-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

HbA1c Test
The HbA1c test, or glycosylated haemoglobin, is a reliable blood test to measure the average blood sugar level of an individual over the past 3 months. This reliable diagnostic test is incredibly helpful in diabetes management and helps doctors make treatment plans to help individuals maintain optimal blood sugar control.
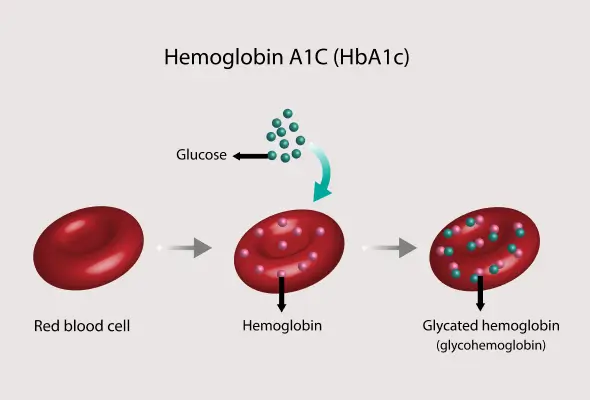
What is the HbA1c Test?
The HbA1c test is crucial to managing diabetes. It is also known as glycated haemoglobin. The body makes glycosylated haemoglobin when the glucose or sugar in the body sticks to the haemoglobin, which is a component of the red blood cells. When the levels of glucose in the blood increase, more sugar sticks to the haemoglobin. The HbA1c test allows doctors to get a percentage of the red blood cells with haemoglobin coated with glucose (sugar).
This test helps doctors see how well you've been managing your blood sugar, especially if you have diabetes. This test helps get an average of three months as red blood cells can live for about 3 months and the glucose can stick to the haemoglobin till these cells are alive. Therefore, the doctors may advise you to get this test done on a quarterly basis.
Purpose of HbA1c Test
The HbA1c test is like a report card for your blood sugar over the past few months. It shows how well your body has been handling sugar (glucose). The test measures the amount of glucose that has stuck to your red blood cells. The higher the glucose levels in your blood, the more glucose sticks to the red blood cells.
In simpler terms, it helps doctors check how well your blood sugar has been controlled over time, giving them a snapshot of your average blood sugar levels. This is important in managing conditions like diabetes and making sure that treatment plans are working effectively.
When is the HbA1c Test Needed?
The HbA1c test is needed if:
- A person has diabetes and the doctor wants to check how well they have been managing their blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months.
- The doctors want to monitor people with diabetes to see if their treatment plan is working effectively.
The test gives a more comprehensive picture compared to daily blood sugar checks, which can vary. If you have diabetes or are at risk, your doctor may recommend an HbA1c test every three months to monitor and manage your condition.
What Happens During the HbA1c Test?
The HbA1c test is done by deriving a small sample of blood, typically from the arm. This is done by a Phlebotomist. The collected sample is sent to a lab for testing purposes.
The HbA1c test measures the average amount of sugar (glucose) in your blood over the past 2-3 months. The test specifically looks at a part of your red blood cells called haemoglobin, which binds to glucose. The more glucose in your blood, the higher the level of HbA1c. This test is commonly used to monitor and manage diabetes because it provides a good indication of how well your blood sugar has been controlled over a longer period.
Uses of HbA1c Test
- Diabetes Control Check: Shows how well you've managed your blood sugar over a few months.
- Long-Term Blood Sugar Average: Provides a 2 to 3 month average, giving a more stable picture.
- Prevents Diabetes Complications: Aids in lowering the risk of heart, kidney, and eye problems.
- Guides Treatment Adjustments: Helps adjust medications or lifestyle based on long-term trends.
- Motivates Healthier Living: Acts as a motivator for positive lifestyle changes.
HbA1c Test Procedure
- Schedule the Test: Talk to your doctor, and if they recommend an HbA1c test, schedule an appointment.
- Fasting (if required): Some tests may require fasting, so check with your doctor if you need to avoid eating or drinking for a specific period before the test.
- Visit the Lab: On the day of the test, go to the lab or clinic where the blood test will be done. Several labs also offer home sample collection facilities.
- Blood Sample Collection: A healthcare professional will collect a small sample of your blood. This is typically done by pricking your finger or drawing blood from a vein in your arm.
- Quick and Painless: The blood drawing process is quick and usually not very painful. You might feel a small pinch or prick.
- Results: Your blood sample is sent to a laboratory for analysis. Results are usually available in a few days.
- Interpretation with Your Doctor: Once the results are ready, schedule an appointment with your doctor to discuss the findings. They will explain what your HbA1c levels mean in relation to your overall blood sugar control.
How Painful is the HbA1c Test?
The HbA1c test itself is not painful. It involves a simple blood draw, similar to routine blood tests. You may feel a brief pinch, but it's usually well-tolerated. The discomfort is minimal and quick. The importance lies in managing diabetes, not the test's pain. Think of it like a tiny bee sting that lasts a second. It's a small price for checking your blood sugar control. Most people find it less painful than a regular injection. The discomfort fades fast; the health insights last longer. It is important to focus on the big picture: preventing diabetes complications.
How to Prepare for the HbA1c Test?
- Eat and drink normally before the test; no fasting is required.
- Continue your regular medications unless your doctor advises otherwise.
- Inform your healthcare provider about any changes in your medications.
- Stay hydrated to make blood drawing easier.
- Be honest about recent illnesses or significant lifestyle changes.
- Relax; stress won't help, and the test reflects a few months, not just one day.
- Avoid vigorous exercise on the day of the test, as it may affect the results.
- If you're feeling unwell, consider rescheduling the test for accurate results.
- Inform your healthcare provider about any supplements or vitamins you're taking.
What do HbA1c Test Results Mean (If it is Lower and Higher than Normal Levels)?
The HbA1c test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months, offering insights into long-term glucose management.
- HbA1c under 4.6% may indicate a risk of hypoglycemia; consult your doctor for adjustments.
- Normal HbA1c levels indicate good long-term blood sugar control and reduced risk of diabetes-related complications.
- Higher-than-normal levels suggest poorer blood sugar control over the past few months.
- Low levels could signal too much medication or insulin; review your treatment plan.
- Elevated levels may require lifestyle changes, medication adjustments, or closer monitoring.
- Aim for the target range advised by your healthcare provider for optimal diabetes management.
- Regular follow-ups help fine-tune your diabetes management based on evolving HbA1c results.
Achieving normal HbA1c levels is crucial for minimising diabetes-related complications and maintaining overall health.
How to Lower your HbA1c Levels?
- Eat a balanced diet with controlled portions, emphasising whole foods.
- Exercise regularly, aiming for at least 150 minutes per week.
- Monitor and manage carbohydrate intake, choosing complex over simple carbs.
- Take prescribed medications as directed by your healthcare provider.
- Stay hydrated and limit alcohol consumption.
- Prioritise stress management through relaxation techniques and adequate sleep.
Conclusion
The HbA1c test, pain-free and vital, empowers you to prevent complications associated with diabetes. Partner with your healthcare team at CARE Hospitals, and together, let’s conquer diabetes for a healthier, happier you.
FAQs
1: What is a normal HbA1c level?
Ans: A normal HbA1c level is typically below 5.7%, indicating good blood sugar control.
2. What happens if the HbA1c level is positive?
Ans: HbA1c levels don't have positive/negative outcomes; they measure average blood glucose over the past 2-3 months.
3: What happens if the HbA1c level is negative?
Ans: HbA1c levels don't have negative outcomes; they provide a measure of blood glucose control.
4: What are some possible complications of the HbA1c level?
Ans: High HbA1c may lead to diabetes-related complications like heart disease, kidney problems, and nerve damage.
5: How long does the HbA1c level take to perform?
Ans: The HbA1c test typically takes a few minutes for blood collection, but results may take a day or more after lab processing.
6: Can I take an HbA1c test at home?
Ans: Currently, HbA1c tests are primarily conducted in clinical settings; home tests are not widely available or recommended.
7: What is Glycosylated haemoglobin HbA1c?
Ans: Glycosylated haemoglobin, or HbA1c, indicates average blood glucose levels, aiding in diabetes diagnosis and treatment assessment.
Still Have a Question?



