-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Vitamin D Deficiency
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D nutrient plays a vital role in keeping bones strong and supporting immune system function, yet millions of people worldwide lack adequate levels of this essential nutrient. This blog explores the causes, symptoms, and effective treatments for vitamin D deficiency, along with guidance on maintaining healthy vitamin D levels through diet, supplements, and lifestyle changes.
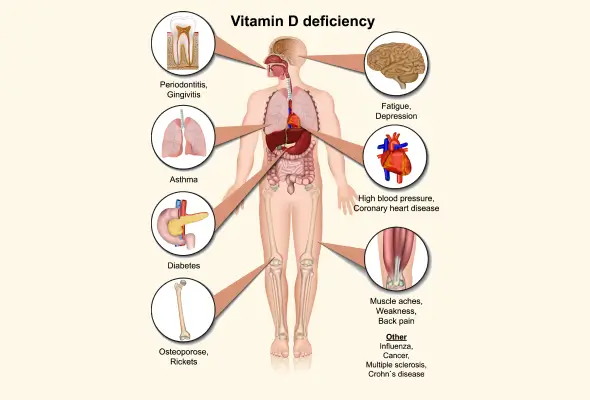
What is Vitamin D Deficiency?
Vitamin D deficiency develops when the body has insufficient levels of this essential nutrient to maintain optimal health. Doctors typically define this condition as having blood vitamin D levels below 20 ng/mL, while levels between 21-29 ng/mL are considered insufficient.
This essential nutrient plays a key role in several body functions, particularly in helping the body absorb and utilise calcium and phosphorus. When vitamin D levels are adequate, the body can:
- Absorb calcium effectively from dietary sources
- Maintain proper bone mineralisation
- Support muscle function
- Enable proper phosphorus absorption
- Maintain healthy bone density
The human body obtains vitamin D through three primary sources: sunlight exposure, dietary intake, and supplements. When ultraviolet radiation from sunlight hits the skin, it triggers vitamin D production. Certain foods, including fish, egg yolks, and fortified products like milk and cereals, also provide this nutrient.
Symptoms of Vitamin D Deficiency
The following are some common vitamin D deficiency symptoms:
- Physical Symptoms:
- Neurological and Mood-related Signs:
- Depression or feelings of sadness
- Sleep disturbances
- Increased sensitivity to pain
- Pins and needles sensation in hands or feet
Vitamin D Deficiency Causes
The primary causes of low vitamin D fall into two main categories: insufficient intake and poor absorption. Many people don't get enough vitamin D through their diet or sunlight exposure, while others have conditions that prevent proper absorption of this vital nutrient.
Conditions that significantly impact vitamin D levels include:
- Digestive Disorders: Cystic fibrosis, Crohn's disease, and celiac disease affect nutrient absorption
- Kidney and Liver Disease: These conditions limit the body's ability to process vitamin D
- Post-surgical Complications: Weight-loss surgeries can reduce nutrient absorption
- Medications: Certain medications, such as steroids, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and seizure medications, can interfere with vitamin D absorption or speed up its breakdown in the body.
Risk Factors
- Age: People over 65 have a reduced ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight exposure.
- Skin Colour: Darker skin requires more sun exposure to produce adequate vitamin D levels.
- Obesity: Higher body mass index reduces vitamin D availability in the body
- Environmental Factors: Living in areas with limited sunlight or consistently using strong sunscreen can also contribute to vitamin D deficiency.
Complications of Vitamin D Deficiency
The most significant side effects of vitamin D deficiency include:
- Bone Disorders:
- Osteoporosis in adults, leading to increased fracture risk
- Osteomalacia, causing weak and soft bones
- Rickets in children, resulting in bone deformities
- Chronic Health Issues:
- Increased risk of cardiovascular disease
- Higher chances of type 1 and type 2 diabetes
- Greater susceptibility to certain cancers
- Compromised immune system function
- Metabolic Problems:
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism
- Disrupted calcium absorption
- Impaired phosphorus metabolism
Diagnosis
Doctors determine vitamin D status through specialised blood tests that measure specific forms of this nutrient in the bloodstream. The most reliable diagnostic tool is the 25- hydroxyvitamin D blood test, also known as the 25(OH)D test, which accurately measures vitamin D levels in the body.
While routine screening isn't common practice, doctors may order vitamin D testing in specific situations, such as individuals with chronic bone pain, systemic conditions affecting nutrient absorption, older adults, people with limited sun exposure, or those taking medications that affect vitamin D metabolism.
Levels above 30 nanograms per millilitre (ng/mL) are considered optimal for health, while readings between 20-30 ng/mL indicate insufficiency. Results below 20 ng/mL confirm a vitamin D deficiency that requires medical attention and treatment.
Treatment
Doctors typically recommend vitamin D3 (cholecalciferol) supplements as the primary treatment choice, as research shows they are more effective than vitamin D2 in raising blood levels.
The recommended vitamin D deficiency treatment varies based on age and condition severity:
- Adults: 6,000 IU daily or 50,000 IU weekly for 8 weeks
- Children: 2,000 IU daily for 6 weeks
- Infants: 8.5 to 10 micrograms daily throughout the year
- High-risk Individuals: 10,000 IU daily initially
- Maintenance Dose: 1,000-2,000 IU daily after achieving optimal levels
For those with specific health conditions or risk factors, such as obesity or malabsorption disorders, doctors may prescribe higher maintenance doses ranging from 3,000 to 6,000 IU daily.
When to See a Doctor
People should schedule an appointment with their doctor if they experience persistent unexplained symptoms, particularly frequent infections or bone pain without apparent cause. Those with multiple risk factors should discuss the need for regular vitamin D level monitoring with their doctor, even if they aren't experiencing symptoms.
Prevention
Preventing vitamin D deficiency requires a comprehensive approach combining dietary choices, safe sun exposure, and appropriate supplementation when necessary. The daily recommended intake varies by age, with adults needing 15 micrograms (600 IU) and those over 71 requiring 20 micrograms (800 IU).
A balanced diet enriched in vitamin D foods can help maintain adequate levels. Natural food sources include:
- Fatty fish (salmon, tuna, mackerel)
- Egg yolks
- Mushrooms exposed to UV light
- Beef liver
- Leafy greens like kale and fenugreek leaves
- Fortified products (milk, cereals, orange juice)
- Cod liver oil
- Seeds (chia seeds, sesame seeds)
- Cheese cheddar, parmesan, mozzarella
Conclusion
Understanding personal risk factors and taking proactive steps through diet, lifestyle changes, and medical guidance helps prevent vitamin D deficiency and its complications. This approach, combined with regular health check-ups, supports long-term health and well-being.
FAQs
1. Whom does vitamin D deficiency affect?
Vitamin D deficiency impacts people across all age groups and demographics. From breastfed infants to elderly adults, this condition doesn't discriminate. Research shows that even doctors and individuals living in sunny climates can develop insufficient vitamin D levels.
2. What happens if your vitamin D is low?
Low vitamin D levels can trigger various health issues, including:
Immediate effects:
- Persistent fatigue
- Muscle weakness
- Bone pain
- Increased susceptibility to infections
3. How can I increase my vitamin D level quickly?
Several effective strategies can help boost vitamin D levels:
- Take supplements as prescribed by doctors
- Spend 15-20 minutes in sunlight three times weekly between 10 am - 2 pm
- Consume vitamin D-enriched foods like fatty fish and fortified products
- Consider cod liver oil supplements
4. Who is most at risk for vitamin D deficiency?
The highest risk groups include:
- People over 65 years
- Individuals with darker skin
- Those with limited sun exposure
- People with obesity
- Individuals with digestive disorders
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
To Book an Appointment, call:
Still Have a Question?




