food, drinks, or utensils with someone who has the infection. The bacteria can also survive on surfaces for a short time, so touching contaminated objects and then touching your nose or mouth can result in infection.
Several factors can increase the susceptibility of developing strep throat. These can be:
- Age with children between 5 and 15 years old being most susceptible.
- Time of year also plays a role, with infections being more common during winter and early spring.
- Close contact with a person who has strep throat
- Weakened immune system
- Living or working in crowded environments like schools or childcare centres
Complications
While strep throat is usually a mild condition, it can result in serious complications if left unattended. These include:
- Pneumonia, which is a lower respiratory infection that causes inflammation in the alveoli
- Meningitis, which affects the membranes and fluids around the spinal cord and brain
- Ear infections can also develop if the strep bacteria travel into the ear's eustachian tubes or middle ear
- Throat abscess resulting in a pocket of infected pus in the throat tissue.
- Toxic shock syndrome, though rare, is a serious side effect that occurs when the infection spreads throughout the body, potentially leading to organ failure.
- Rheumatic fever is a common and serious complication of strep throat, which causes inflammation and scarring in the heart structures.
- Other possible complications include scarlet fever, inflammation of the kidneys, and post-streptococcal reactive arthritis.
Diagnosis of Strep Throat
Physical Evaluation and Specific Tests: Your doctor will assess your condition & inquire about your symptoms. They will prescribe strep tests to confirm the presence. Here are two main types of strep tests:
- The Rapid Antigen Test: The rapid test is quick and can provide results in about 15-20 minutes. It involves swabbing the back of your throat and tonsils with a long cotton swab.
- The Throat Culture: If the rapid antigen test is positive, it confirms a strep throat infection, and your doctor will prescribe antibiotics. However, if the test is negative, your doctor might perform a throat culture to double-check the results. A throat culture is more accurate, but it usually takes 1-2 days to obtain results.
Treatment for Strep Throat
- Antibiotics: Strep throat treatment typically involves antibiotics to kill the bacteria causing the infection. Penicillin and amoxicillin are commonly prescribed for this purpose. If you're allergic to penicillin, your doctor can recommend alternative antibiotics. These strep throat medications are usually taken for ten days, and it's crucial to complete the entire course, even if you start feeling better.
- Pain Medications: Over-the-counter Pain Relievers can help ease symptoms and reduce fever.
- Rest: Remember, strep throat is highly contagious. It's crucial to stay home until you've been on antibiotics for at least 24 hours and no longer have a fever.

When to See a Doctor
If you suspect you have strep throat, talk to a doctor immediately. Seek medical attention if:
- If you experience severe throat pain, difficulty swallowing, or a fever above 38°C.
- If your child seems seriously unwell, has a high fever, eats or drinks much less than normal, or shows signs of dehydration.
- If you experience difficulty breathing or noisy breathing
- If you see blue or grey skin, tongue, or lips
- If you experience extreme drowsiness or unresponsiveness
- If the symptoms do not improve or worsen after taking antibiotics for 48 hours
Home Remedies for Strep Throat
While antibiotics are essential for treating strep throat, various strep throat treatments at home can help ease its symptoms and promote comfort during recovery. These are:
- Drinking water in optimal quantity can prevent dehydration and moisten the throat, making swallowing easier.
- Consuming soothing foods like broth, soups, and soft fruits can provide relief.
- Gargling with lukewarm salt water several times daily can help ease throat pain and reduce swelling.
- Rest is vital in fighting the infection, so getting plenty of sleep & avoiding strenuous activities is essential.
- A humidifier in your room can add moisture to the air, easing discomfort.
- Honey, renowned for its soothing properties, can be added to warm tea or water to help lessen pain and suppress coughs.
- Avoiding irritants like cigarette smoke and cleaning product fumes is crucial, as these can worsen throat irritation.
Prevention
Preventing strep throat involves adopting good hygiene practices and taking proactive steps to reduce the spread of infection, such as:
- One of the most effective ways to prevent strep throat is by frequently washing your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds or using an alcohol-based hand sanitiser. This is especially important before eating and after coughing or sneezing.
- Covering your nose & mouth while coughing or sneezing is crucial in preventing the transmission of strep throat. Use a tissue if possible, and dispose of it immediately after use. If you don't have a tissue, sneeze or cough into your elbow or upper sleeve rather than your hands.
- Avoiding sharing personal items is another important preventive measure. Don't share drinking glasses, eating utensils, or other personal items with someone suffering from strep throat.
- Taking time off from regular activities when you're sick can prevent the spread of strep throat to others in your community. This is particularly important in settings where infections can spread quickly, such as schools, childcare centres, and workplaces.
Conclusion
Strep throat is a prevalent bacterial infection that can cause severe discomfort and complications if not treated promptly. By following good personal hygiene practices and seeking proper treatment when needed, you can manage strep throat effectively and reduce its impact on your health and daily life. Remember, while home remedies can provide relief, antibiotics are crucial to treating the infection and preventing complications.
FAQs
1. Who does strep throat affect?
Strep throat can affect all individuals irrespective of their age, but it's most common in children between 5 and 15 years old. Adults who have close contact with children, such as parents, teachers, and daycare workers, are also at higher risk. People in crowded settings like schools, daycares, and military barracks are more likely to contract strep throat.
2. How common is strep throat?
Strep throat is quite common, especially among children. Globally, doctors see more than 616 million new cases of strep throat each year.
3. How do you get strep throat?
The causative factor of strep throat is group A Streptococcus bacteria. You can get it through close contact with an infected person. The bacteria spread through inhaling respiratory droplets when an infected person sneezes, coughs, talks, or sings. You can also get it by touching contaminated items and surfaces and then touching your mouth or nose.
4. Is strep throat contagious?
Yes, strep throat is highly contagious. Even people without symptoms can spread the bacteria. The infection is most contagious during the two to five days after exposure before symptoms appear. With antibiotic treatment, a person usually becomes less contagious after 24 to 48 hours.
5. How long does strep last?
Typically, strep throat lasts three to five days if untreated. Most people start feeling better with antibiotic treatment within one to two days. However, it's crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics, which usually lasts 7 to 10 days, to prevent complications and recurrence.
6. Does strep throat go away by itself?
While strep throat can sometimes resolve on its own, it's not recommended to leave it untreated. An antibiotic course is essential to reduce the risk of complications, ease symptoms, and prevent the spread of infection to others.
To Book an Appointment, call:
Still Have a Question?




