-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Enlarged Prostate
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Enlarged Prostate
Prostate enlargement affects nearly 50% of all men over age 50, becoming more common as they age. While not usually dangerous, this condition can significantly impact daily life through various urinary symptoms and discomfort. Current medical advances offer several effective treatment options, from lifestyle changes to medication & surgical procedures, helping men manage their symptoms and maintain their quality of life.
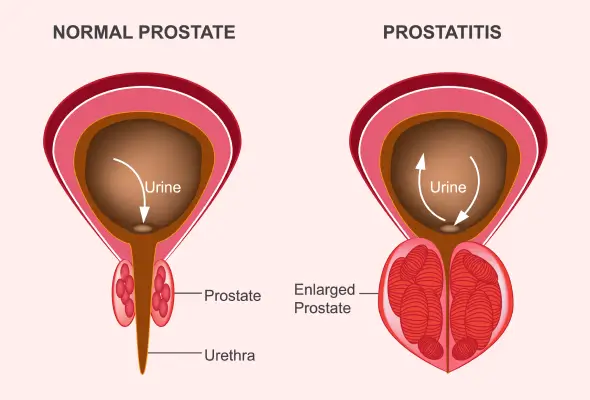
What is an Enlarged Prostate?
A small, walnut-sized organ, the prostate gland plays an elementary role in the male reproductive health by producing fluid that helps carry sperm. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or enlarged prostate, occurs when this gland grows bigger as men age. This condition is not cancer and does not increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.
The prostate gland surrounds the urethra. It is a tubular structure that takes urine from the bladder out of the body. As the prostate enlarges, it can press against the urethra and bladder, leading to various urinary symptoms. This growth happens in two main phases:
- The first growth phase occurs during puberty
- The second phase begins around age 25 & continues throughout life. The prostate typically enlarges enough to cause noticeable symptoms and the bladder wall becomes thicker over time. The bladder may gradually lose its ability to empty completely.
Enlarged Prostate Symptoms
The following are some of the most common symptoms and signs of an enlarged prostate:
- Urination Difficulties:
- Trouble starting urination
- Weak urine stream
- Straining to urinate
- Stop-start pattern while urinating
- Frequency and Urgency Issues:
- Frequent need to urinate, especially at night
- Sudden, urgent need to urinate
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
- Need to urinate again shortly after finishing
- Incontinence Problems:
- Dribbling after urination ends
- Leaking before reaching the toilet
- Uncontrolled leakage when coughing or sneezing
Enlarged Prostate Causes
The medical community continues to research the exact reason for prostate enlargement, though hormonal changes play a significant role. As men age, their bodies experience shifts in hormone levels, particularly in the balance between testosterone and other hormones, which can trigger prostate growth.
Several risk factors contribute to the development of an enlarged prostate:
- Age-related Factors:
- Symptoms rarely appear before age 40
- Risk increases significantly after age 50
- The prostate grows approximately 2-2.5% each year in older men
- Genetic Influences:
- Family history increases the risk significantly
- Men with inherited forms show earlier symptoms
- Genetic factors may contribute
- Health Conditions:
- Diabetes and heart disease increase risk
- Obesity links to larger prostate volume
- Metabolic syndrome
- Lifestyle Factors:
- Lack of physical activity
- Poor dietary choices
- Obesity and excess weight
Complications
The most common complications include:
- Urinary Retention:
- Complete inability to urinate
- May require catheter placement
- Can lead to emergencies
- Bladder Problems:
- Formation of bladder stones
- Weakening of bladder muscles
- Incomplete emptying of the bladder
- Increased risk of urinary tract infections
- Kidney Complications:
- Pressure buildup affecting kidney function
- Potential permanent kidney damage
- Risk of infection spreading to kidneys
Diagnosis
Doctors use several diagnostic tools to evaluate prostate enlargement:
- Basic Diagnostic Tests
- Symptom assessment and medical history review
- Physical examination, including digital rectal exam
- PSA blood test to check prostate-specific antigen levels
- Urine investigations to check for infection or other abnormalities
- Post-void residual volume measurement
- Specialised Diagnostic Tests
- Uroflowmetry to measure urine flow rate
- Transrectal ultrasound to visualise the prostate's size and shape
- Some men might need advanced imaging like MRI or CT scans, mainly if surgery is being considered.
Referral to a urologist is necessary when initial treatments haven't helped, urinary infections persist, or PSA levels are elevated. The specialist may perform additional tests such as cystoscopy. This test involves the insertion of a thin, flexible tube with a camera to visualise the bladder and urethra.
Enlarged Prostate Treatment
Treatment options for enlarged prostate have evolved significantly in recent years, offering men various approaches based on their symptom severity and overall health condition. Doctors typically recommend a stepped approach, starting with the least invasive options before considering more aggressive treatments.
The main treatment categories include:
- Watchful Waiting:
- Regular monitoring of symptoms
- Lifestyle modifications
- Suitable for mild symptoms
- Medication Options:
- Alpha-blockers to relax prostate muscles
- 5-alpha reductase inhibitors to shrink the prostate
- Combination therapy for better results
- Procedures:
- Several surgical and minimally invasive procedures are available for managing an enlarged prostate in men with moderate to severe symptoms; these include transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), which remains the most common surgical treatment.
- Newer treatment options like laser therapy and water vapour treatment may offer faster recovery with fewer complications.
The treatment depends on several factors, including prostate size, symptom severity, and overall health status. Some men find relief through simple lifestyle changes, while others may warrant medication or surgical intervention. Regular consultation with doctors helps determine the most effective treatment approach as symptoms progress or change over time.
When to See a Doctor
Recognising when to seek medical attention for prostate-related symptoms can prevent serious complications. Men should not ignore or delay medical consultation when experiencing urinary changes, as early intervention often leads to better outcomes.
Immediate medical intervention is necessary for these emergency symptoms:
- Complete inability to urinate
- Blood in urine or semen
- Severe pain or burning during urination
- Fever and chills with urinary symptoms
- Persistent pain & discomfort in the pelvic area or lower region of the abdomen
- Frequent urinary tract infections
Even if symptoms seem mild, scheduling a consultation with a doctor is essential for proper evaluation. A simple blood investigation, known as the PSA test, serves as the initial screening tool for prostate problems. Men should inform their doctor about any family history of prostate conditions, as this can influence their risk assessment and screening schedule.
Regular prostate screenings become particularly important as men age. The doctor can explain beneficial lifestyle changes and behaviours that may help reduce the risk of prostate enlargement. Through proper monitoring and timely medical intervention, many complications associated with an enlarged prostate can be prevented or effectively managed.
Conclusion
Prostate enlargement stands as a common health challenge for men, particularly those over fifty years old. Medical science offers numerous ways to manage this condition, from simple lifestyle changes to advanced surgical procedures. Men who notice urinary changes or other prostate-related symptoms should not delay seeking medical help, as early treatment prevents serious complications.
Regular prostate screenings, proper medical care, and lifestyle adjustments help men maintain their quality of life while dealing with enlarged prostate symptoms. The condition, though challenging, remains manageable with proper medical guidance and consistent monitoring. Most men can find relief through appropriate treatment options suited to their symptoms and overall health condition.
FAQs
1. What is the main reason behind prostate enlargement?
The exact cause of prostate enlargement remains unclear, though research points to hormonal changes as the primary factor. As men age, their bodies experience shifts in hormone levels, particularly dihydrotestosterone (DHT). This male hormone appears at higher levels in older men, potentially triggering prostate cell growth and enlargement.
2. At what size of prostate requires surgery?
Surgical intervention typically becomes necessary when the prostate volume measures between 30-80 cubic centimetres. However, size alone does not determine the need for surgery. Doctors consider several factors:
Severity of symptoms
- Response to medication
- Impact on quality of life
- Presence of complications
- Overall health condition
3. What is the age limit for prostate surgery?
Modern medical guidelines focus on overall health status rather than age alone when considering prostate surgery. While previously restricted, current research shows that healthy men over 75 can safely undergo prostate procedures if they have:
- Life expectancy greater than 10 years
- Good overall health status
- Minimal other health conditions
- Significant prostate symptoms affecting the quality of life

Still Have a Question?



