-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Hiatal Hernia
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Hiatal Hernia
Hiatal hernia is a common ailment that affects millions of people worldwide. This condition can cause numerous symptoms, from mild sensation of discomfort to severe pain, and in some cases, may require surgery. Understanding the signs of hiatal hernias and its potential complications is crucial for those affected by this condition.
This article takes an in-depth look at hiatal hernia, exploring its types, symptoms, and causes. It delves into the various treatment options, including medications and surgical interventions for large hiatal hernias.
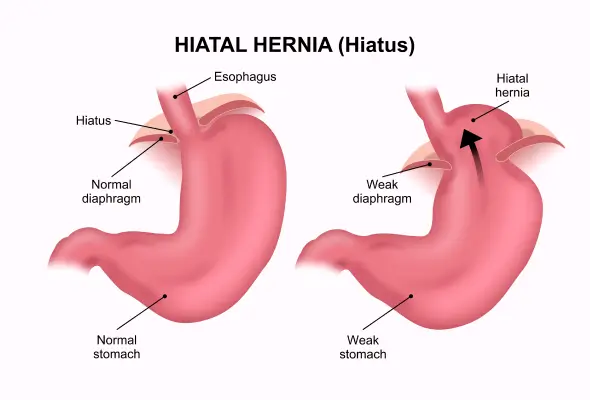
What is Hiatal Hernia?
A hiatal hernia grows when a portion of the stomach or other abdominal organs push upwards through a diaphragmic opening (the diaphragm is the muscle separating the chest and abdominal cavity). This opening called the oesophageal hiatus, typically allows the oesophagus to pass through and connect to the stomach. However, when this hiatus enlarges or weakens, it can enable part of the stomach to protrude into the chest, resulting in numerous symptoms and complications.
Types of Hiatal Hernia
Hiatal hernias are four distinct types, each with unique characteristics:
- Type 1: Also called sliding hiatal hernia, the most common hiatal hernia type, accounting for approximately 95% of all cases. In this form, the gastroesophageal junction, where the oesophagus connects to the stomach, slides up through the widened hiatus and then back down intermittently.
- Type 2: Also known as rolling hiatal hernia, it involves the upper part of the stomach pushing up through the hiatus alongside the oesophagus, forming a bulge next to it.
- Type 3: This type involves the sliding of the gastroesophageal junction through the hiatus at times, while another part of the stomach also bulges alongside it.
- Type 4: This type is the rarest and most complex form of hiatal hernia. It occurs when the hiatus is wide enough to allow two different organs to herniate through it.
Hiatal hernia types 2, 3, and 4 are collectively known as paraesophageal hernias, meaning they occur beside the oesophagus.
Symptoms of Hiatal Hernia
Most of the signs of hiatal hernia disease are related to gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and may include:
- Heartburn or a burning sensation in the chest, especially after eating
- Noncardiac chest pain, which can be mistaken for angina.
- Indigestion or a feeling of fullness soon after eating, accompanied by a burning type of abdominal pain.
- Difficulty swallowing or feeling of a lump in their throat when swallowing.
- Sore throat and hoarseness when speaking
Causes and Risk Factors of Hiatal Hernia
The exact cause of hiatal hernia disease remains unclear, but several factors contribute to its development.
While some individuals are born with an unusually large hiatus, others may develop a hiatal hernia due to cumulative damage from years of daily stress and strain. Factors that increase abdominal pressure and contribute to hiatal hernias include:
- Chronic coughing or sneezing
- Persistent constipation
- Obesity (BMI greater than 30)
- Frequent vomiting
- Intense exercise
- Heavy lifting
- Pregnancy and childbirth (as they put significant pressure on the abdominal cavity)
- Injury or trauma to the upper abdominal area, such as force from a seatbelt during an accident Age with the condition is more common in individuals over 50, possibly due to the natural weakening of muscles and tissues as people age.
Complications of Hiatal Hernia
Hiatal hernias can lead to serious complications in some cases, such as:
- Oesophagitis: Chronic acid reflux can cause oesophagitis, an inflammation of the oesophageal lining resulting in pain, difficulty swallowing, and, in severe cases, ulcers and bleeding or oesophageal strictures in the long run, where scar tissue narrows the oesophagus, making swallowing challenging and painful.
- Barrett's Oesophagus: Barrett's oesophagus is considered precancerous and may increase the risk of oesophageal cancer.
- Gastrointestinal Obstruction: In this condition, the stomach or another organ becomes trapped in the hiatus, causing a blockage.
- Ischaemia: Rarely, a tightly compressed hernia can cut off its own blood supply, resulting in tissue death and requiring immediate medical attention.
Diagnosis
Hiatal hernia diagnosis involves a combination of medical procedures, including:
- Gastroscopy: A doctor inserts a long, thin, flexible tube called a gastroscope into the patient's mouth and down the throat. This device, equipped with a light and video camera, sends multiple images to an external monitor, allowing for a detailed examination of the oesophagus and stomach.
- Barium Meal X-ray (Barium Swallow Test): During this test, the patient drinks a barium solution, a non-toxic chemical solution that shows up clearly on X-rays. As the barium moves through the digestive system, radiologists take a series of X-rays to identify any abnormalities, including signs of hiatal hernia.
- Upper Endoscopy: This diagnostic procedure involves inserting an endoscope down the throat, providing a view of the oesophagus, stomach, and the beginning of the small intestine.
- Oesophageal Manometry: It measures muscle contractions in the oesophagus. This test evaluates the coordination and force used by the oesophageal muscles during swallowing.
Hiatal Hernia Treatment
Lifestyle changes and medication may be sufficient for many individuals with mild symptoms. These include:
- Eating smaller
- More frequent meals
- Avoiding lying down after eating
- Eliminating foods that trigger acid reflux
- Over-the-counter Antacids: These medications can help alleviate symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) related to hiatal hernia.
- Surgery: Doctors recommend surgery if the hernia is large and causing severe symptoms. The most common surgical procedure is laparoscopic Nissen fundoplication. This minimally invasive technique involves taping the upper part of the stomach around the lower part of the oesophagus to strengthen the barrier between the stomach and the oesophagus.
When to See a Doctor
People should schedule an appointment with their doctor if they experience persistent symptoms of hiatal hernia that cause concern. These may include:
- Frequent heartburn
- Difficulty swallowing,
- A feeling of fullness soon after eating.
- Chest pain
- If indigestion or acid reflux is accompanied by unexplained weight loss, frequent vomiting, or blood in vomit
Prevention
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of hiatal hernia, there are several proactive steps people can take to diminish their risk and manage symptoms:
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- A balanced diet and regular exercise
- Avoiding large meals and opting for smaller, more frequent food portions throughout the day can help prevent excessive pressure on the stomach. Refraining from eating for at least three hours before bedtime is advisable to reduce the risk of acid reflux.
- Elevating the head of the bed by 10 to 20 centimetres can also help prevent stomach acid from travelling up towards the throat during sleep.
- Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption
- Avoiding tight-fitting clothing around the waist
- Identifying and avoiding trigger foods that worsen symptoms, such as fatty, spicy, or acidic foods
- Integrating relaxation techniques into daily routines can help manage stress, which may exacerbate hiatal hernia symptoms.
Conclusion
Hiatal hernia is a common condition that has an impact on millions of people worldwide. Managing hiatal hernia involves a combination of approaches tailored to each individual's needs. While some people may find relief through simple lifestyle adjustments, others might need medical intervention to address their symptoms.
FAQS
1. How common are hiatal hernias?
Hiatal hernias are quite common, especially among older adults. According to the Oesophageal Cancer Awareness Association, up to 60% of people have a hiatal hernia by the age of 60. The prevalence increases with age, affecting approximately 55% to 60% of individuals older than 50.
2. What is hiatal hernia pain like?
Hiatal hernia pain can vary. Some people may experience chest pain or abdominal discomfort. However, the most common symptom is heartburn, a burning sensation in the chest. It's important to note that many people with hiatal hernias don't experience any
symptoms.
3. How does a hiatal hernia develop acid reflux?
A hiatal hernia can cause acid reflux by affecting the function of the lower oesophageal sphincter (LES). When part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm, it can weaken the LES, allowing stomach acid to flow back into the oesophagus. This can lead to symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
4. How serious is a hiatal hernia?
Most hiatal hernias are not serious and don't require treatment if they're not causing symptoms. However, large hiatal hernias or those causing persistent symptoms may lead to complications such as oesophagitis, ulcers, Barrett's oesophagus, or a strangulated hernia (rare), which is a medical emergency.
5. What is the recovery process after hiatal hernia surgery?
Recovery from hiatal hernia surgery typically takes three to four weeks. Most people spend at least one night in the hospital. During recovery, patients follow a specific diet, starting with liquids and progressing to soft foods. They're advised to avoid heavy lifting and strenuous activities for several weeks.
6. How can I manage my hiatal hernia at home?
Home treatment for hiatal hernia symptoms includes lifestyle changes like eating smaller, more frequent meal portions, avoiding lying down after eating, elevating the head of the bed, and avoiding trigger foods like spicy or fatty foods. Over-the-counter antacids may also provide relief for occasional heartburn.
7. Can hiatal hernia be cured?
While lifestyle changes and medicines can manage symptoms, surgery is the only way to cure a hiatal hernia. However, not everyone with a hiatal hernia requires surgery. Many individuals can effectively manage their hiatal hernia symptoms with conservative treatments.
8. What food should I avoid with a hiatal hernia?
Foods to avoid a hiatal hernia include those that can trigger acid reflux, like tomatoes, citrus fruits, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, fatty foods, and spicy foods. It's also advisable to avoid large meals and eating close to bedtime.
9. How can I shrink my hernia naturally?
While it's not possible to shrink a hiatal hernia naturally, specific lifestyle changes can help manage symptoms. These include eating smaller meals, maintaining a healthy weight, quitting smoking, and avoiding foods that trigger symptoms. However, these methods won't reduce the size of the hernia itself.
Dr. Prashant Bhowate

Still Have a Question?



