-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Blepharospasm
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Blepharospasm
Blepharospasm, a disorder that causes involuntary muscle contractions around the eyes, may lead to uncontrollable eye twitching. It can significantly impair a person's daily life, making simple tasks like reading or driving challenging. Getting a thorough understanding of this condition is crucial for those who suffer from it and their loved ones.
In this article, we'll explore blepharospasm and its symptoms, causes, and diagnosis. We'll also discuss various blepharospasm treatment options, including medication and home remedies, to help manage this condition.
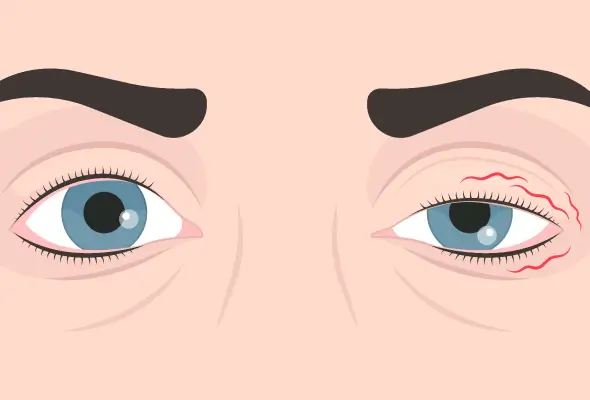
What is Blepharospasm?
Blepharospasm (benign essential blepharospasm) is a condition that causes uncontrollable eye twitching or blinking. It involves rapid and involuntary contractions of the muscles around the eyes. In severe cases, these spasms can force the eyes shut, limiting a person's eyesight. Blepharospasm primarily stems from neurological issues, with the eyes playing a role in when and how the spasms occur.
There are two main types of blepharospasm:
- Primary (Benign Essential Blepharospasm): This form occurs on its own and is usually harmless, though disruptive.
- Secondary: This type happens due to an identifiable cause and is often a symptom of other conditions.
Symptoms of Blepharospasm
Blepharospasm typically begins with occasional small eyelid twitches that gradually increase in frequency.
- The primary symptom is abnormal blinking and involuntary twitching, affecting both eyes simultaneously.
- Patients often experience forced eye closure, difficulty opening their eyes, and increased blinking rates.
- Other symptoms include blurry vision, light sensitivity, and dry eyes.
- In severe cases, continuous muscle contractions can lead to functional blindness, though this is rare.
- Unique features of blepharospasm include:
- Involuntary and uncontrollable spasms
- Synchronised twitching of both eyelids
- Patterned rather than random spasms
- Temporary improvement with 'sensory tricks' like humming or face-touching
- These symptoms can significantly impact routine tasks such as reading or driving, making early diagnosis and treatment crucial for managing the condition effectively.
Causes of Blepharospasm
Blepharospasm occurs when the brain's control over eyelid muscles malfunctions. Experts believe it stems from issues in the basal ganglia, which coordinates movements, or the facial nerve (Cranial Nerve VII). Unusual activity in these areas can trigger or contribute to blepharospasm.
The condition has two main types:
Primary Blepharospasm: This form is idiopathic, meaning its exact cause remains unknown.
Secondary Blepharospasm: This type can result from various factors, including:
- Other movement disorders like Meige syndrome
- Eye inflammation conditions
- Light sensitivity
- Certain medications, especially those treating Parkinson's disease
While blepharospasm sometimes runs in families, and women aged 40-60 are more susceptible, doctors often can't pinpoint a specific cause in most cases.
Risk Factors for Blepharospasm
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing blepharospasm.
- Age: The condition is most common between 50 and 70 years old.
- Gender: Women are two to four times more likely to develop blepharospasm than men.
- Genetics contribute, with 20% to 30% of patients having a family history of the condition.
- Environmental Factors: High levels of urbanisation and stressful 'white-collar' jobs are associated with increased risk.
- Certain Activities: Activities causing eye strain, such as prolonged reading, television watching, and computer use, may aggravate the condition. Stress and fatigue can trigger or worsen blepharospasm symptoms.
- Medical History: Previous head or facial trauma, eye conditions like dry eyes or blepharitis, and certain medications, particularly those for Parkinson's disease, can contribute to blepharospasm development.
- Mental Health Conditions: Certain conditions, including obsessive-compulsive disorder, depression & anxiety, are also linked to increased risk.
Diagnosis of Blepharospasm
Diagnosing blepharospasm can be challenging, often requiring consultations with multiple specialists. Ophthalmologists frequently see patients first due to eye-related symptoms. Neurologists play a crucial role in diagnosis, as blepharospasm primarily affects the nervous system. The diagnostic process typically involves a comprehensive eye exam, medical history review, and neurological assessment.
There are no definitive diagnostic criteria for blepharospasm. Doctors rely on clinical evaluation to rule out other conditions. Key diagnostic features include:
- Recognition of involuntary eye spasms
- Presence of sensory tricks that temporarily relieve symptoms
- Increased blinking
- Inability to voluntarily suppress spasms
Doctors may sometimes conduct electromyography to characterise muscle involvement, though this is uncommon in clinical practice. Imaging and laboratory studies generally have limited utility in confirming the diagnosis.
Treatment for Blepharospasm
While there's no cure for blepharospasm, several effective treatments can help manage symptoms.
- The most common first-line blepharospasm treatment is onabotulinumtoxinA injections. Doctors use these to weaken specific muscles around the eyes, limiting spasm-causing signals without affecting blinking. Patients typically receive four to eight tiny injections, which start working within days and last for three to four months.
- Special tinted glasses can help those sensitive to light. FL-41 lenses, often called "blue light glasses," philtre out blue wavelengths and can reduce symptoms.
- If injections don't work, doctors may recommend surgery. This involves permanently thinning the affected muscles. Some patients find relief through acupuncture, though it's less common.
- Lifestyle changes can also help. These include managing stress, getting enough sleep, and reducing caffeine intake.
- Treating underlying conditions, like dry eye, may also alleviate symptoms.
Complications of Blepharospasm
Blepharospasm can lead to significant disruptions in daily life. The involuntary eyelid movements can make it difficult to see and, in severe cases, force the eyes shut completely. The condition can also contribute to mental health concerns. Many people with blepharospasm feel anxious about having an attack in public, leading to social isolation and depression.
Treatment complications can also arise. Botulinum toxin injections, a common treatment, may cause side effects such as ptosis (drooping eyelid), diplopia (double vision), and blurred vision. Some patients experience dry eyes or exposure to keratitis due to weakness in the eye muscles. However, these complications often decrease with repeated treatments.
When to See a Doctor
Individuals should consult an eye doctor if their eyelids continue twitching for over a few weeks. Medical attention is also necessary if the eyes close completely during twitches or other facial muscles start twitching.
Prevention
While there's no known way to prevent benign essential blepharospasm, individuals can take steps to manage symptoms and reduce their severity.
- Avoiding triggers like bright light or treating underlying conditions such as blepharitis or dry eye may help with secondary blepharospasm.
- Lifestyle changes play a crucial role in symptom management. These include stress reduction, ensuring adequate sleep, and limiting caffeine intake.
- Using tinted lenses or hats can alleviate light sensitivity.
- Some people find relief through sensory tricks, which they can learn and apply.
- In cases where medication causes blepharospasm, adjusting the dosage under medical supervision might provide relief.
Remember, while prevention isn't possible, proactive management can significantly improve the quality of life for those with blepharospasm.
Conclusion
Blepharospasm can significantly influence the daily lives of those affected, causing challenges in simple tasks and potentially leading to social isolation. Understanding its symptoms, causes, and available treatments empowers individuals to take control of their condition. While there's no cure, various management options, from botulinum toxin injections to lifestyle changes, can help alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
Early diagnosis and a tailored treatment approach are crucial to manage blepharospasm effectively. Individuals with blepharospasm can navigate their condition more confidently by working closely with doctors and staying informed about the latest developments. Remember, with proper care and support, many people with blepharospasm lead fulfilling lives, adapting to their symptoms and finding ways to thrive despite the challenges.
FAQ's
1. What is the leading cause of blepharospasm?
The exact cause of blepharospasm remains unknown. Experts suspect issues in the basal ganglia or the facial nerve (Cranial Nerve VII) may contribute. While some cases run in families, doctors often can't pinpoint a specific cause.
2. What is the difference between blepharospasm and ptosis?
Blepharospasm involves involuntary eyelid closure due to muscle contractions. Ptosis, however, is a drooping of the upper eyelid caused by weakness in the muscle that lifts it.
3. Can blepharospasm be cured?
There's no cure for blepharospasm, but treatments can manage symptoms. These include botulinum toxin injections, tinted lenses, and, in some cases, surgery.
4. Is blepharospasm painful?
Blepharospasm can cause discomfort around the eyes, including tension and eyelid heaviness. Some patients report a feeling of constant squinting.
5. How do you treat blepharospasm at home?
Home treatments include stress management, adequate sleep, and reducing caffeine intake. Some find relief using tinted lenses or hats to alleviate light sensitivity.
6. How do you test for blepharospasm?
Diagnosis typically involves clinical observation by an ophthalmologist or neurologist. They look for signs like stereotyped, bilateral eye spasms and increased blinking.
Still Have a Question?




