-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Leaky Gut Syndrome: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Updated on 13 February 2024

Leaky gut syndrome is a medical condition related to the digestive system wherein the intestinal lining leaks and allows toxins and bacteria to get through inside the gut and into the bloodstream. While leaky gut syndrome is not a recognised medical condition that can be diagnosed, further research in this area can help improve understanding concerning the permeability of bacteria and other toxins into the bloodstream that may play an important role in various health conditions like Crohn's disease.
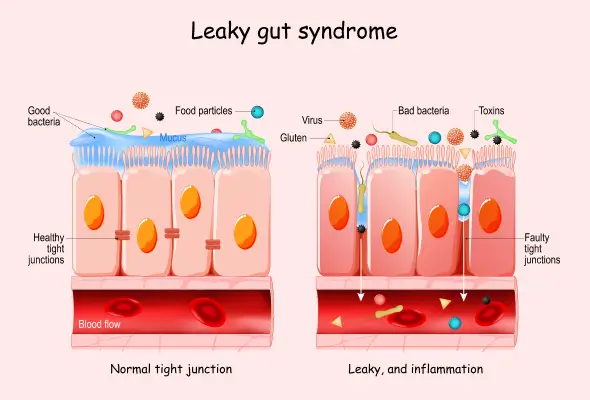
What is Leaky Gut Syndrome?
The term "leaky gut" refers to damage to the gut lining for various reasons. The stomach and the intestines are laden with digestive enzymes and healthy gut bacteria that assist in breaking down nutrients from food and water into usable and absorbable molecules for producing energy as well as for growth and repair. The intestinal walls allow the absorption of water and nutrients to pass through the bloodstream while preventing harmful substances from passing through. Such selective permeability of the intestines is known as intestinal permeability.
A chronic increase in the condition of intestinal permeability is usually referred to as leaky gut syndrome. In this condition, the bacteria, toxins, and even food particles start entering the bloodstream.
Who Gets a Leaky Gut?
The known and possible causes of leaky gut syndrome involve systematic erosion of the intestinal lining. It occurs gradually rather than suddenly. While it is possible that it may be injured temporarily, the gut is designed to be repaired and replenished constantly. Although the gut is designed to repair and replenish itself constantly, complete erosion to the extent that particles and toxins can penetrate the lining requires significant effort. Chronic conditions, prolonged use of certain substances like alcohol or drugs, or chronic disease may lead to increased permeability of the gut, leading to a leaky gut syndrome. Radiation therapy may also lead to leaky gut syndrome in some people.
The causes of leaky gut syndrome involve constant and regular injuries to the gut lining that may lead to increased permeability. Therefore, everyday common stress factors like diet, sedentary lifestyle, and chronic stress may cumulatively work to wear the gut lining down.
Symptoms of Leaky Gut Syndrome
There are no obvious symptoms associated with the leaky gut syndrome or increased permeability. However, this condition may result from injury to the intestinal lining. Leaky gut syndrome symptoms can vary widely and may include the following:
- Gas and bloating
- Diarrhoea
- Painful indigestion due to loss of intestinal mucosa
- Burning feeling in the gut
- Gastrointestinal mucositis from radiation therapy
- Low energy or chronic tiredness
- Headache
- Changes in the digestive system, like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Skin problems like eczema, acne, and rashes
- Weak immune system
- Confusion and difficulty concentrating
- Food allergies and/or intolerance
- Mental health problems like depression, anxiety, and attention deficit disorder
Causes of Leaky Gut Syndrome
A number of factors are believed to be the causes of leaky gut syndrome, such as:
- Excessive alcohol intake: Individuals who consume alcohol heavily and on a daily basis are often at an increased risk of developing leaky gut syndrome.
- Chronic stress: Stress, in general, may lead to a number of conditions. Chronic stress for a prolonged period of time may lead to conditions, including leaky gut syndrome.
- Nutritional deficiencies and poor diet: The reason for leaky gut syndrome may be mostly attributed to long-term deficiency of essential nutrients like zinc, and vitamin deficiencies. Increased intake of certain foods like sugars, particularly genetically modified foods, fructose, dairy products, etc., may also cause permeability to increase, leading to leaky gut syndrome.
- Use of NSAIDs: Using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs may contribute to an increased risk of permeability that may lead to leaky gut syndrome.
Leaky Gut Diagnosis
There is no standard diagnostic procedure for leaky gut diagnosis, as the symptoms may include a range of unrelated problems. Additionally, there is no leaky gut test to measure intestinal permeability that may indicate a leaky gut. However, various tests may be used to look for evidence of increased intestinal permeability. These tests may include the following.
- Blood test: A blood test for leaky gut diagnosis may help determine bacterial infiltration. Pathologists may look for certain antibodies and endotoxins that may provide an understanding of gut permeability.
- Urine test: A urine test may help measure sugar levels in urine to understand which sugars can pass through the intestinal walls.
- Tissue biopsy: Laboratory examination of a sample of tissue from the intestine may help understand the permeability factor of the intestinal lining.
- Endoscopy test: An advanced endoscopic test may help doctors examine the intestinal lining with greater focus and magnification to understand the degree of permeability of the gut lining.
- Allergy test: Allergy testing may help determine the IgE levels to identify any allergies that may be causing leaky gut syndrome.
Leaky Gut Treatment
The only known leaky gut cure is to treat the underlying cause. Specific treatment of conditions that may possibly lead to increased permeability of the gut can help repair the intestinal lining. The most effective leaky gut treatment involves making dietary and lifestyle modifications to facilitate the healing of the gut lining. Implementing such changes may not only alleviate general symptoms of the gastrointestinal system but also enhance the overall health and integrity of the gut lining. In addition to dietary adjustments, the following lifestyle changes may help improve digestion and contribute to repairing a leaky gut:
- Exercising regularly
- Managing and reducing stress
- Getting enough sleep every night
- Quitting smoking and alcohol consumption
- Avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics
Risk Factors
An imbalance in the gut microbes may impact the overall health of the intestines, which may include an increase in permeability of the gut. Such problems may trigger the body's immune system, leading to inflammation and an increase in permeability, causing leaky gut syndrome. Some other conditions also increase the risk of developing leaky gut syndrome, including:
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
- Crohn's disease
- Celiac disease
- Diabetes
- Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS)
- Chronic liver disease
- Food allergies
Some studies also suggest that leaky gut syndrome may be triggered by mental health conditions like anxiety and depression. However, more research is needed to identify the triggers and risk factors of leaky gut syndrome.
Leaky Gut Syndrome Diet – Foods to Eat and Avoid
The best natural treatment for leaky gut syndrome is to make dietary and lifestyle changes. Patients with leaky gut syndrome are advised to make certain modifications to achieve the desired recovery, such as:
- Consuming Probiotics: Specially prepared probiotics may help to restore the balance of good bacteria and restore the barrier of the intestinal lining. Probiotics may also help to improve the general health of the intestinal lining by preventing overgrowth of the wrong kind of bacteria in the gut.
- Including Prebiotics in Diet: Prebiotics are taken for improving the amount of good bacteria in the gut and help them to fight off infections. These prebiotics may be obtained from vegetables.
- Avoiding Fats and Sugars: It is important to reduce the consumption of sugars and fats to prevent the growth of the wrong kinds of bacteria, along with releasing harsh dietary emulsifiers that may cause inflammation of the gut.
- Maintaining Proper Nutrition: Consuming a balanced diet consisting of all the essential micronutrients and macronutrients like vitamins and minerals may help to fortify the gut and help improve the condition of healthy gut bacteria. These nutrients may help to repair the intestinal lining.
Conclusion
Leaky gut syndrome is not an officially recognized health condition but may involve a wide range of problems that lead to increased permeability of the intestinal lining, allowing bacteria, toxins, and other particles to enter the bloodstream. A number of factors are believed to cause a leaky gut, including stress, diet, and other common factors like chronic health conditions. Reducing stress and managing other problems may help to treat leaky gut. Seeking professional medical help may also be beneficial to manage the problem.
At CARE Hospitals, we have a team of the most brilliant gastroenterologists with extensive experience in diagnosing various gastrointestinal conditions, including a leaky gut, and providing personalized solutions. To schedule an appointment, reach out to our team today.
FAQs
1. What is the fastest way to heal a leaky gut?
One of the best ways to treat a leaky gut is eating a healthy diet. The diet should be rich in foods that promote the growth of healthy bacteria in the gut, such as fruits, vegetables, lean meats, healthy fats, and fibrous foods.
2. Which drinks heal a leaky gut?
Probiotic-rich drinks may be beneficial for repairing the intestinal lining and healing a leaky gut.
3. How can I test for leaky gut at home?
A urine test at home may help test for a leaky gut at home. A healthcare provider may help understand the steps involved in a urine test.
4. Can you fix a leaky gut naturally?
Treating a leaky gut at home naturally involves making dietary and lifestyle changes like consuming a healthy and balanced diet, exercising regularly, and avoiding the consumption of alcohol, saturated unhealthy fats, sugars, etc.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (51)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (30)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (10)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Upper Gastrointestinal (GI) Bleed: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment
Stomach Flu (Viral Gastroenteritis): Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Direct Anterior Approach in Total Hip Replacement: Advantages and Challenges
10 April 2025
Read More
-

Zinc Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
9 April 2025
Read More
-

Chest Pain When Coughing: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
9 April 2025
Read More
-

12 Health Benefits of Eating Mushrooms
8 April 2025
Read More
-

7 Health Benefits of Blood Donation You Should Know About
8 April 2025
Read More
-

Implantation Bleeding Vs Periods: Know the Difference
28 February 2025
Read More
-

Bloating During Ovulation: Symptoms, Causes and Remedies
28 February 2025
Read More
-

Itching During Dengue: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
18 February 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.