-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Peroral Endoscopic Myotomy (POEM) for Achalasia Cardia
Updated on 23 January 2024

POEM, or peroral endoscopic myotomy, is a minimally invasive endoscopic procedure that is employed for the treatment of a condition known as achalasia cardia. Achalasia cardia is the medical term referring to an abnormality of the oesophagus in which it becomes tough for the person suffering from it to swallow any kind of food. The procedure of POEM can also help treat other disorders associated with the process of swallowing.
POEM is a minimally invasive procedure that insinuates that no incisions are made through the skin and often causes much less pain, along with offering the possibility of a short hospital stay and faster recovery than other more invasive surgical procedures. POEM is a novel procedure that has come up as a minimally invasive alternative to other treatments for achalasia cardia.
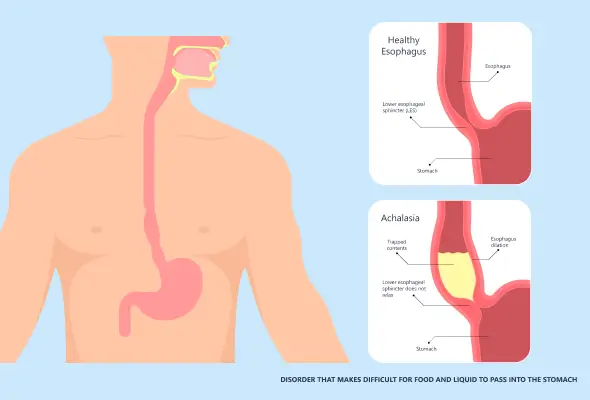
What is Achalasia Cardia?
Achalasia cardia is a swallowing disorder occurring due to the oesophagus. People with this condition face swallowing issues (dysphagia) owing to the failure of relaxation of the lower oesophagal sphincter.
The lower oesophagal sphincter, located at the terminus of the oesophagus at the junction of the stomach, regulates the passage of food into the stomach. People with achalasia cardia aren't able to swallow bolus; rather, it remains inside the oesophagus and goes down slowly into the stomach. This condition may lead to symptoms of chest pain and vomiting out undigested food. It may even lead to weight loss eventually.
Treatment therapies for achalasia cardia aimed at providing relief from the swallowing disorder may help relax the lower oesophagal sphincter muscles to allow easy passage of bolus and undigested food into the stomach without much obstruction. Among the myriad of treatments available for achalasia cardia, pneumatic dilation is a prominent one that involves the insertion and inflation of a balloon that unblocks the passageway into the stomach. Alternatively, Botox injection and medicine administration may also allow relaxation of the lower oesophagal sphincter, but all of these offer only a temporary solution.
Heller myotomy, of which the POEM is an endoscopic alternative, offers longer-lasting results but requires open surgery.
What are the Indications for POEM?
The POEM procedure may be employed mainly for the treatment of achalasia cardia at the lower end of oesophagus. Additionally, people experiencing extreme difficulties in the process of swallowing, leading to deterioration in the quality of life of a person, should opt for POEM.
Who is a Candidate for POEM?
Although the POEM procedure may be recommended mainly for the treatment of achalasia cardia, it may also help address other associated conditions of dysphagia or muscle spasms in the oesophagus in patients of all age groups. Such conditions may include:
- Distal Oesophageal spasm (DES)
- Jackhammer Oesophagus, also known as the Hypercontractile Oesophagus
- Nutcracker Oesophagus, also known as Hypertensive Oesophageal Peristalsis
- Esophagogastric (EG) junction outflow obstruction
Apart from these conditions, POEM may be recommended for patients who have previously undergone alternative treatment for achalasia cardia, such as Botox injections, Heller myotomy, or balloon dilation.
While the POEM procedure is considered to be safe, it may not be suitable for patients with certain health conditions or complications, including those with:
- A severe liver disease
- Blood clotting disorders
- A severe esophagitis
- A severe bullous lung disease
Patients who have damaged tissues in their oesophagus due to previous surgery may also be advised to refrain from this procedure.
What Happens Before the POEM Procedure?
A patient deemed fit for the POEM procedure may need to follow the specific instructions of their treating doctor. Such a patient may need to follow a strict liquid diet for a recommended period, along with a day of fasting prior to the procedure.
Certain medications or supplements the patients take may have a counter impact on the procedure. Any medicine or supplement taken by the patients should be notified to the doctor or gastroenterologist, and they may need to consume it with an altered dosage or stop using it for the period before the procedure.
Furthermore, patients may expect a physical examination and a thorough evaluation of their overall health condition before the procedure to ensure optimal success of the procedure.
What Happens During the POEM Procedure?
The POEM procedure may be performed under general anaesthesia after a thorough patient assessment. Being a minimally invasive procedure, no incisions are made through the skin. Instead, a special endoscope (flexible tube with a camera) is passed through the mouth and extended till the end of the oesophagus. The endoscope allows visualisation of the internal structures for the surgeons to operate seamlessly.
With the assistance of the endoscope, the surgeon can pass a knife to make an incision into the inner layer of the oesophagus to form a tunnel. Furthermore, the adjoining muscular layers on the side of the oesophagus, along with the lower oesophagus and upper portion of the stomach, are surgically removed following the process of myotomy.
After the removal of necessary muscular layers and construction of the submucosal tunnel, the top incision is clipped off. This procedure would allow normal passage of food down the oesophagus into the stomach and relieve tightness.
What Happens After the POEM Procedure?
After the procedure has been performed successfully, the patients are put under constant monitoring and evaluation of health for postoperative care. During the hospital stay, assessment of risks and recovery in the patient may be performed through imaging tests. An X-ray barium test may provide insights into the passageway through the oesophagus and ensure unrestricted flow of food into the stomach.
Recovery after POEM
After getting discharged from the hospital, patients need to take medications as advised. They may also need to visit the hospital for follow-up check-ups to ensure the success of the procedure along with treating dysphagia.
Some patients may require medications to address symptoms of pain during the recovery period, although in most cases, there may be no pain after a day or two. Dietary changes may be recommended by the doctor. In the beginning, patients may be required to follow a diet consisting of soft foods and progress towards normal foods as deemed fit post-check-up during regular visits to the doctor. It is possible to feel soreness in the throat for a few days or weeks following the procedure.
Patients may be able to return to work within one or two days following discharge from the hospital but may be restricted from lifting heavy weights.
Risks & Complications Associated with POEM
Although the POEM procedure is a minimally invasive procedure which is generally considered to be safe, there are certain complications associated with this procedure. While such complications and postoperative risks are rare, there is still a slight likelihood of occurrence. Complications and risks associated with the POEM procedure may include the following:
- Tears in the mucosal lining of the oesophagus
- Infection
- Bleeding as a result of injury to the oesophagus
- Inflammation of the oesophagus
- Collapsed lung or pneumothorax
- Pneumomediastinum (a condition in which air is present in the mediastinum, the space between the lungs)
An additional problem that may come up post-POEM procedure is gastrointestinal reflux disease or GERD, in which there is much less resistance to stomach acid flowing up the oesophagus. However, this problem may be managed quite effectively with the help of medications targeted to prevent GERD.
FAQs
1. Is the POEM procedure safe?
POEM is a safe and effective procedure that provides better long-term results than most other treatments for achalasia cardia or other conditions leading to dysphagia. Complications are possible but rare and can be managed endoscopically.
2. Is the POEM procedure painful?
Patients aren't likely to feel pain during the procedure as it may be performed under general anaesthesia. There may be some discomfort or pain post-operation or while swallowing in the first few days, but most patients recover quickly.
3. How long does it take to perform the POEM procedure?
It may take around 2-3 hours to complete the POEM procedure, including administering general anaesthesia before the operation and myotomy.
To Book an Appointment, call:
ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Endoscopic Mucosal Resection (EMR): What it is, Procedure and Recovery Process
Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD): What it is, Procedure, Side Effects and Recovery Process
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Preterm Birth (Premature Birth): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
13 May 2025
Read More
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
9 May 2025
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
9 May 2025
Read More
-

Venous Malformations: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Foam Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation Treatment for Varicose Veins: Know More
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Endovenous Laser Ablation: Procedure, Benefits, Risks
30 April 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.