-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Varicocele
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Varicocele
Varicocele is a common medical condition that affects many men worldwide, causing discomfort and potential fertility issues. Varicocele occurs when veins in the scrotum become enlarged, similar to varicose veins in the legs. Understanding varicocele causes, symptoms, and treatment approaches is crucial for men's health and well-being.
This article explores varicocele, covering its symptoms, causes, and diagnosis. We'll discuss various treatment approaches, including surgery and non-surgical options, as well as potential complications and risk factors.
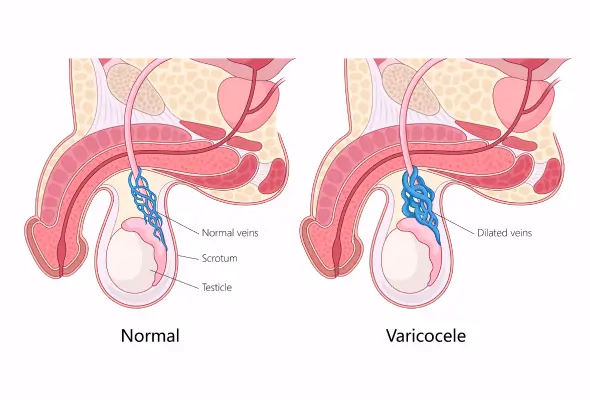
What is a Varicocele?
A varicocele is a common disorder that causes the veins in the scrotum to enlarge. The scrotum, a pouch of skin behind the penis, typically contains the testicles. Varicoceles resemble varicose veins, which cause swelling and misshaping of leg veins. Although not life-threatening, varicoceles can significantly impact fertility for those trying to have biological children. They can affect individuals with testicles at any age, but doctors believe many are present at birth. People often notice varicoceles during their teenage years, possibly due to increased blood circulation to the genitals during puberty. While varicoceles don't pose immediate health risks, they require attention, especially for those concerned about their reproductive health.
Symptoms of Varicocele
Varicoceles often go unnoticed, as they typically don't cause symptoms. However, some men may experience certain signs. These include:
- A dull, continuous ache or pain in the scrotum, which often improves when lying down
- Swelling in the testicles or scrotum
- Some men might notice a small lump above the affected testicle
- In some cases, varicoceles can lead to testicular atrophy, causing the testicles to shrink
- This condition can also contribute to fertility issues, making it difficult for couples to achieve pregnancy after a year of trying.
It's important to note that while these symptoms can occur, many men with varicoceles remain symptom-free.
Causes of Varicocele
Medical experts remain uncertain about the exact causes of varicoceles. They suspect faulty valves in the spermatic cord veins may play a role. These valves normally regulate blood flow from the testicles back to the body. When they malfunction, blood can accumulate in the veins, causing them to swell over time.
Varicoceles can affect individuals with testicles at any age. Many are believed to be present at birth, but they often become noticeable during teenage years. This timing may relate to increased blood flow to the genitals during puberty. In some cases, varicoceles can hinder proper testicle growth.
While the precise cause remains unclear, understanding these potential factors helps doctors address the condition effectively.
Diagnosis of Varicocele
Doctors diagnose varicoceles through a combination of methods.
- Medical History and Physical Analysis: The doctor will ask about symptoms and review the patient's medical history. A physical examination follows, where the provider feels the scrotum for enlarged veins. The Valsalva manoeuvre, which involves straining while holding one's breath, helps make varicoceles more noticeable during the exam.
- Pelvic Ultrasound: This non-invasive imaging test provides a detailed view of the testicular veins.
- Semen Analysis: This test checks sperm health to see if fertility concerns exist.
- Blood Test: Hormone levels, including FSH and testosterone, are evaluated.
After confirming the presence of a varicocele, the provider grades its severity. These diagnostic steps help doctors develop an appropriate treatment plan for each patient's specific condition.
Treatment for Varicocele
Doctors treat varicoceles through various methods, depending on the severity and symptoms.
- For low-grade varicoceles, doctors often recommend at-home treatments. These include:
- Avoiding activities that cause discomfort
- Avoid wearing tighter-fitting underwear during exercise
- Applying ice to the scrotum
- Using over-the-counter pain medications
- Surgery: The most common surgical approach is varicocelectomy, where a surgeon cuts and seals off affected veins to redirect blood flow. The microsurgical subinguinal approach has become the gold standard due to its lower complication rates and better outcomes.
- Microsurgical Varicocelectomy: It is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to treat varicocele, a condition where veins in the scrotum become enlarged. This condition can cause pain, discomfort, and even infertility. During the procedure, a surgeon uses a high-powered microscope to carefully tie off the affected veins, which helps to restore proper blood flow and improve sperm quality. Microsurgical varicocelectomy is often recommended for men experiencing symptoms related to varicocele, particularly if it affects fertility or causes significant discomfort
- Percutaneous Embolisation: A minimally invasive procedure where a radiologist blocks the problematic vein using coils or a scarring solution. This technique offers a quicker recovery time, with patients typically resuming work within 1-2 days.
Risk Factors for Varicocele
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing varicocele.
- Age: Adolescent boys and young adults aged 15-25 are more susceptible. Genetics: Individuals with a family history face a higher risk.
- Several anatomical factors, such as abnormal vein structures, can predispose some men to varicocele.
- Physical exertion, particularly activities involving prolonged standing or heavy lifting, may increase the risk.
- Conversely, a sedentary lifestyle can hinder blood circulation and raise venous pressure.
- Certain occupations, like truck driving or construction work, pose a higher risk.
- Obesity and exposure to excessive heat in the scrotum can also contribute to varicocele development.
Complications of Varicocele
Varicoceles can lead to several complications, such as:
- Larger varicoceles may increase the risk of low testosterone, also known as male hypogonadism. This condition can cause shrinkage of the testicles, reduced sex drive, decreased muscle mass, and depression.
- Another potential complication is azoospermia, where no sperm is present in the ejaculate, leading to male infertility.
- Interestingly, varicocele has been linked to male infertility, affecting 35-40% of men with fertility issues.
- Varicocele repair, while effective, carries its risks. These include persistent or recurrent varicocele, bruising, infection, and testicular tenderness. A hydrocele (water collection around the testis) may occur in rare cases.
- Non-surgical repairs have an additional risk of reaction to the contrast agent used. Although extremely rare, there's a slight risk of testicular loss. Despite these potential complications, varicocele treatment remains crucial for managing symptoms and preserving fertility.
When to See a Doctor
Men should consult a doctor if they experience varicocele symptoms or have difficulty getting their partner pregnant. A varicocele often causes no pain or discomfort and may be discovered during a routine wellness exam or fertility treatment. However, if someone feels pain, discomfort, or swelling in the scrotum or groin, they should consult their doctor. If you have concerns about your ability to have a biological child, talk to a doctor.
Prevention
Medical experts remain uncertain about the exact causes of varicoceles, making prevention challenging. However, individuals can take steps to promote overall vascular health, such as:
- Regular exercise, such as swimming or brisk walking, encourages healthy blood flow and circulation. Try at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise weekly.
- A diet enriched in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids may help reduce inflammation in blood vessels.
- Staying hydrated is crucial.
- Smoking damages blood vessels, so quitting can improve vascular health and lower the risk of blood clots.
- While these measures don't guarantee prevention, they contribute to overall health. It's important to note that varicoceles often develop during puberty due to increased blood flow to rapidly growing testicles, a process beyond individual control.
Conclusion
Varicoceles, while often asymptomatic, can have a significant influence on men's health and fertility. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment modalities is crucial to managing this condition effectively. From at-home remedies to surgical interventions, various approaches address varicoceles based on their severity and impact on an individual's life.
Ultimately, staying informed about varicoceles empowers men to make well-informed decisions about their health. Regular check-ups and open communication with doctors are key to early detection and effective management. By taking some proactive steps and seeking timely medical advice, men can mitigate the potential complications of varicoceles and maintain their overall well-being.
FAQ's
1. What is the leading cause of varicocele?
The exact cause of varicocele remains uncertain. Medical experts believe faulty valves in the spermatic cord veins may play a role. These valves normally regulate blood flow from the testicles, but blood accumulates in the veins when they malfunction, causing them to swell.
2. Can varicocele be cured?
While varicoceles can't be cured completely, they can be effectively managed. Treatment options include varicocele surgery and non-surgical procedures like varicocele embolisation. The treatment approach depends on the severity of symptoms and individual circumstances.
3. Can you fix varicocele without surgery?
Yes, varicocele can be treated without surgery. Varicocele embolisation, a non-surgical procedure performed by an interventional radiologist, is an effective alternative. It involves blocking the problematic vein using coils or chemicals, redirecting blood flow to healthier vessels.
4. How do you reduce varicocele naturally?
Natural methods to manage varicocele include:
- Regular exercise to improve blood circulation
- Wearing supportive underwear
- Applying ice packs to relieve discomfort
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Practising yoga poses like Ananda Balasana and Viparita Karani
5. What if a varicocele is left untreated?
If left untreated, a higher-grade varicocele can potentially cause permanent testicular damage. It may also lead to fertility issues, low sperm count, and poor sperm quality.
6. Which food should I avoid in varicocele?
Foods to avoid with varicocele include:
- Junk and processed foods
- High-sugar foods
- Refined grains
- Excessive caffeine
- Salty foods
Instead, focus on a fibre-rich diet and antioxidant-rich foods like berries, kale, and dark chocolate.
To Book an Appointment, call:
Still Have a Question?




