-
Doctors
-
Specialities
Clinical Services
- Anaesthesia
- Cardiac Anesthesia
- Cardiology
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Critical Care Medicine
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology
- ENT
- General Medicine
- General Surgery
- HPB
- Lab Medicine
- Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery
- Microbiology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Oncology
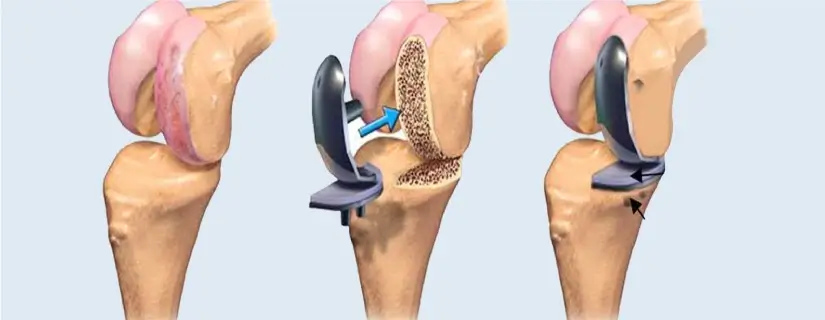
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Pain and Palliative care
- Pathology
- Plastic Surgery
- Pulmonology
- Radiology
- Rheumatology
- Robot - Assisted Surgery
- Surgical Gastroenterology
- Surgical Oncology
- Urology
- Woman & Child Institute
Professions Allied to Medicine
- Ambulance
- Dietetics
- Physiotherapy
- Pharmacy / Dispensary
- Blood Transfusion Services
- Clinical Bio Chemistry
- Clinical Microbiology & Serology
- Clinical Pathology
- Cytology/FNAC Information for Patients
- Haematology
Pharmacy
Laboratory Services & Transfusion Services
-
Health Check Packages
-
Book an Appointment
-
Contact Us