-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Skin Ulcers
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Skin Ulcers
Skin ulcers are open wounds on the body that can cause discomfort and concern. These persistent lesions affect millions of people worldwide, making it crucial to understand their nature and management. Skin ulcers on the body can vary in size, depth, and severity, impacting a person's quality of life and overall health.
Let's explore the different types of skin ulcers, their causes, and effective ways to identify and manage them.
What are Skin Ulcers?
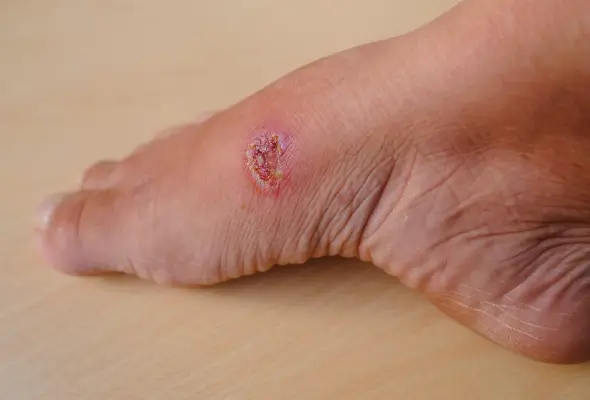
Skin ulcers are open sores on the body caused by poor blood circulation. These persistent wounds can appear on various body parts, including the legs, hips, feet, buttocks, and back. They often develop when minor injuries fail to heal properly due to inadequate blood flow. Skin ulcers typically look like round, open sores with raised and thick outer borders. The affected area may show discolouration as they form, appearing red and warm or shiny and blue in darker skin tones. As the condition worsens, the ulcer takes on a crater-like appearance and may weep clear fluid or blood. Skin ulcers can vary in severity and may take a long time to heal, potentially leading to complications if left untreated.
Types of Skin Ulcers
Skin ulcers on the body can be classified into four main types, each with distinct causes and symptoms. The following are different types of skin ulcers:
- Decubitus Ulcers: Also known as pressure sores, they develop due to contin uous pressure on specific areas, often affecting bony regions like the back, hips, and heels.
- Venous Ulcers: These are the most common type of skin ulcers, resulting from poor blood circulation in leg veins, and typically occur between the knee and ankle.
- Arterial Skin Ulcers: Ischaemic or arterial ulcers develop due to blocked arteries and inadequate blood flow, usually appearing on the lower leg, feet, and toes.
- Neuropathic Skin Ulcers: These skin ulcers are often associated with diabetes, arise from nerve damage, and commonly affect pressure points on the feet.
Causes of Skin Ulcers
Skin ulcers on the body primarily result from poor blood circulation. When blood flow is inadequate, minor injuries fail to heal correctly, leading to open sores. Several factors contribute to this condition, such as:
- Diabetes can cause nerve damage, diminishing sensation in the feet and legs and making injuries go unnoticed. High sugar concentration in the blood may also slow wound healing.
- Atherosclerosis narrows arteries, limiting blood supply to tissues. If the part of the body doesn't get enough blood supply, the skin tissue breaks down and results in skin ulcers.
- Prolonged pressure on one area squeezes blood vessels, blocking circulation and causing skin ulcers.
- Venous insufficiency, often caused by varicose veins or blood clots, leads to blood pooling in leg veins, causing swelling and ulceration. Understanding these causes is crucial for effectively identifying and managing different skin ulcer types.
Symptoms of Skin Ulcers
Skin ulcers typically appear as round open sores on the body. The following are some common symptoms of skin ulcers:
- The outer border of these sores often looks raised and thick
- Skin discolouration in the affected area
- Clear fluid or blood discharge
- Swelling of the skin surrounding ulcers
- Tenderness
- Itchiness
- Pain
- Changes in skin texture.
- In case of infection, yellow or green pus discharge
- The affected skin may look red and feel warm, while darker skin tones might appear shiny or bluish.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the possibility of developing skin ulcers, such as:
- Limited mobility (being bedridden or using a wheelchair) puts constant pressure on the skin.
- Increasing age is linked to atherosclerosis and venous insufficiency, making older individuals more susceptible.
- Hypertension and high blood cholesterol levels can damage arteries and disrupt blood flow.
- Poor nutrition and dehydration can weaken the skin, making it more vulnerable to ulceration.
- Obesity raises the risk of diabetes and increases pressure in leg veins.
- A history of blood clots also increases the chances of blood flow issues.
- Other risk factors include pregnancy, which may cause leg vein problems, and cigarette smoking, which hardens arteries.
Complications
Skin ulcers can lead to serious complications if left untreated, such as:
- Cellulitis, a bacterial infection affecting deep skin layers and soft tissues, can cause warmth, swelling, and discolouration of the affected area.
- Bone and joint infections, such as osteomyelitis, may develop.
- In rare cases, chronic wounds can progress to squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer.
- Sepsis, a life-threatening complication, can occur when infections spread to the bloodstream.
- Other potential complications include damage to tendons, ligaments, and muscles, as well as permanent physical disability.
- Gangrene may also develop due to poor blood supply, potentially leading to tissue death and amputation in severe cases.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing skin ulcers involves a thorough assessment by a doctor. They examine the appearance of the ulcer and review the person's medical history and symptoms to determine the underlying cause.
Skin biopsies are often used to confirm unclear diagnoses. The preferred method is an incisional biopsy of the ulcer border and surrounding skin. Multiple biopsies may be necessary for complex cases. Punch biopsies, typically 4 mm in diameter, are commonly used after local anaesthetic injection. A larger biopsy may be divided for histological and microbiological evaluations for suspected infectious ulcers. Additional tests, such as blood screenings and imaging techniques, help identify associated conditions and guide treatment options.
Treatment for Skin Ulcers
The management of skin ulcers involves a multifaceted approach.
- Medical interventions often include topical and systemic medications to manage pain, treat infection, and promote healing.
- Compression therapy is commonly used to improve blood circulation for venous ulcers.
- Wound care is crucial, with debridement to remove nonviable tissue and appropriate dressings to maintain optimal moisture balance.
- Doctors sometimes recommend surgical options like skin grafts or flaps for large, non-healing ulcers.
- Advanced therapies like hyperbaric oxygen therapy or bioengineered skin substitutes are advisable for recalcitrant cases.
When to See a Doctor
It's crucial to seek medical guidance:
- If you suspect you have a skin ulcer or if a wound is healing slowly
- If an ulcer doesn't show improvement after a week to 10 days
- If the ulcer becomes large, deep, or increasingly painful
- If you notice signs of infection, such as increased redness, swelling, drainage, or a foul odour, are present.
- If you experience fever or chills or notice skin discolouration around the affected area, especially if it turns dark brown or black, seek emergency care.
- Early treatment of skin ulcers on the body can prevent complications and promote faster healing.
Home Remedies for Skin Ulcers
Several home remedies can help manage mild skin ulcers, such as:
- Elevating the affected leg above heart level promotes blood flow and reduces swelling.
- Compression socks aid circulation by helping blood return to the heart.
- Cleaning the ulcer with a saline solution can prevent infection.
- Applying turmeric paste, known for its antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties, may speed up healing.
- Honey, with its antibacterial benefits, can be applied to a dressing and placed on the painful skin ulcer.
- Aloe vera gel and coconut oil are also effective in treating skin ulcers due to their healing properties.
Preventions
Preventing skin ulcers in the body involves several key strategies, including:
- Regularly changing position is crucial, especially for those with limited mobility. This helps to relieve pressure on vulnerable areas.
- Using pressure-relieving mattresses and cushions can distribute weight more evenly.
- Proper skin care is essential, including keeping the skin clean, dry, and well-moisturised.
- A well-balanced diet and adequate hydration support skin health.
- For those at higher risk, such as pregnant women or smokers, extra precautions may be necessary.
- Quitting smoking and managing systemic conditions like high blood pressure (hypertension) can also lower the risk of developing skin ulcers.
- Early intervention and consistent care are vital in preventing these troublesome wounds.
Conclusion
Understanding and managing skin ulcers is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being. These persistent wounds can significantly impact a person's quality of life, making early identification and proper care essential. Each type requires a tailored treatment approach, from pressure sores to venous and arterial ulcers. Individuals can take certain proactive steps to prevent and manage these troublesome sores by recognising the symptoms, risk factors, and potential complications. By staying vigilant, maintaining good skin care practices, and addressing underlying health conditions, people can reduce their risk of developing skin ulcers and improve their chances of swift healing if they do occur. Early intervention and proper care are the cornerstones of effective skin ulcer management.
FAQ's
1. What deficiency causes skin ulcers?
Vitamin C deficiency can lead to poor wound healing and skin ulcers due to impaired collagen synthesis. Vitamin B6 deficiency may result in eczema and seborrheic dermatitis. Vitamin A deficiency can cause phrynoderma, characterised by dry, hyperkeratotic papules. Vitamin B12 deficiency is associated with skin hyperpigmentation and hair changes.
2. How long do skin ulcers last?
Skin ulcers typically heal within a few weeks to a few months. However, serious ulcers may take up to two years to recover fully. The healing time depends on factors such as the type and size of the ulcer, quality of wound care, overall health, blood circulation, and pressure from walking or standing.
3. What foods are good for skin ulcers?
A well-balanced diet is crucial for wound healing. Foods rich in protein, like meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products, help repair tissues. Zinc-rich foods aid in collagen synthesis. Iron-containing foods like red meat, fish, and leafy vegetables support healing. Vitamin C-rich fruits and vegetables are essential for collagen formation and immune function.
4. Why am I getting skin ulcers?
Skin ulcers often result from poor blood circulation. Conditions like diabetes, atherosclerosis, and venous insufficiency can impair blood flow, leading to ulcer formation. Prolonged pressure on one area, such as in bedridden individuals, can cause skin ulcers. Other factors include nutrient deficiencies, infections, and certain medical conditions affecting skin health and wound healing.

Still Have a Question?