-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Paronychia
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Paronychia
Painful, swollen skin around a fingernail or toenail affects millions yearly. This condition, known as paronychia (nail infection), occurs when bacteria or fungi enter the soft tissue surrounding the nail, resulting in inflammation and discomfort. While anyone can develop paronychia, certain habits like frequent hand-washing, nail-biting, or manicures can increase the risk. This comprehensive article explores the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for paronychia, along with effective prevention strategies to help protect nail health.
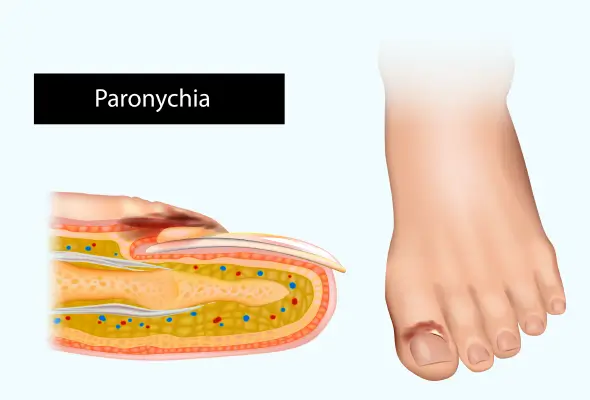
What Is Paronychia (Nail Infection)?
Paronychia is a prevalent soft tissue infection that develops in the skin surrounding fingernails or toenails. This condition occurs when the protective barrier between the nail and nail fold breaks down, allowing harmful organisms to enter the sensitive tissue.
The infection affects the areas around the nail, including:
- The cuticle (skin at the base of the nail)
- The lateral nail folds (skin on the sides of the nail)
- The proximal nail fold (where the skin and nail meet)
Paronychia affects women more commonly than men, with a female-to-male ratio of 3:1. Middle-aged females face the highest risk, particularly those whose occupations involve frequent hand exposure to water or chemicals.
Types of Paronychia
Doctors classify paronychia into two distinct types based on the duration and nature of the infection.
- Acute Paronychia: This type develops rapidly, typically lasting less than six weeks. It usually occurs following direct trauma to the nail or surrounding tissue, such as from aggressive manicuring or nail biting. The primary cause is bacterial infection, with Staphylococcus aureus being the most common pathogen.
- Chronic Paronychia: This form develops gradually and persists for six weeks or longer. It represents a more complex condition involving multiple factors and organisms. People who frequently expose their hands to water, chemicals, or irritants face a higher risk of developing chronic paronychia. The fungus Candida albicans typically causes chronic cases.
Key characteristics of both types include:
- Acute paronychia:
- Rapid onset
- Usually affects a single nail
- Often results from identifiable trauma
- Primarily bacterial in nature
- Chronic paronychia:
- Slow development
- May affect multiple nails
- Linked to repeated environmental exposure
- Often involves both fungal and bacterial organisms
Symptoms of Paronychia
The primary symptoms include:
- Pain and Tenderness: The affected area becomes sensitive to touch and pressure
- Swelling: The skin around the nail appears puffy and inflamed
- Redness: The affected area becomes noticeably red and warm
- Pus Formation: A white to yellow abscess may develop under the skin
- Nail Changes: The nail may show:
- Abnormal growth patterns
- Yellow or green discolouration
- Separation from the nail bed
- Unusual ridges or waves
- Dry and brittle texture
- Severe Cases: If the infection spreads, patients may experience additional symptoms such as fever, chills, and red streaks along the skin.
Risk Factors and Causes of Paronychia
Several key factors contribute to the development of paronychia:
- Occupational Risks:
- Frequent hand exposure to water (dishwashers, bartenders)
- Regular contact with chemicals or irritants
- Jobs requiring repeated hand trauma
- Personal Habits:
- Aggressive manicuring or pedicuring
- Nail biting or finger sucking
- Picking at hangnails
- Excessive hand washing
- Medical Conditions:
- Diabetes
- HIV infection
- Various types of cancer
- Compromised immune system
- Medications:
- Retinoids, anti-cancer drugs, and some HIV medications elevate the risk of infection.
Complications of Paronychia
The condition can lead to several significant complications:
- Nail Deformities:
- Thickened and discoloured nail plates
- Pronounced transverse ridges
- Abnormal growth patterns
- Complete nail separation and loss
- Progressive Infections:
- Deeper tissue involvement
- Bone infection (osteomyelitis)
- Tendon inflammation
- Systemic infection through blood circulation
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: Doctors generally identify the affected nail area through careful visual examination of nail fold inflammation and assessment of tenderness and swelling.
- Laboratory Testing:
- Pus sample analysis to identify specific bacteria
- Gram staining to determine the bacterial type
- KOH (potassium hydroxide) smears to detect fungal infections
Treatment
The paronychia treatment approach follows a structured progression:
- Conservative Management:
- Warm water soaks (about 15 minutes 3-4 times daily)
- Over-the-counter pain relievers
- Keeping the affected area dry and clean
- Paronychia Medication-based Treatment:
- Topical antibiotics with or without corticosteroids
- Oral antibiotics for severe bacterial infections
- Antifungal medications for chronic cases
- Surgical Intervention:
- Drainage of accumulated pus
- Removal of the affected nail portion
- Marsupialisation for chronic cases
When to See a Doctor
Immediate medical intervention is necessary if any of these warning signs develop:
- Severe pain that interferes with daily activities
- Fever or chills accompanying the infection
- Red streaks extending from the infected area
- Formation of pus-filled abscess
- Joint or muscle pain in the affected area
- Symptoms that persist or worsen despite treatment
Home Remedies for Paronychia
The cornerstone of paronychia treatment at home is the warm water soak method. Individuals should fill a bowl or basin with warm water (not too hot) and add two tablespoons of salt or saline solution. The affected finger or toe should be soaked for 20 minutes, three to four times daily. The water temperature should be comfortable but not hot enough to cause discomfort.
Essential steps for home remedies for paronychia include:
- Thoroughly dry the affected area after each soak
- Apply a fine layer of petroleum jelly to protect broken skin
- Cover with a clean bandage if working with hands
- Keep the area dry between soaking sessions
- Avoid using harmful chemicals like alcohol or hydrogen peroxide
Prevention
Preventing nail infections requires consistent attention to nail care and protection of the surrounding tissue. Essential prevention guidelines are:
- Keep nails trimmed and smooth using sharp manicure tools
- Avoid cutting nails too short or trimming cuticles
- Wear protective gloves with cotton liners when working with water
- Maintain proper hand hygiene without excessive washing
- Use gentle soaps that don't irritate the skin
- Apply moisturiser after washing hands
- Change socks daily and alternate shoes to prevent moisture buildup
Conclusion
Paronychia remains a common but manageable nail infection when caught early and treated properly. Understanding paronychia's causes, symptoms, and treatment options helps people take better care of their nail health. Regular monitoring, proper hygiene practices, and prompt medical attention when needed ensure successful management of this common condition.
FAQs
1. How common is paronychia?
Paronychia stands as the most prevalent hand infection worldwide, affecting people of any age and accounting for 35% of all hand infections. The condition affects women three times more frequently than men, with middle-aged females facing the highest risk, particularly those working in wet environments.
2. Can paronychia heal by itself?
Mild cases of acute paronychia can resolve on its own with proper care and attention. However, the healing process requires:
- Keeping the affected area clean and dry
- Avoiding further trauma to the nail
- Protecting the nail from chemical exposure
3. Is paronychia treatable at home?
Most mild cases respond well to home treatment. Warm water soaks for 15 minutes, performed 3-4 times daily, often prove effective for early-stage infections. However, professional medical attention becomes necessary if symptoms persist beyond two days or worsen.
4. How many days does paronychia last?
The duration varies and depends on the type and severity of the infection. Acute cases typically resolve within a few days with proper treatment, while chronic paronychia may persist for several weeks or months. Treatment adherence and avoiding irritants significantly influence recovery time.
Dr. Shradhha Mahalle

Still Have a Question?



