-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Female Infertility
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cause of Female Infertility
Have you ever wondered why some women struggle to conceive? Female infertility is an intricate issue that affects millions of women worldwide. It can cause emotional distress and put a strain on relationships, making it crucial to understand its root causes. This comprehensive blog aims to shed light on the factors contributing to female infertility, offering valuable insights for those seeking answers.
We'll explore the various aspects of female infertility, from its definition and symptoms to its causes and available treatments. You'll learn about the most common reasons behind infertility in women, the diagnostic tests used to identify problems, and the current options for treatment. We'll also discuss risk factors, potential complications, and prevention strategies, providing a well-rounded view of this sensitive topic.
What is Female Infertility?
Female infertility is a medical condition that affects a woman's ability to conceive. It occurs when a woman fails to achieve pregnancy after 12 months of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse if she's under 35 or after six months if she's over 35. This condition not only has physical implications but also impacts psychological, mental, and spiritual well-being. It's unique in that it affects both the patient and her partner as a couple.
Symptoms of Female Infertility
The foremost symptom of female infertility is the inability to get pregnant after one whole year of regular, unprotected sexual intercourse. However, other signs may indicate potential fertility issues. These may include:
- Irregular menstrual cycles, lasting less than 21 days or more than 35 days, can suggest problems with ovulation
- Women may also experience very heavy or painful periods, potentially signalling conditions like endometriosis.
- Pain during sex, known as dyspareunia, can indicate underlying health problems affecting fertility.
- Some women might notice unexplained weight gain, severe acne, or facial hair growth due to hormonal imbalances.
It's important to note that some women with infertility may not show any apparent symptoms beyond difficulty conceiving.
Causes of Female Infertility
Female infertility has an impact on many women worldwide. The following are some common causes of female infertility:
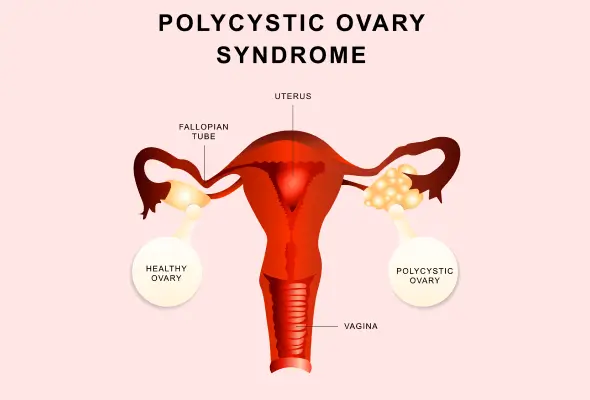
- The most common cause is ovulation problems, which account for most cases. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) leads the pack, causing hormone imbalances that affect ovulation. Other ovulation-related issues include hypothalamic dysfunction and primary ovarian insufficiency.
- Fallopian tube blockage or damage, often due to pelvic inflammatory disease or previous pelvic surgeries, can prevent sperm from reaching the egg.
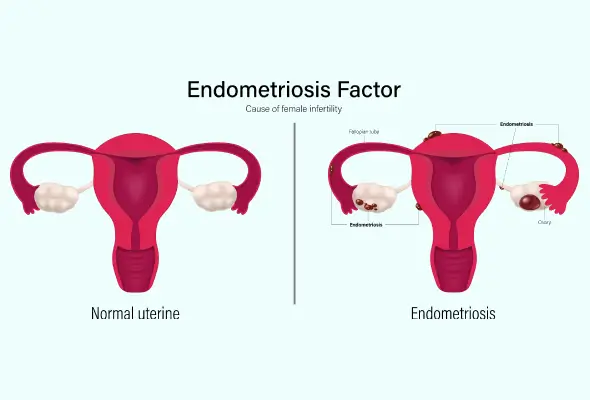
- Endometriosis (uterine tissue grows outside the uterus) can interfere with conception.
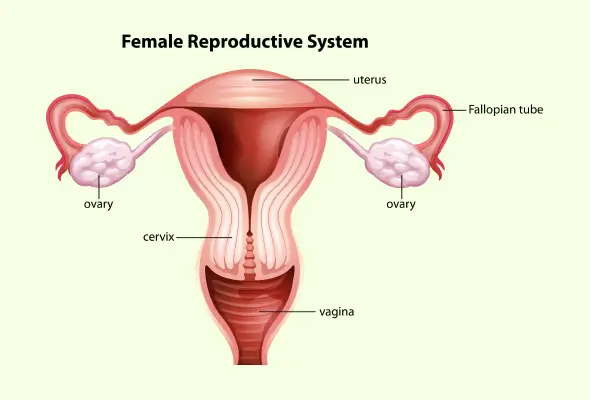
- Uterine issues like fibroids or abnormal shapes may also play a role.
- Some cervical problems, such as stenosis or inadequate mucus production, can also contribute to infertility.
- In some cases, the cause remains unexplained, possibly due to a combination of minor factors in both partners.
Diagnosis of Female Infertility
Doctors diagnose female infertility through a series of tests and examinations. They start with a detailed medical history and physical exam. They will ask about your menstrual periods, past pregnancies, unusual vaginal discharge, past uterine or vaginal infections, including sexually transmitted infections, and previous abdominal or pelvic surgeries.
- Blood Tests: To check hormone levels, including those for ovulation and thyroid function. Ovulation testing uses over-the-counter kits or blood tests to confirm egg release.
- Imaging test: Various imaging studies examine the reproductive organs, such as pelvic ultrasounds and hysterosalpingography. Hysterosalpingography uses X-rays and contrast dye to check for fallopian tube blockages.
- Ovarian Reserve Testing: This test assesses egg quantity and quality.
- Additional Tests: In some cases, doctors may recommend more invasive procedures like laparoscopy or hysteroscopy to view the reproductive organs directly.
- Genetic Testing: Sometimes, doctors may also perform genetic testing to identify genetic factors contributing to infertility.
Treatment for Female Infertility
Doctors treat female infertility based on the underlying cause. They use various methods to restore fertility or help women get pregnant.
- Fertility drugs are the one of the most commonly used infertility treatments for female. These medications work like natural hormones to trigger ovulation. Each fertility drug targets specific fertility issues. However, these medications carry risks such as multiple pregnancies and ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
- In some cases, surgical procedures can be a cure for infertility in a woman. These include laparoscopic or hysteroscopic surgery to fix uterine issues and tubal surgeries to address fallopian tube blockages.
- For more complex cases, doctors may recommend reproductive assistance methods like intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in vitro fertilisation (IVF).
Risk Factors for Female Infertility
Several factors can raise a woman's risk of infertility, such as:
- Age plays a crucial role, as fertility begins to decline in the 30s, with egg quality and quantity decreasing more rapidly in the mid-30s.
- Smoking damages the cervix and fallopian tubes, increases miscarriage risk, and may prematurely deplete eggs.
- Weight problems, both being overweight and underweight, can affect ovulation.
- Sexual history matters, too, as sexually transmitted infections can damage fallopian tubes.
- Excessive alcohol consumption reduces fertility.
- Other risk factors include endometriosis, chronic diseases like diabetes and lupus, hormone imbalances, and exposure to workplace toxins.
- Uterine abnormalities, fibroids, and previous pelvic surgeries can also contribute to infertility.
Complications of Female Infertility
Female infertility and its treatments can lead to various complications, such as:
- Fertility medications used to stimulate ovulation may cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome (OHSS), resulting in painful and swollen ovaries.
- There's also a higher chance of multiple pregnancies (twins, triplets, etc.) with these treatments.
- Ectopic pregnancies are two to three times more likely in infertile patients, especially those with tubal factor infertility.
- Social and emotional complications often accompany infertility, including relationship troubles, depression, anxiety, social stigma, and stress. These psychological effects can significantly impact a woman's overall well-being and quality of life.
When to See a Doctor
- Women under 35 should consult a doctor if they have been trying to conceive for 12 months without success. For those between 35 and 40, seeking help after six months of trying is advisable. Women over 40 should consider immediate consultation.
- Certain conditions warrant prompt medical attention, regardless of age. These include irregular or painful periods, a history of pelvic inflammatory disease, repeated miscarriages, or known fertility issues.
- Couples should also seek help if the male partner has abnormal semen analysis results or experiences problems like erectile dysfunction or ejaculation difficulties.
- Women with symptoms such as absent periods, irregular cycles, or unusually heavy bleeding should consult a specialist.
- Those with conditions like PCOS, endometriosis, or a history of cancer treatment should seek early medical advice.
Prevention
Women can take several steps to prevent female infertility, including:
- Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and moderate exercise is crucial, as obesity and being underweight can affect ovulation.
- Quitting smoking is essential, as tobacco use can damage reproductive organs and increase miscarriage risk.
- Avoiding alcohol consumption is also essential, as it can decrease fertility and harm foetal development.
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques can improve fertility treatment outcomes.
- Practising safe sex helps prevent sexually transmitted infections, which can cause infertility.
- Women should also be aware of workplace hazards, such as exposure to toxins that can affect reproductive health.
- When ready to conceive, seeking timely medical advice is crucial, especially for women over 35 or those with irregular cycles.
Conclusion
Female infertility is a complex issue that has an impact on many aspects of a woman's life. This guide has shed light on the various causes, symptoms, and treatments available to those struggling to conceive. Understanding the risk factors and potential complications allows women to take proactive steps to protect their fertility. By seeking timely medical advice and making lifestyle changes, many women can improve their chances of having a successful pregnancy.
The journey through infertility can be challenging, but knowledge is power. Armed with information about diagnostic tests and treatment modalities, women can make informed decisions about their reproductive health. Remember, each case is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. Working closely with doctors to develop a personalised approach is crucial. With ongoing advancements in reproductive medicine, there's hope for many couples facing fertility challenges.
FAQ's
1. How does age impact female infertility?
Age significantly affects a woman's fertility. A woman's peak reproductive years occur in her late teens to late 20s. Fertility starts to decline at 30 and speeds up in the mid-30s. By 45, natural pregnancy becomes unlikely. This decline happens because egg quality and quantity decrease with age, increasing the risk of miscarriage and chromosomal abnormalities.
2. How to test if a woman is infertile?
Doctors use various tests to diagnose female infertility:
- Ovulation testing through blood tests or at-home kits
- Hormone level checks, including thyroid function
- Hysterosalpingography to inspect the uterus and fallopian tubes
- Ovarian reserve testing to assess egg quantity and quality
- Imaging tests like pelvic ultrasound or sonohysterogram
- Laparoscopy for a direct view of reproductive organs
3. Can a woman's infertility be cured?
While infertility can't always be cured, many treatments can help women conceive:
- Fertility medications to regulate ovulation
- Surgery to correct structural issues
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- In vitro fertilisation (IVF)
- Antibiotics for infections
The success of these treatments depends on the underlying cause of infertility and the woman's age.
4. What foods increase female fertility?
Certain foods may boost female fertility:
- Beans and Lentils: High in fibre, protein, and folic acid
- Sunflower Seeds: Rich in vitamin E, zinc, and selenium
- Berries: Contain antioxidants and anti-inflammatory phytonutrients
- Avocados: Provide healthy fats and folic acid
- Quinoa: Offers protein, zinc, and folic acid
- Greek Yoghurt and Cheese: Contains calcium and probiotics
- Salmon: High in omega-3s and vitamin D
- Asparagus: Rich in folic acid and various vitamins
- Walnuts: Packed with omega-3s and omega-6s
- Eggs: Yolks contain vitamin B and omega-3s
5. What is the primary cause of female infertility?
The foremost cause of infertility in women is ovulation disorders. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the primary cause, affecting hormone balance and ovulation. Other ovulation-related issues include hypothalamic dysfunction and primary ovarian insufficiency. Fallopian tube damage, endometriosis, and uterine or cervical problems can also contribute to infertility.
Still Have a Question?




