-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Dystonia
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Dystonia
Have you ever wondered what losing control of your body movements is like? Dystonia, a neurological disorder, causes just that. It leads to involuntary muscle contractions and abnormal postures, affecting millions worldwide. This condition can significantly impact a person's quality of life, making everyday tasks challenging and often painful.
Let's take a closer look at dystonia, its symptoms, and the various dystonia treatment options available. We'll explore the possible causes and risk factors behind this complex disorder and the complications it can bring about.
What is Dystonia?
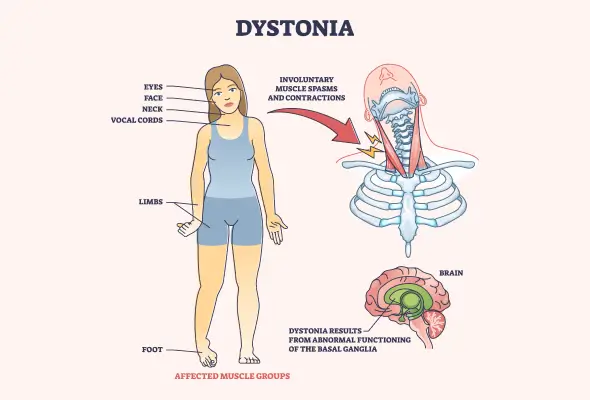
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder affecting approximately 1% of the population. It involves involuntary muscle contractions that cause abnormal, sometimes painful movements and postures. These contractions can be sustained or intermittent and may involve twisting, repetitive motions, or even trembling.
The disorder can affect various body parts, including the neck, torso, limbs, eyes, face, and vocal cords. In some cases, dystonia may involve a single muscle or muscle group, while in others, it can affect multiple parts or even the entire body. The severity of dystonia varies widely, ranging from symptoms that come and go away to severe, debilitating effects that significantly impact a person's quality of life.
Dystonia Symptoms
The severity of symptoms varies widely and sometimes can impact a person's quality of life.
The most common symptoms of dystonia include:
- Uncontrolled muscle spasms and cramps that often worsen with movement or stress.
- Parts of the body twisting into unusual positions, such as the neck being pulled to the side or feet turning inwards.
- Shaking or tremors
- Excessive blinking
- Unusual, awkward postures
It's important to note that dystonia does not typically cause muscle weakness. Some people can temporarily interrupt dystonic movements or postures by performing a specific action, known as a 'sensory trick'. For example, touching the chin might temporarily alleviate cervical dystonia.
Dystonia Causes
Dystonia occurs due to disruptions in brain function, particularly in the basal ganglia, which coordinates movement. The causes of dystonia can be categorised into three main types:
- Primary dystonia is often idiopathic, meaning it happens for unknown reasons. Genetic factors play a role, with several genes linked to the condition.
- Secondary dystonia may result from environmental or disease-related brain or central nervous system damage. Diseases that cause dystonia include brain tumours, stroke, cerebral palsy, infections like encephalitis, and exposure to certain medications or toxins.
- Dystonia plus' conditions are neurological disorders where dystonia is a main symptom alongside other neurological issues. These can include conditions like dopa-responsive dystonia and rapid-onset dystonia-parkinsonism.
Risk Factors
Risk factors for dystonia are not fully understood but may include:
- A family history of the condition .
- Certain genetic mutations
- Exposure to specific environmental factors
Complications of Dystonia
- Dystonia can lead to a range of complications that affect both physical and emotional well-being.
- Dystonia may cause hypertrophy and pain in affected muscles.
- Over time, dystonia can result in permanent bone deformity, contractures, and impaired function.
- The uncontrolled movements can interfere with daily activities such as walking, eating, and dressing.
- Vision problems, particularly affecting the eyelids.
- Difficulties with jaw movement, swallowing, or speaking
- The uncontrolled movements may cause fatigue.
- Dystonia may affect a person's ability to work or drive, limiting their independence and social interactions.
- Emotionally, living with dystonia can be challenging, potentially leading to withdrawal from social events. This isolation, combined with the physical challenges, can cause depression and anxiety.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing dystonia can be a complex process, often requiring the expertise of a neurologist specialising in movement disorders.
- Medical History: The neurologist will ask about your symptoms, any other conditions you might have, and your family history. They will ask about the factors that trigger symptoms.
- Neurological Examination: Doctors will conduct a physical and neurological exam to assess muscle tone, coordination, reflexes, and the pattern of muscle contractions.
- Blood Tests and Urinalysis: Doctors may conduct blood or urine investigations to check for any underlying problems that could contribute to dystonia.
- Brain Scans: These can help rule out structural brain abnormalities, tumours, strokes, or other causes of dystonia.
- Genetic Testing: Doctors may recommend genetic testing, especially if there's a family history of dystonia.
Dystonia Treatment
Treatment for dystonia aims to manage symptoms and improve quality of life. While there's no cure, various options are available to help control muscle spasms and reduce pain.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe drugs that increase dopamine levels, block acetylcholine, or boost GABA levels. These medical treatments for dystonia can help relax muscles and reduce involuntary movements.
- Botulinum Toxin Injections: These injections are particularly effective for focal dystonias, such as blepharospasm or cervical dystonia. The injection is given directly to affected muscles, weakening them and reducing spasms.
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: These dystonia therapies improve muscle control, reduce pain, and increase range of motion. Exercises may include stretching, strengthening, and balance training.
- Speech Therapy: Speech therapy may become necessary for some patients if dystonia affects their voice.
- Surgery: In severe cases where other treatment modalities have been ineffective, doctors suggest surgical modalities. Deep brain stimulation (DBS) is a procedure where electrodes are implanted in specific sections of the brain to help control muscle contractions. For cervical dystonia, selective denervation surgery might be an option.
When to See a Doctor
- If you think you might have dystonia, it's best to get the symptoms checked out, even though the condition is uncommon.
- Contact your doctor if your symptoms change or worsen, disrupting your life and routine.
- Contact your doctor if medications or other treatments stop working effectively or lead to side effects that are hard to manage.
Prevention
Although you can't prevent primary dystonia, which is inherited or develops for unknown reasons, you can lower your chances of secondary dystonia through certain lifestyle choices and preventive measures. These may include:
- Maintain a balanced diet & a healthy weight. Do not have caffeine & alcohol, as these can make dystonia symptoms worse.
- Many conditions related to heart and circulatory health, particularly stroke, can damage areas of the brain, potentially leading to dystonia. By preventing or reducing the severity of these conditions, you can significantly impact your risk of developing dystonia.
- Don't ignore infections, especially those affecting the eyes and ears. These infections require prompt treatment as they can spread to the brain, causing inflammation (encephalitis) that may result in dystonia.
- Wearing safety equipment is essential in reducing your risk of traumatic brain injuries, which can damage your brain and cause dystonia.
- Managing chronic health conditions is also vital in preventing dystonia. Conditions like Type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and epilepsy can contribute to other conditions that lead to dystonia.
Conclusion
Dystonia is a challenging condition that affects millions worldwide, causing involuntary muscle contractions and abnormal postures. While there's no cure, various treatment options are available to manage symptoms & improve quality of life. Those experiencing dystonia disease symptoms should seek medical advice promptly for proper diagnosis and care. Living with dystonia can be tough, but with the appropriate support and management strategies, many people lead fulfilling lives. By staying informed and working closely with doctors, individuals with dystonia can find ways to cope with their symptoms & maintain their quality of life.
FAQs
1. Is dystonia serious?
Dystonia can range from mild to severe, affecting a person's quality of life to varying degrees. While it's not typically life-threatening, dystonia can cause significant discomfort and disability. The seriousness depends on the type and extent of symptoms, ranging from minor muscle contractions to debilitating movements affecting daily activities.
2. Who does dystonia affect?
Dystonia can affect people of any age, gender, race, or ethnic background. However, some forms are more common in certain groups. For instance, some types of dystonia are more likely to develop in childhood, while others typically appear in adulthood. Women are slightly more likely to be affected than men.
3. How common is this condition?
Dystonia is the third most common movement disorder (essential tremor & Parkinson's disease occupy the first two spots). It's estimated that dystonia affects about 1% of the population. However, the true prevalence may be higher due to underdiagnosis and misdiagnosis.
4. How does dystonia affect my body?
Dystonia causes involuntary muscle contractions, leading to abnormal movements and postures. These can affect various body parts, including the neck, limbs, torso, eyes, and vocal cords. Symptoms can include muscle spasms, tremors, and difficulty with specific tasks like writing or speaking. The effects can be painful and may interfere with daily activities.
5. What age does dystonia start?
The dystonia can be seen in any age group, depending on the underlying cause. Some forms of dystonia begin in childhood (early-onset dystonia), while others typically develop in adulthood (adult-onset dystonia).
6. What deficiency causes dystonia?
While a deficiency doesn't typically cause dystonia, vitamin E deficiency has been linked to a rare form called ataxia with vitamin E deficiency (AVED). This condition can cause dystonia-like symptoms, including involuntary muscle contractions and abnormal postures. However, most cases of dystonia are not related to nutritional deficiencies.
7. What is the difference between dystonia and dyskinesia?
Both dystonia & dyskinesia are movement disorders, but they differ in their characteristics. Dystonia involves sustained muscle contractions causing twisting or repetitive movements and abnormal postures. On the other hand, dyskinesia refers to involuntary, often fluid or jerky movements. Dyskinesia is a common side effect of long- term Parkinson's disease treatment, while dystonia can occur independently or as part of various neurological conditions.
8. What foods should you avoid if you have dystonia?
While there's no specific diet for dystonia, some individuals find that certain foods or substances can worsen their symptoms. These include caffeine, alcohol, excessive sugary and simple carbohydrates-riched products. However, dietary effects can vary among individuals, so it's best to consult with a doctor for personalised advice.

Still Have a Question?



