-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Hives (Urticaria): Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment
Updated on 24 January 2024
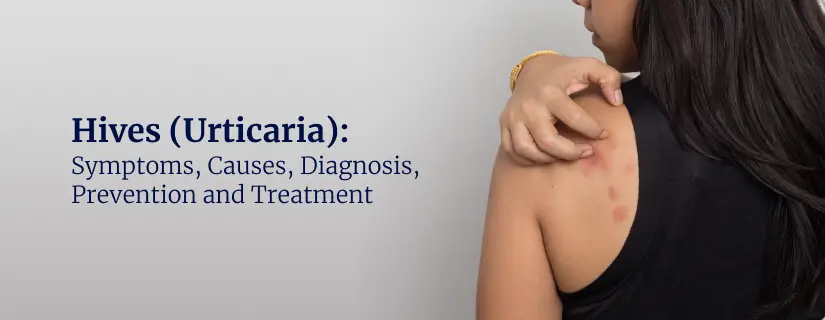
Hives, also known as urticaria, is a common skin condition characterised by red, itchy welts on the skin. It can occur due to various factors and ranges in severity from mild to severe. While acute hives last only a few days, chronic hives can persist for months or years. Thankfully, various treatment options are available to provide relief. This comprehensive article covers all key aspects surrounding hives.

Causes of Hives
Hives occur when immune cells release histamine and other chemicals, leading to swelling, fluid leakage, and severe itchiness of the skin. It represents an abnormal immune response to potential triggers, such as:
- Allergic reactions to foods, medications, insect bites, or stings
- Viral or bacterial infections
- Exposure to extreme hot or cold temperatures
- Sun exposure to the skin
- Emotional stress
- Physical causes like pressure, tight clothing, or vibration from jogging
- Autoimmune disorders
- Fluctuating hormonal levels
In many cases, the trigger behind an outbreak remains unidentified. Sometimes, minor dietary changes or stress might provoke episodes without a clear source.
Symptoms of Hives
Typical symptoms include:
- Sudden appearance of red, swollen welts and flare patches on the skin.
- These can emerge without warning, seemingly almost instantaneously on any part of the body.
- The welts can initially resemble insect bite marks or nettle stings before expanding into larger blotchy areas.
- Individual hives lesions vary in size and shape.
- Small localised hives can remain coin-sized.
- Bigger merged wheals may span larger skin zones, up to several inches wide.
- Their shape keeps changing from circular to arc-like to ring-shaped patterns as they evolve or subside.
- Burning, tingling-type itch or pruritus.
- This can range from mild prickliness to severely intense itchiness, provoking urges to scratch.
- The itchy sensation seems to intensify based on the number and size of hives present.
- Occasional deeper painful swelling called angioedema.
- In some cases, histamine release causes swelling in the deeper dermal skin layers, yielding raised, tense, painful patches around sites like the eyes, lips, hands, or genitals.
- Throat angioedema may dangerously obstruct breathing.
The welts can emerge anywhere without warning. While uncomfortable, hives generally do not pose serious health risks. However, swelling in the throat or face requires immediate medical care.
Diagnosis
To correctly diagnose hives, doctors first visually examine the appearance of wheals. They also explore possible links through a detailed history, including information about:
- The exact size, shape, and distribution of lesions.
- The frequency, severity, and triggers of outbreaks.
- Existing illnesses, such as infections, cancers, or autoimmune conditions.
- Recent medication, food, or allergen exposures.
Blood tests help detect associated conditions like thyroid disease or allergic reactions. Rarely, a skin biopsy is undertaken to inspect tissue under a microscope. Maintaining a symptom diary helps establish patterns.
Treatment
The necessity and type of treatment depend on multiple factors, such as the severity and recurrence of symptoms:
- Mild acute hives
- These generally respond well to oral antihistamines like cetirizine, loratadine, or fexofenadine, which block histamine receptors, providing relief from itching.
- Topical hydrocortisone cream helps with localised skin inflammation.
- Identifying and avoiding triggers is also important.
- Severe flares
- Potent H1 antihistamines offer limited benefit when dozens of hives lesions cause intense discomfort.
- A short course of oral corticosteroids like prednisone acts rapidly to resolve swelling.
- Stronger immunosuppressants may sometimes be needed for angioedema flares obstructing airways.
- Chronic hives
- Low-dose corticosteroids cannot be continued long-term due to side effects.
- Regular immunomodulators, like cyclosporine, which reduce immune over-activity, help achieve disease remission.
- Biologics, such as omalizumab, show good response rates by targeting specific inflammatory pathways.
- Refractory symptoms
- Phototherapy, intravenous immunoglobulin, and plasmapheresis are done when first and second-line drugs fail, before considering experimental options.
Identifying and avoiding triggers, staying cool, and managing anxiety/stress levels also help minimise recurrent outbreaks along with medications.
Complications
Hives generally do not result in any long-term health issues or chronic complications on their own. However, the following problems can occasionally develop:
- Bacterial skin infections from excessive scratching
- Dangerous swelling in the throat (angioedema) leading to breathing difficulty
- Significant sleep loss, impairment of daily activities, lowering the quality of life
If respiratory distress, difficulty swallowing, or a drop in blood pressure develops, contact emergency healthcare services promptly.
Prevention
While it's challenging to prevent unpredictable recurrences, you can still take suitable precautions:
- Avoid known food or medicine triggers.
- Stay adequately cool and hydrated.
- Exercise with caution.
- Learn to manage stress effectively through counselling or techniques like meditation.
- Bathe/change clothes following inadvertent exposures to suspected allergens.
- Take prescribed antihistamines regularly as advised.
Though remissions commonly occur over time, early optimal treatment helps control chronic hives
Home Remedies of Hives
Certain natural remedies may provide additional relief from hives when combined with medical therapy:
- Cold compresses for instant soothing
- Applying a cold washcloth to the hives can help reduce inflammation and ease itching by constricting blood vessels.
- Oatmeal baths to ease irritated skin
- Oatmeal relieves itchiness through its anti-inflammatory properties.
- Add one cup to lukewarm bathwater.
- Alternatively, use soothing oatmeal-containing cleansers.
- Light moisturisers to hydrate skin
- Frequent showers remove skin-protecting natural oils, worsening dryness.
- Apply gentle, fragrance-free moisturizing creams.
- Loose, breathable cotton clothing
- Avoid wool and tight clothes that may overheat the skin or cause friction, leading to flare-ups.
- Herbal remedies
- Chamomile/green tea compresses, licorice, nettle, turmeric, and evening primrose oil seem beneficial for some patients.
- Discuss suitability with doctors first regarding dosage and possible herb-drug interactions.
While not universally effective, these wallet-friendly alternative strategies offer additional options to help control hives recurrences better.
When to see a doctor
Arrange an early doctor consultation if you experience:
- Facial/throat swelling, leading to breathing issues
- Hives uncontrolled by over-the-counter antihistamines
- Recurrent symptoms persisting over 6 weeks
- A major disruption of normal activities/sleep
Dermatologists can best evaluate chronic hives cases, diagnose any underlying medical condition, and provide appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Hives represent an abnormal immune response causing uncomfortable skin inflammation due to various reasons. Acute outbreaks usually clear quickly, while chronic hives necessitate expert care and the avoidance of potential triggers. Antihistamines constitute the first-line treatment, while immunosuppressants manage stubborn cases. Over time, the majority of hives cases enter remission. Paying attention to warning signs allows timely intervention if any complications develop.
FAQS
1. Is it OK to scratch hives?
Avoid scratching, as it can worsen skin inflammation and even cause infections. Apply cold packs/compresses to ease the itching. Over-the-counter antihistamines also reduce the urge to scratch.
2. How long do hives last?
Acute hives outbreaks typically clear within 24-48 hours but can persist for up to 6 weeks. Chronic hives last over 6 weeks and come and go episodically. With treatment, chronic hives often go into remission eventually.
3. Do touching hives spread?
No, the rash is not contagious. Touching/scratching can spread the release of histamine to other areas locally, but close contacts do not catch hives. Proper hygiene lowers the risk of infection from scratching.
4. What stops hives from itching?
Oral antihistamines like cetirizine or hydroxyzine effectively curb itching in most cases. Corticosteroid creams, cold packs, and oatmeal baths also provide relief. Identifying and avoiding triggers is key to preventing recurrences accompanied by severe itching.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (51)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (30)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (10)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
How to Get Rid of Ringworm: 7 Effective Treatments To Cure
Dark Circles Under The Eyes: Causes, Home Remedies and Treatments
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Direct Anterior Approach in Total Hip Replacement: Advantages and Challenges
10 April 2025
Read More
-

Zinc Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
9 April 2025
Read More
-

Chest Pain When Coughing: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
9 April 2025
Read More
-

12 Health Benefits of Eating Mushrooms
8 April 2025
Read More
-

7 Health Benefits of Blood Donation You Should Know About
8 April 2025
Read More
-

Implantation Bleeding Vs Periods: Know the Difference
28 February 2025
Read More
-

Bloating During Ovulation: Symptoms, Causes and Remedies
28 February 2025
Read More
-

Itching During Dengue: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
18 February 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.