-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Cervical Dystonia
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Cervical Dystonia
Have you ever woken up with a stiff neck that won't budge? For those with cervical dystonia, this discomfort is a daily reality. Cervical dystonia is a neurological condition that results in involuntary contractions in the neck muscles, leading to abnormal head positions and movements. This disorder can significantly impact a person's quality of life, making simple tasks challenging and often causing pain and embarrassment.
Understanding cervical dystonia disease is crucial for effective management and treatment. Let's explore the symptoms, causes, and early signs of cervical dystonia, as well as various treatment options available.

What Is Cervical Dystonia?
Cervical dystonia (spasmodic torticollis) is a neurological ailment that affects the brain and nerves, causing involuntary muscle contractions in the neck. This rare disorder can occur in people of any age group but most often affects middle-aged people, with women being more susceptible than men.
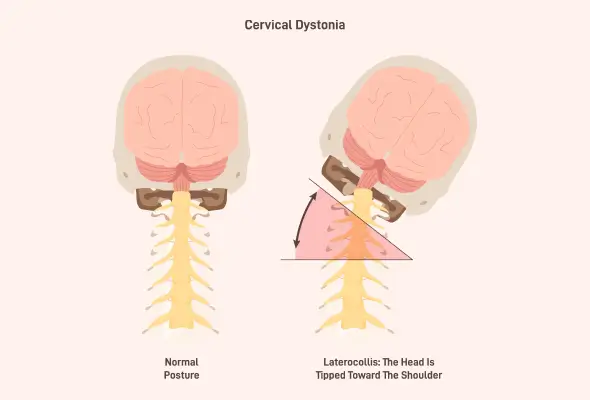
The condition forces the neck muscles to contract involuntarily, leading to abnormal head positions and movements. These contractions can result in various head postures, including but not limited to:
- Chin straight up
- Chin toward shoulder
- Chin straight down
- Ear toward shoulder
The most common type of twisting movement associated with cervical dystonia involves the chin being pulled toward the shoulder. Some individuals may experience a combination of these abnormal head postures, and a jerking motion of the head can also occur.
Cervical dystonia disease is classified into two types based on its cause:
- Primary
- Secondary
Symptoms typically begin gradually and eventually reach a plateau where they don't worsen substantially.
Symptoms of Cervical Dystonia
Cervical dystonia causes a range of involuntary movements that affect the neck and head. The primary symptoms include:
- Spasms: The neck muscle spasms may cause sudden jerking movements or twitches.
- Tremors: Uncontrollable shaking can occur in certain body parts, particularly the arms.
- Posture changes: The condition affects a person's posture, leading to various head positions:
- Rotation: The head turns to one side.
- Tilting: The head moves forward, backwards, or side to side at a slight angle.
- Bending: The neck and head curve forward, backwards, or sideways.
- Pain: Many individuals experience pain or a burning sensation in their shoulders and neck. This pain can radiate, causing discomfort beyond the immediate area.
- Headaches: These often accompany muscle contractions and posture changes.
Causes of Cervical Dystonia
The exact cause of cervical dystonia remains unknown for most people. Doctors have not yet identified a specific trigger for all cases. However, research suggests that the basal ganglia, the part of the brain responsible for regulating muscle movements, may not function correctly in individuals with this condition.
In some instances, cervical dystonia has a genetic component (gene mutations in the GNAL, THAP1, CIZ1, and ANO3 genes).
Certain factors may increase the risk of developing cervical dystonia:
- Having biological family members with the condition
- Experiencing a brain injury
- Parkinson's disease
- In some cases, head, neck, or shoulder injuries.
Diagnosis of Cervical Dystonia
Doctors diagnose cervical dystonia through a comprehensive assessment of clinical manifestations.
- Medical History and Physical Evaluation: Doctors conduct a physical examination to review symptoms and inquire about the patient's medical history, including any family history of the condition. During the consultation, doctors may ask about your symptoms, triggers, relieving factors, and ongoing medications.
- Additional Tests: Doctors might recommend additional tests to rule out underlying conditions. These may include:
- Blood tests
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
- Neuroimaging is helpful in hemidystonia or generalised dystonia in adults due to a higher likelihood of disclosing structural causes.
- Doctors may recommend genetic testing for early-onset isolated dystonias.
When cervical dystonia combines with other neurological or systemic features, additional workup is warranted. The specific laboratory tests depend on the associated features and age of onset.
Treatment for cervical dystonia
While there is no definitive cure for cervical dystonia, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and improve quality of life. The cervical dystonia therapy modalities are aimed at alleviating neck pain, enhancing neck alignment and reducing abnormal movements.
- Medications:
- Botulinum toxin injections are among the most effective cervical dystonia treatment options, typically repeated every three to four months.
- Oral medications with muscle-relaxing effects may complement botulinum toxin therapy. These can enhance results or help reduce the dosage and frequency of injections.
- Non-medical Approaches:
- Sensory Tricks: Touching specific areas, like the opposite side of the face, may temporarily stop spasms.
- Heat Packs and Massage: These can help relax neck and shoulder muscles.
- Exercises: Activities that improve neck strength and flexibility may prove beneficial.
- Stress Management: Learning relaxation techniques is crucial as stress often worsens symptoms.
- Surgery:
- For severe cases unresponsive to other treatments, surgical options exist. These include deep brain stimulation, where electrical pulses interrupt problematic nerve signals, and selective denervation, which involves cutting specific nerves carrying contraction signals to affected muscles.
Risk Factors for Cervical Dystonia
Cervical dystonia can affect anyone, but certain factors may increase the likelihood of developing this condition, including:
- Age: While it can occur at any age, the disorder most commonly begins after age 30. The highest risk group falls between the ages of 30 and 60.
- Gender: Women are more susceptible to this condition than men.
- Certain Medications: People who use dopamine antagonists or antipsychotics may have a higher risk of developing cervical dystonia.
- Brain Injury: Those who have experienced a brain injury are more susceptible to developing this condition.
Complications of Cervical Dystonia
Cervical dystonia can lead to various complications that affect a person's daily life & overall well-being.
- Severe pain and muscular discomfort in the overactive muscles
- Simple activities like combing hair or brushing teeth may become challenging due to tremors, spasms, and limited neck movement.
- Compression of nerve roots may cause tingling, numbness, or decreased sensation in the weakness in the arms, hands, head, and shoulder.
- Speech, swallowing, and physical coordination can also suffer, potentially affecting work performance and quality of life.
- If left untreated, cervical dystonia may spread to nearby areas such as the face, jaw, arms, and trunk.
- Secondary problems can arise from cervical dystonia, such as cervical spine arthritis and cervical stenosis (narrowing of the spinal cord in the neck).
- In some cases, bone spurs may develop, reducing space in the spinal canal. This can result in tingling, numbness, and weakness in the arms, hands, legs, or feet, further impacting mobility and comfort.
When to See a Doctor
- Individuals should visit a doctor if they notice muscle spasms or tightness in their neck.
- If cervical dystonia symptoms interfere with daily activities
- If people experience treatment side effects or worsening symptoms
- If individuals experience tingling, numbness, or weakness in their arms, hands, legs, or feet
Prevention
While prevention remains elusive, early detection and management can help control symptoms and enhance quality of life. Individuals should pay attention to any involuntary muscle contractions in the neck area, as these may indicate the onset of cervical dystonia. The condition typically begins gradually, with symptoms reaching a plateau over time.
It's crucial to consult a doctor if any signs of cervical dystonia appear. Early intervention can help manage symptoms effectively and prevent potential complications, such as spreading muscle contractions to nearby areas or developing bone spurs.
Conclusion
Managing cervical dystonia requires a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments with lifestyle adjustments. From botulinum toxin injections to stress management techniques, there are various strategies to help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. Early diagnosis and intervention significantly impact treatment outcomes, highlighting the importance of seeking medical advice when symptoms first appear. This approach allows people with cervical dystonia to better cope with symptoms and maintain a fulfilling life despite the challenges posed by this neurological disorder.
FAQ's
1. Does cervical dystonia go away?
Cervical dystonia is a lifelong condition with no known cure. In rare cases, individuals may experience spontaneous remission, often temporary. Less than 1% of affected people have permanent remissions. While the condition doesn't affect life expectancy, symptoms may progressively worsen or plateau over time.
2. Can stress cause cervical dystonia?
Stress doesn't cause cervical dystonia, but it can exacerbate symptoms. Psychological stress has been identified as a potential triggering factor. Some patients report excessive stress preceding the onset of cervical dystonia by several months. Learning stress management techniques is crucial for managing symptoms effectively.
3. What foods should I avoid with cervical dystonia?
While there's no specific diet for cervical dystonia, some dietary changes may help manage symptoms. Avoiding excess sugar, simple carbohydrates, caffeine, and alcohol can prevent blood sugar fluctuations that may affect brain function. Some individuals find relief by eliminating gluten and dairy, though this varies from person to person. A balanced diet enriched in fruits, vegetables, lean meats, and raw nuts can contribute to overall well-being.
4. What is the root cause of cervical dystonia?
The exact cause of cervical dystonia remains unknown in most cases. Research suggests that the basal ganglia, the part of the brain controlling muscle movements, may not function properly. Some instances have genetic links, with mutations in genes like GNAL, THAP1, CIZ1, and ANO3 identified. Secondary causes can include complications from psychiatric medications, traumatic brain injury, or Parkinson's disease.
5. What kind of doctor treats cervical dystonia?
Neurologists typically diagnose and treat cervical dystonia. These specialists have expertise in disorders affecting the nervous system. Treatment often includes a multidisciplinary approach, which may include physical therapists for exercises and pain management and, in some cases, surgical procedures like deep brain stimulation.
Still Have a Question?