-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals

FNAC Test
The term FNAC test stands for 'Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology.' It is a quick, cost-effective, and simple test designed to evaluate a specific condition or a particular area of the body. This procedure, also known as an aspiration biopsy, is conducted for various reasons to assist a physician in making an accurate diagnosis. It does not cause any pain to the patient, and there are almost no complications or side effects.
What is the FNAC Test?
The FNAC method is typically performed in an outpatient department for sampling masses, such as those observed in the neck, breast, and diseases like lymphoma, tuberculosis, etc. It serves as the initial step in identifying the underlying cause of abnormal swellings. An aspiration cytology test is recommended when a lump is discovered in the breast or neck. This test is used to determine if the lump is cancerous. Additionally, it is employed in diagnosing thyroid disease, salivary gland disease, and lymph node disease.
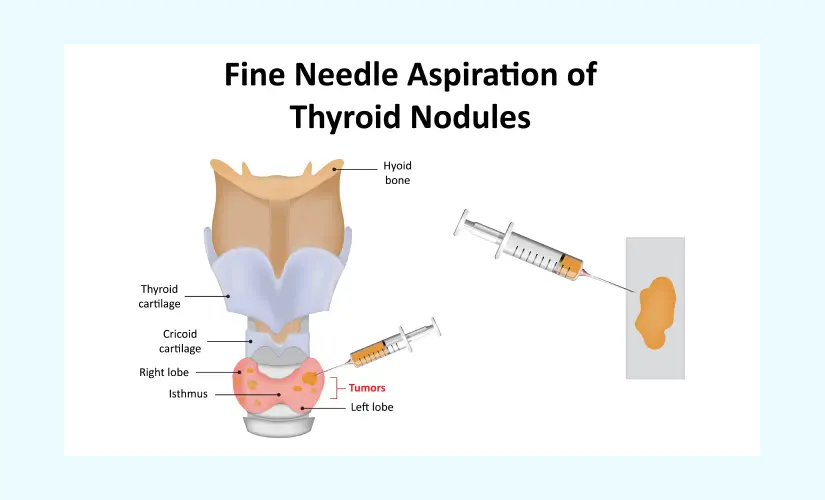
Purpose of FNAC Test
In most cases, a fine needle aspiration procedure is performed on a swelling or lump that is just below the surface of the skin. The primary purpose of fine needle aspirations is to detect cancer, but it can also be employed to test swellings for conditions such as lymphomas, lymphomatous lymphoma, tuberculosis, toxoplasmosis, granulomatous lymphadenitis, and other diseases. Fine needle aspirations are most commonly performed in the following areas:
- the breast,
- the thyroid gland, and
- lymph nodes in the neck or armpit.
Additionally, fine needle aspiration cytology can be used to examine patients for cytological abnormalities. It is also a valuable tool for examining cysts, lymph nodes, and other solid lumps found in the body.
What happens during the FNAC Test?
The majority of fine needle aspiration procedures are performed in outpatient settings. It is a type of biopsy that involves inserting a thin needle into an area of tissue or body fluid that appears to be abnormal. Like other types of biopsies, the sample taken during fine needle aspiration may be used to diagnose or rule out conditions such as cancer. Whether local anaesthesia should be administered depends on the extent of the tissue mass, whether it is superficial or extensive. There are no potential side effects. However, there can be mild bruising or temporary tenderness in the affected area in some cases.
Uses of FNAC Test
This method is employed for a variety of testing procedures, including chorionic villus sampling, body fluid sampling, breast abscess sampling, breast cyst sampling, and seroma sampling, all of which are conducted through ultrasound-guided aspiration. Fine needle aspiration cytology is particularly useful in detecting breast cancer and testing swellings for various malignancies, including those associated with lymphoma, granulomatous lymphadenitis (GLL), tuberculosis (TB), and transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSE), among others. Additionally, it aids in studying the cytological alterations that a patient may be undergoing.
FNAC test procedure
The procedure of the FNAC test includes:
- An antiseptic solution will be used to clean the skin above the site of the procedure. The area will then be draped with a sterile towel or drape.
- A numbing agent may be administered to the affected area beneath the skin.
- Ultrasound can be utilised during the procedure to aid in identifying the appropriate site for fine needle aspiration.
- A thin needle connected to a syringe is inserted into the abnormal site through the skin.
- A vacuum is created inside the syringe, which causes the suction (aspiration) of body fluid or tissue into the syringe and needle.
- The fine needle aspiration procedure is typically completed in less than ten minutes.
- The biopsy sample can then be sent to a laboratory for further analysis.
- Normally, an ice pack is provided following the test procedure to offer immediate pain relief.
How painful is the FNAC test?
The degree of pain associated with an FNAC test may vary from person to person. However, some discomfort may be felt during the needle insertion process. The doctor may use local anaesthesia to numb the area before the needle insertion, which helps reduce pain during the procedure. After the procedure, there may be some mild pain or discomfort at the needle insertion point, but this usually subsides quickly. In general, most individuals find the procedure to be painless and manageable.
How to prepare for the test?
The FNAC test does not require any specific preparation. However, the physician may provide additional guidance based on the sampling site and type. Here are some general considerations to help prepare for the test:
- Inform the doctor about any medications or supplements the patient is taking before the test. In some cases, temporary discontinuation of certain medications, such as blood thinners, may be necessary.
- Wear comfortable clothing. Depending on the sampling site, partial or complete undressing may be required.
- Let the physician know if the patient has a history of bleeding disorders or is taking medications that may affect blood clotting.
- To ensure the accuracy and safety of the test, it is important to follow any instructions provided by the physician.
What do FNAC test results mean?
The following information is provided to assist in interpreting the results of a fine needle aspiration cytology test:
- A lump or nodule can be tested to determine if it is benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous).
- The results are typically presented as either a definitive diagnosis or an inconclusive diagnosis that requires further investigation.
- The accuracy of the test depends on factors such as the size and location of the nodule, the location from where the sample is taken, the expertise of the practitioner performing the test, and the proficiency of the pathologists interpreting the results.
The FNAC report will vary depending on the size of the mass or lump being analysed and the possible underlying disease. The following discusses the results of FNAC tests and their interpretations:
|
FNAC test result |
Interpretation |
|
Benign |
The cells appear to be normal and non- malignant. |
|
Suspicious |
These cells look abnormal and they need to be further evaluated to see if they are malignant or not. |
|
Malignant |
These cells appear to be abnormal and potentially cancerous. |
FNAC Test Positive Means
|
Test result |
Interpretation |
|
Positive |
An abnormal or malignant cell count appears in the aspirate, indicating the presence of cancer cells. |
FNAC Test Negative
|
Test result |
Interpretation |
|
Negative |
|
It is essential to discuss the results of the FNAC test normal report with the doctor, as they can provide a more comprehensive explanation based on individual circumstances.
Conclusion
It is recommended to seek medical attention when noticing persistent and unexplained swelling. If you are experiencing constant swelling in superficial areas of your body, please schedule an appointment at CARE Hospitals for your check-up.
FAQs
1. Is the FNAC test for TB?
Ans. Yes, fine needle aspiration cytology test is a cost-effective, fast, and secure approach to diagnose tuberculosis.
2. What happens if the FNAC test is positive?
Ans. A positive FNAC test result does not necessarily indicate a diagnosis of cancer. The physician may recommend additional tests to determine the definitive diagnosis, taking into account the patient's pre-existing medical condition, symptoms, complaints, and clinical examination.
3. What happens if the FNAC test is negative?
Ans. A negative result in an FNAC test report does not rule out the presence of the disease. An open biopsy should be conducted to confirm the diagnosis through histopathological examination.
4. What are some possible complications of the FNAC test?
Ans. Complications such as bleeding, infection, or bruising at the needle site may occur but are rare.
5. How long does the FNAC test take to perform?
Ans. While the test itself typically only takes a few minutes to complete, the entire appointment can last up to one hour, depending on the location of the mass and whether additional imaging tests are required.
Reference:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/19610510/
https://www.webmd.com/a-to-z-guides/fine-needle-aspiration
https://www.ucsfhealth.org/education/biopsy-for-breast-cancer-diagnosis-fine-needle-aspiration-biopsy
Still Have a Question?



