-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Angina
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Angina
Angina is a common heart condition that affects millions worldwide and serves as a warning sign of underlying heart disease. Angina manifests as tight, squeezing pain in your chest and occurs when the heart doesn't receive enough oxygen-rich blood, often due to narrowed or blocked arteries. Understanding angina symptoms, causes, and treatment options is crucial for managing this condition and preventing more serious heart problems.
What is Angina?
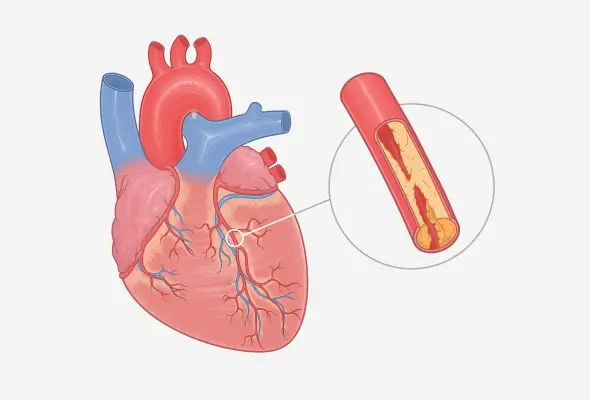
Angina, medically known as angina pectoris, is a type of chest pain or discomfort and occurs when the heart doesn't receive enough oxygen-rich blood. The term 'angina' comes from the Latin word for 'choking' or 'strangling', which aptly describes the sensation many patients experience.
Different Types of Angina
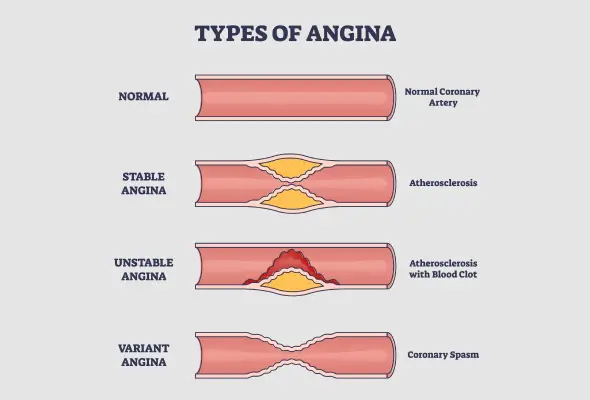
Angina manifests in various forms, each with distinct characteristics and triggers. Understanding these types helps in recognising symptoms and seeking appropriate treatment.
- Stable Angina: Stable angina, the most common type, has a predictable pattern. It typically occurs during physical activity or emotional stress when the heart requires more oxygen-rich blood. The pain usually lasts a few minutes and goes away with rest or medication. People often describe it as a squeezing or pressure in the chest.
- Unstable Angina: Unstable angina is more severe and unpredictable. It can happen even at rest and doesn't follow a pattern. The pain may be stronger or last longer than stable angina. This type results from a sudden decrease in blood flow to the cardiac muscle, often due to plaque buildup in the coronary arteries.
- Variant Angina (Prinzmetal's Angina): This rare form of angina occurs due to spasms in the coronary arteries. It typically happens at rest, often between midnight and early morning. The pain can be severe and may not respond to typical angina medications. Variant angina can affect anyone and is more common in younger, healthier individuals compared to other types of angina.
- Microvascular Angina: Microvascular angina involves pain in the chest that can be more intense and last longer than stable angina. It can occur both during rest and after exercise. This type affects the heart's smallest arteries and may not always respond well to standard angina treatments.
- Refractory Angina: Refractory angina refers to persistent angina disease symptoms that last for months despite a combination of medicines and lifestyle changes. This type can significantly impact a person's quality of life and requires specialised management strategies.
Angina Causes
Angina occurs when the heart muscle doesn't receive enough oxygen-rich blood. This lack of blood flow, known as myocardial ischaemia, impacts the heart's ability to function correctly. Several conditions can lead to reduced blood flow to the heart, causing angina pain symptoms, such as:
- Coronary Artery Disease (CAD): CAD develops when plaque, a fatty and waxy substance, builds up in the coronary arteries. As plaque accumulates, it narrows and hardens the arteries, a process called atherosclerosis.
- Coronary Microvascular Disease: This condition affects the tiny blood vessels branching from the coronary arteries.
- Coronary Artery Spasms: Spasms or repeated constriction and relaxation of the coronary arteries can temporarily restrict blood flow to the heart.
Symptoms of Angina
Angina manifests through a range of symptoms, primarily centred around chest discomfort.
- The most common symptom is chest pain or pressure, which patients often describe as a squeezing sensation or tightness.
- Some individuals compare it to indigestion, which typically originates behind the breastbone and may spread to other upper body parts.
- The pain or discomfort can radiate to various areas, such as the neck, jaw, shoulders, arms, or back.
- Fatigue
- Shortness of breath
- Excessive sweating
It's crucial to note that women may experience angina differently from men. They may experience:
- Discomfort in the neck, jaw, teeth, or back
- Nausea or vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Stabbing pain instead of chest pressure
- Stomach pain
Risk Factors for Angina
Several factors can enhance a person's risk of developing angina. These may include:
- Age: As people grow older, their chances of experiencing angina increase, with adults aged 60 and above being most susceptible.
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with parents or siblings who have had heart disease or a heart attack are more likely to develop angina themselves.
- Lifestyle Choices: Tobacco use, lack of physical activity, excess alcohol consumption, and obesity– all of which increase angina risk.
- Medical Conditions: If left untreated, certain medical conditions, such as diabetes, high blood pressure, and high LDL cholesterol and triglycerides levels in the blood, can lead to increased angina risk. Other health conditions that elevate angina risk include chronic kidney disease, peripheral artery disease, metabolic syndrome, and a history of stroke.
- Environmental Factors: Cold temperatures may provoke Prinzmetal angina, while exposure to particle pollution from various sources like roads, farms, and construction sites can contribute to angina risk.
- Emotional stress and certain medications, particularly certain migraine treatments, can induce angina symptoms.
Complications
The most significant complication associated with angina is the increased risk of a heart attack. During a heart attack, a prolonged reduction in blood flow leads to the death of heart tissue. That's why recognising the warning signs, such as pressure or squeezing pain in the chest lasting more than a few minutes, radiating pain, shortness of breath, and excessive sweating, is crucial.
Treatment of Angina
The treatment and management approach depend on the type and severity of angina.
For stable angina, lifestyle changes and medicines often prove effective.
- Lifestyle Changes:
- Adopting a heart-healthy diet
- Engaging in regular exercise
- Quitting smoking
- Managing stress
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe several medicines based on the symptoms and severity of the condition:
- Nitrates
- Aspirin and other anti-platelet drugs
- Beta-blockers
- Statins
- Calcium channel blockers
- Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP) Therapy:
- EECP therapy can improve blood flow to the heart. This non-invasive treatment involves wrapping pressure cuffs around the legs and inflating them in sync with the heartbeat.
- Angioplasty with Stenting:
- It is a common procedure which helps keep the artery open and improves the angina symptoms.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG:)
- Doctors generally recommend CABG in complex angina cases to bypass the blocked heart artery and increase blood flow to the heart.
When to See a Doctor
Some specific conditions that warrant immediate medical attention are:
- Chest pain lasting longer than a few minutes and not relieved by rest or angina medicines
- New or unfamiliar chest discomfort
- Worsening or changing symptoms in those with stable angina
Prevention
Preventing angina involves adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle and managing risk factors, such as:
- Heart-healthy Diet
- Consume the Mediterranean diet, enriched in vegetables, fruits, legumes, nuts, whole grains, and fish.
- Replacing saturated fats with more healthy monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats options
- Reducing dietary sodium intake
- Regular Physical Activity
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercises or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity activities per week.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight
- People should try to achieve and maintain a healthy weight through dietary regulation or exercise.
- Avoid Tobacco
- It is a significant risk factor for angina.
- Managing Underlying Conditions
- Reducing sodium intake and following a DASH diet can significantly lower blood pressure.
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Management includes dietary modifications, physical activity, and weight loss if necessary.
What can I do at Home to Manage Angina?
Managing angina at home involves adopting heart-healthy lifestyle changes.
- Choose foods that help prevent or lower high blood pressure and high cholesterol levels.
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Regular physical activity after consulting their doctor
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Individuals should try to avoid or limit stressful situations.
- Quitting smoking
- Getting enough quality sleep helps heal and repair the heart and blood vessels.
- Avoid very hot or cold conditions.
- Eating smaller meal portions throughout the day can help if large meals lead to chest pain.
Conclusion
Angina serves as a crucial warning sign of underlying heart issues, emphasising the importance of early detection and proper management. Understanding the different types of angina, its symptoms, and risk factors can impact individuals' ability to recognise and address this condition effectively. Adopting heart-healthy lifestyle changes and working closely with doctors can significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of more serious heart problems.
FAQ's
1. Are angina attacks serious?
Angina attacks can be serious and should not be ignored. They serve as a warning sign that the heart isn't receiving enough oxygen-rich blood.
2. Will angina go away?
Angina disease symptoms can be managed and may improve with proper treatment, but the underlying condition causing angina doesn't go away completely.
3. What are the first signs of angina?
The first signs of angina include chest pain or discomfort. Many people describe it as a squeezing, pressure, or tightness in the chest. This discomfort usually begins behind the breastbone and may spread to other upper body parts, including the neck, jaw, shoulders, arms, back, or belly.
4. At what age does angina start?
Angina can occur at any age, but the risk increases as people get older. In men, the chance of having heart disease, which can lead to angina, starts to rise at age 45. For women, the risk begins to increase after age 55.
5. How to test angina at home?
While it's not possible to definitively diagnose angina at home, there are some ways to monitor your heart health:
- Measure your pulse
- Stair test: Try climbing about four flights of stairs (approximately 60 stairs) in 90 seconds. If you can do this easily, it may indicate good heart health.
- Keep a symptom diary: Note when you experience chest pain, what triggers it, and how long it lasts.
6. Where is angina pain located?
Angina pain is typically felt in the chest. Most people describe it as a pressure, squeezing, or tightness behind the breastbone.
7. Is angina pain left or right?
People generally experience angina pain in the centre of the chest, behind the breastbone. However, it can radiate to either the left or right side of the chest or both.
8. What foods should I avoid with angina?
If you have angina, it's essential to follow a heart-healthy diet. Foods to avoid or limit include:
- Foods high in saturated and trans fats
- High-sodium foods
- Processed and fried foods
- Sugary foods and beverages
- Excessive alcohol
Dr Jyotirmaya Sahoo
Consultant - Cardiology

Still Have a Question?



