-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Oral Thrush (Oropharyngeal Candidiasis)
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Oral Thrush
Oral thrush (medically referred to as oropharyngeal candidiasis) is a fungal infection commonly affecting the throat and mouth. It develops due to an overgrowth of a fungus called Candida, which is naturally present in small amounts in the human body. Creamy white patches in the oral cavity and tonsils may cause discomfort while eating or drinking, impacting speech and interpersonal interactions. Oral thrush can cause irritation or soreness in the oral cavity and throat, sometimes leading to complications if left untreated.
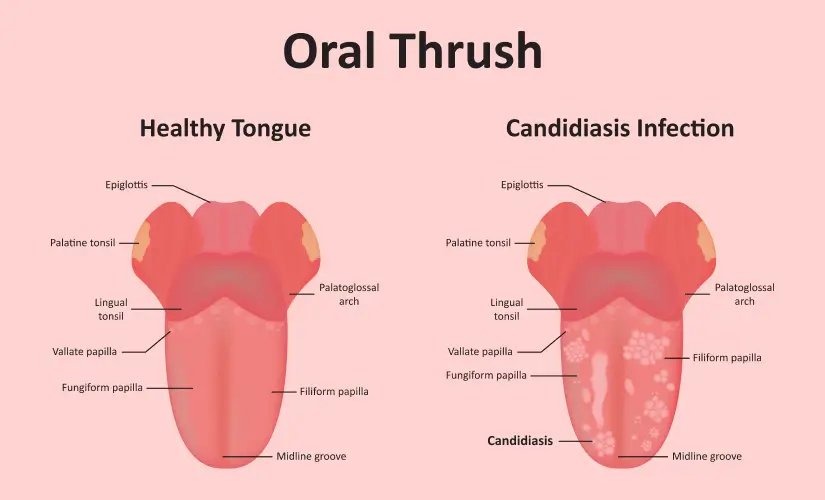
What is Oral Thrush?
Oral thrush is an infection that occurs when Candida, a fungus usually present in the mouth and digestive tract, overgrows. This causes inflammation and white or yellow patches in various areas of the oral cavity, such as the inner cheeks, tongue, and sometimes the roof of the mouth, gums, and tonsils. These patches can be painful and make it difficult to swallow or eat.
Symptoms of Oral Thrush
The key symptom of oral thrush is white or yellow lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, or other mouth areas. Other symptoms may include:
- Redness or soreness in the mouth
- Difficulty swallowing or eating
- Loss of taste
- Cracked or dry lips
- Bleeding from the mouth
What Causes Oral Thrush?
Several factors can trigger the overgrowth of Candida fungus, such as:
- Weakened immune system
- Antibiotic usage
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Dry mouth
- Poor oral hygiene
- Dentures or other oral appliances
- Smoking or excessive alcohol consumption
Risk Factors for Oral Thrush
Several factors can increase the possibility of developing oral thrush, including:
- Weakened immune system (e.g., HIV/AIDS, cancer treatment, organ transplant)
- Diabetes
- Pregnancy
- Dry mouth (xerostomia)
- Use of certain medications (e.g., antibiotics, corticosteroids)
- Dentures or other oral appliances
- Smoking or excessive alcohol consumption
Complications of oral thrush
While oral thrush generally does not cause serious ailments, it can lead to several complications if left untreated, especially in people with weakened immune systems. Potential complications include:
- Difficulty swallowing or eating
- Nutritional deficiencies
- Spread of the oral thrush infection to other parts of the body (e.g., oesophagus, lungs)
- Increased risk of secondary infections
- In rare cases, oral thrush can lead to systemic candidiasis, affecting multiple organs and can be life-threatening if not promptly treated.
When to see a doctor
Immediately seek medical attention if you experience any of the following:
- Severe or persistent oral thrush that does not respond to over-the-counter treatments
- Difficulty swallowing or eating
- Fever or other signs of systemic infection
- Weakened immune system or other underlying systemic conditions
Diagnosis
Your dentist can diagnose oral thrush through a routine oral examination and medical history. The characteristic white lesions on the tongue, inner cheeks, or throat usually indicate the condition. Your doctor may also perform a simple test called a potassium hydroxide (KOH) preparation or culture to confirm the presence of Candida. Additionally, if oral thrush is recurrent or persistent, doctors may recommend further investigations to determine underlying conditions contributing to the infection, such as diabetes or immunodeficiency disorders.
Treatment for Oral Thrush
The treatment for candida oral thrush depends on the intensity of the infection and the underlying cause. Early-stage oral thrush is more receptive to treatment. Common oral thrush treatment modalities include:
- Antifungal medications:
- Topical antifungal medicines are applied directly to the affected areas in the mouth.
- Doctors may prescribe oral antifungal medicines for more severe or persistent cases.
- Probiotics:
- Probiotics, such as Lactobacillus, can restore the balance of beneficial bacteria in the mouth and digestive tract.
- Dietary changes:
- Lower the consumption of sugary and refined carbohydrate foods, which are candidial growth-promoting agents. Instead, focus on a balanced meal rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins. Limiting alcohol and caffeine consumption can further support your body's ability to protect itself from the oral thrush infection.
- Improved oral hygiene:
- Practice good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth properly twice daily, floss your teeth, and use an antimicrobial mouthwash.
- Managing underlying conditions:
- In cases where underlying conditions contribute to candida oral thrush, addressing these conditions is essential for effective treatment.
Oral Thrush Prevention
To help prevent oral thrush, practicing good oral hygiene and maintaining a healthy immune system is crucial. Here are some tips:
- Brush your teeth with the proper technique twice a day and floss regularly
- Use an antimicrobial mouthwash
- Clean and replace dentures or other oral appliances regularly
- Avoid excessive consumption of sugary or refined carbohydrate foods
- Manage underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes
- Maintain a balanced diet and take probiotics or supplements if recommended by your doctor
Conclusion
Oral thrush, a common fungal infection, can cause discomfort and sometimes lead to complications if left untreated. By understanding the causes, manifestations, and risk factors, you can take several measures to effectively prevent and manage oral thrush. If you experience persistent mouth discomfort or any symptom of oral thrush, don't hesitate to consult your doctor.
FAQs
1. How serious is the problem of Oral thrush?
Oral thrush is usually not a serious ailment, but it can cause discomfort and, in some cases, lead to complications if left untreated. These complications are more common in individuals with weakened immune systems or chronic systemic conditions.
2. What is the main cause of mouth thrush?
The primary cause of oropharyngeal candidiasis is an overgrowth of the Candida fungus. Several components, such as a weakened immune system, antibiotic use, diabetes, pregnancy, dry mouth, poor oral hygiene, dentures or other oral appliances, and smoking or excessive alcohol consumption, can contribute to this overgrowth.
3. How can I get rid of the problem of oral thrush fast?
To get rid of oral thrush quickly, follow your doctor's recommended treatment plan, including antifungal medications, probiotics, dietary changes, and improved oral hygiene. Over-the-counter antifungal medications can also provide temporary relief, but persistent or severe cases may require prescription-strength medications.
4. Can saltwater heal oral thrush?
Saltwater can help alleviate the symptoms of oral thrush by reducing inflammation and promoting healing. However, it is not a cure for oral thrush and should be used in conjunction with other treatments recommended by your doctor.
5. Can oral thrush cure itself?
In some cases, mild oral thrush may resolve on its own, primarily if the underlying cause of oral thrush is addressed (e.g., improving oral hygiene, managing diabetes, or restoring a healthy immune system). However, seeking medical guidance is essential if the symptoms persist or worsen, as untreated oral thrush can lead to several complications.

Still Have a Question?



