-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

Alopecia Areata
Symptom, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata, affects millions worldwide, causing thinning hair, excessive hair fall, and emotional distress. Alopecia areata is an autoimmune ailment causing hair loss on the scalp and other body parts. This article will take us through the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for alopecia areata.
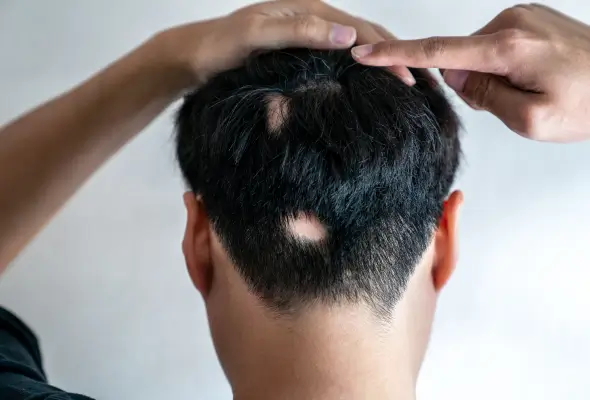
What is Alopecia Areata?
It is a widely known autoimmune disorder that causes sudden hair loss. It typically begins with round or oval smooth balding patches on the scalp or beard. However, hair loss can occur anywhere on the body, including eyebrows, eyelashes, and legs.
Types of Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata has several distinct forms, each causing varying degrees of hair loss.
- The most common type is patchy alopecia areata, which results in coin-sized, round or oval bald spots on the scalp or other body areas. This form can progress to more severe types, such as alopecia totalis, which causes complete scalp hair loss, or alopecia universalis, leading to total body hair loss, including eyebrows and eyelashes.
- Other types include ophiasis alopecia, characterised by a band-like pattern of hair loss along the sides and back of the head, and diffuse alopecia areata, which causes sudden hair thinning across the entire scalp.
- Some individuals may experience persistent patchy alopecia areata, where hair loss continues over an extended period without developing into more extensive forms.
Symptoms of Alopecia Areata
- Alopecia areata typically begins with sudden hair loss in oval or round patches on the scalp. However, it can affect any body part, including eyebrows, eyelashes, and beards in men.
- The bare patches usually show no irritation, redness, or scarring.
- Some individuals experience tingling, burning, or itching sensations before the hair falls out.
- Alopecia areata in women generally manifests as thinning hair, widening partition, and reducing the width of their braids.
- In more severe cases, alopecia areata can progress to whole-scalp hair loss (alopecia totalis) or complete body hair loss (alopecia universalis). Nail changes like tiny dents or pits often accompany extensive hair loss.
Causes of Alopecia Areata
An autoimmune disorder, alopecia areata, happens when the immune system mistakenly attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss. This condition can affect any body part that grows hair. While the exact trigger remains unknown, genetic factors play a significant role. People with a family history of alopecia areata are more susceptible to developing the condition.
Other autoimmune diseases, such as psoriasis, thyroid disorders, and vitiligo, are also linked to an increased risk.
Alopecia areata may also caused by environmental factors like stress or certain medications.
Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing alopecia areata, including:
- Stress and emotional factors may trigger the onset in susceptible individuals.
- Men face a higher risk of severe alopecia areata, as do those with nail changes or disease duration exceeding one year.
- Age at diagnosis also determines prognosis, with childhood onset often indicating a less favourable outlook.
- Atopic conditions like hay fever and eczema are associated with an increased risk.
Complications
The sudden loss of hair, especially in visible areas, can be emotionally devastating and decrease self-esteem and social confidence. Women with alopecia areata often face particular challenges, as hair loss can have a significant effect on their self-image.
Additionally, some people may develop nail abnormalities, such as pitting or ridges, which can cause discomfort and affect daily activities.
Diagnosis for Alopecia Areata
Doctors typically diagnose alopecia areata through a physical examination. They assess the areas of hair loss and examine the nails for any changes. Doctors use a handheld magnifying device to inspect the hair and follicle openings closely. A thorough medical and family history is taken, focusing on the onset of hair loss and any family history of autoimmune disorders.
If the diagnosis remains inconclusive, additional tests may be necessary. These can include:
- Scalp examinations for signs of infection
- Hair sample analysis
- Scalp biopsies to check for skin diseases
- Blood tests to rule out other conditions that might cause similar hair loss patterns.
Treatment for Alopecia Areata
Treatment modalities for alopecia areata vary depending on the severity of hair loss.
- For mild cases, corticosteroids are often the first choice. These can be applied topically or injected directly into affected areas to reduce inflammation and promote hair regrowth.
- As a topical solution, Minoxidil may be used alone or with other alopecia areata treatments to stimulate hair growth.
- Doctors might recommend topical immunotherapy or oral medications like JAK inhibitors for more extensive hair loss.
When to See a Doctor
If you observe sudden hair loss or thinning hair, it's crucial to consult a dermatologist. They can determine if alopecia areata or another condition is causing your hair loss. Regular check-ups are essential, as people with alopecia areata have a higher risk of developing thyroid disease, eczema, or other autoimmune disorders. Early diagnosis of these conditions makes them easier to manage.
Alopecia Areata Prevention
While there is no guaranteed way to prevent alopecia areata, certain measures may help manage the condition and reduce its impact.
- Avoiding unnecessary hair or scalp trauma
- Reducing stress through relaxation techniques or counselling
- Analysing your diet and ensuring proper nutrition
- Monitoring for signs of other autoimmune conditions, such as thyroid disease or lupus.
- Regular check-ups can translate into early detection & management of these related conditions.
Natural Remedies for Alopecia Areata
Here are some home remedies for alopecia areata:
- Aloe Vera Gel: Soothes the scalp and promotes hair growth.
- Onion Juice: Contains sulfur to stimulate hair follicles.
- Rosemary Oil: Enhances hair growth and circulation.
- Coconut Oil: Moisturises and strengthens the scalp.
- Peppermint Oil: Boosts blood circulation to hair roots.
- Green Tea: Rich in antioxidants, it can support hair health.
- Lavender Oil: Promotes hair growth and reduces stress-induced hair loss.
- Biotin-rich Foods: Eggs, nuts, and seeds support hair strength.
Conclusion
Alopecia areata has a significant influence on the lives of those affected, causing not only physical changes but also emotional challenges. Understanding the causes, symptoms & available treatment options empowers individuals to manage this condition effectively. While there's no cure, various treatments can encourage hair regrowth and improve quality of life. It's crucial to remember that alopecia areata is not a reflection of overall health and doesn't lead to serious medical problems.
- Autoimmune diseases
- Patients can experience hair loss, ranging from thinning to complete loss on the scalp and body.
- This condition often occurs with other autoimmune disorders like hypothyroidism, anemia, psoriasis, and rheumatoid arthritis.
- Sometimes, it can happen suddenly, and hair may change color to white.
- In some cases, it can resolve on its own without treatment.
- Stress, anxiety, hypertension, and asthma can make the condition worse.
- A qualified dermatologist should treat Alopecia Areata after proper evaluation.
- Many oral and topical medications are available, but they should be prescribed by a doctor.
FAQ's
1. What is the biggest cause of alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata, hair thinning condition, has an influence on the immune system, causing it to attack hair follicles mistakenly. While the exact trigger remains unknown, genetic factors play a significant role.
2. What is the fastest way to cure alopecia?
There is no fastest way to cure for alopecia areata.
3. What age does alopecia start?
Alopecia areata can develop at any age.
4. Can lack of vitamin D cause alopecia areata?
No, vitamin D deficiency may not contribute to hair loss.
5. What to avoid in alopecia areata?
Nothing, since it is autoimmune disorder.

Dr. P L Chandravathi
MBBS, MD, FAAD, FISD
CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills, Hyderabad
To Book an Appointment, call:
Still Have a Question?



