-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Eosinophilia: Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment
Updated on 12 September 2023
Table of Content
Eosinophils are a kind of white blood cell and an essential component of the immune system. They help the immune system trigger an allergic reaction by destroying allergens and harmful invaders like parasites. Eosinophils, produced by the bone marrow, fight infections brought on by bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other parasites. Eosinophilia is the medical term for an increase in the level of eosinophils. High eosinophil levels are a side effect of several medical disorders and medications.
This article offers a thorough analysis of eosinophilia, including its causes, symptoms, treatments, and preventative measures.
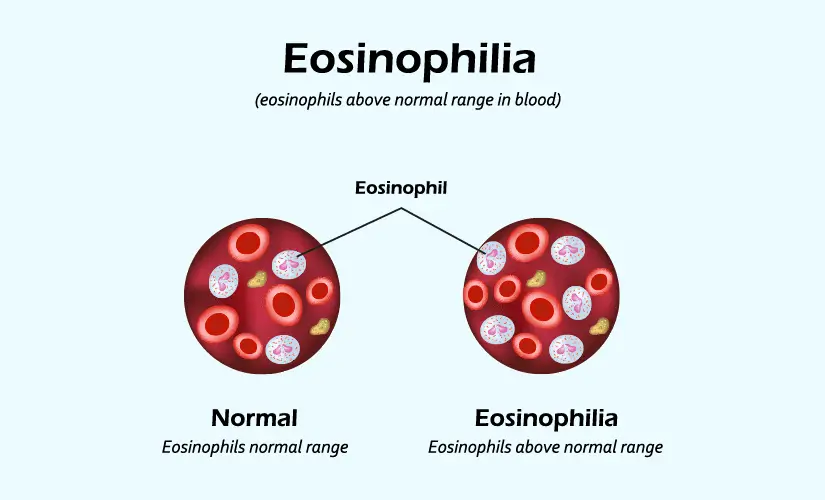
What Is Eosinophilia?
Eosinophilia is a medical disorder in which the eosinophil count is abnormally high. Eosinophils are one of the categories of white blood cells that help defend the body from parasite and fungal diseases, as well as allergies. Eosinophils in the body have two distinct functions in the immune system. They are:
- Regulating inflammation - Eosinophils help in the promotion of inflammation, which is helpful in determining and managing a disease site. However, excessive inflammation can occasionally result in severe symptoms or even tissue damage. Other immune system conditions can also be a factor in chronic inflammation.
- Getting rid of alien substances - Eosinophils have the capacity to ingest foreign substances, which may be helpful in fighting against a parasite infection.
Eosinophils account for around 0.0 to 6.0 percent of white blood cells, according to a blood sample differential count. Your doctor could advise an absolute eosinophil count if the findings are outside the usual range. A normal absolute eosinophil level is considered to be from 0 to 500 cells per microliter.
What Causes Eosinophilia?
There are several potential causes of an increased eosinophil count. Some of the causes of eosinophilia are benign and don't require treatment. Several medical disorders cause an increase in blood eosinophil levels, including:
- Allergic reactions
- Endocrine disorders
- Skin problems
- Fungal and parasitic infections
- Adrenal conditions
- Autoimmune disorders
- Tumours
Tissue or blood eosinophilia can also be caused by certain illnesses, such as:
- Eczema or atopic dermatitis
- Allergy to medications
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome
- Crohn’s disease
- Hay fever
- Asthma
- Acute myelogenous leukaemia
- Churg-Strauss syndrome
- Hodgkin’s lymphoma
Among the more prevalent causes of eosinophilia are parasitic illnesses and drug-induced allergic responses. The term "hypereosinophilic syndrome" refers to hypereosinophilia that results in organ damage. This condition usually has an uncertain cause or is brought on by specific cancers, including lymph node or bone marrow cancer.
What Happens If The Eosinophil Count Is High?
Eosinophilia is the medical term for a high eosinophil count. It is a symptom of another health issue rather than a medical condition. Numerous illnesses can be indicated by a high number of eosinophils. A person may have a high eosinophil count if they have:
- Certain cancers, including leukaemia
- Parasitic infections
- Allergies
- Asthma
- Eczema
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome, a condition with no known cause, which is characterized by high eosinophil levels.
- Autoimmune diseases
How Is Eosinophilia Treated?
Doctors address the underlying condition or problem that is causing elevated eosinophil levels. For instance, when a patient has eosinophilic esophagitis, doctors may administer steroids or other drugs. The doctor may advise allergy tests to identify the sources of the allergic reaction that caused the patient's high levels of eosinophils, especially if they have chronic sinusitis or allergies. In most cases, the doctor will advise discontinuing the medicine if it is the cause of eosinophilia. If cancer or an infection is the cause of eosinophilia, the doctor will treat either condition.
The course of treatment will depend on the specific cause of eosinophilia. Here are some of the treatment options:
- In the event of moderate eosinophilia, constant monitoring is required, with recurrent lab tests to ascertain the eosinophil count.
- If a certain medication is causing changes in your eosinophil levels, your doctor may recommend discontinuing its use.
- For the treatment of hypereosinophilic disorders, steroids like prednisone may be suggested.
- Enhancing the treatments for asthma, allergies, and eczema is also important in managing eosinophilia.
- For parasitic infections, anti-parasitic medication may be prescribed.
How Do Doctors Diagnose Eosinophilia?
Eosinophilia is detected on a complete blood count (CBC), like the majority of blood diseases. Eosinophils are one type of white blood cells that may be identified in the differential section of the complete blood count (CBC). The patient's respiratory, gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, renal, and neurological systems should all be thoroughly examined.
Basic blood counts that detect eosinophilia are usually accompanied by other tests, such as:
- A peripheral blood smear is performed to look for aberrant eosinophils.
- Imaging tests based on symptoms or indications of organ involvement, such as a chest or abdomen CT scan.
- Bone marrow biopsy.
- Genetic testing.
- Stool examinations to rule out infection with parasites.
- Tissue biopsies for parasites.
- Testing for pulmonary function.
How Can Eosinophilia Be Prevented?
Treatment to manage the body's allergic responses can help avoid allergy-related eosinophilia. Eosinophilia can occasionally be a symptom of a more serious disorder that may not always be treatable. Precautionary actions, such as the following, can assist in lowering the prevalence of eosinophilia:
- Preserving appropriate personal hygiene.
- Avoid raw fish, meat, prawns, snails, slugs, and other aquatic animals to prevent parasitic infections.
- Wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly to avoid ingesting parasites.
- Living in a clean and dust-free environment.
- Staying away from drugs to which you are allergic.
Avoiding allergens that are known to cause eosinophilia is an all-around preventative approach.
How to Reduce Eosinophil Count?
The treatment of how to reduce eosinophilia is dependent on the underlying cause. If an allergic response is the reason, avoiding allergens or taking allergy medications can help lower eosinophil levels. Medication to inhibit the immune system may be recommended if eosinophilia is associated with an autoimmune disorder. It is critical to consult a healthcare practitioner to identify the best treatment approach for the individual based on their specific disease and medical history.
How to Reduce Eosinophils in Blood Naturally?
After addressing the underlying reason, eosinophil levels often drop. The use of anti-inflammatory medications and adopting a healthy lifestyle, however, may help reduce exceptionally high levels. Following these suggestions can help you understand how to reduce eosinophil count naturally:
- Recognize possible allergens and make an effort to avoid coming into contact with them.
- Consult a doctor if you have seasonal allergies and take the medication as directed.
- Stress and anxiety-related illnesses might cause your eosinophilia. By taking a few minutes to relax, you can manage your eosinophil levels.
- Stop taking any medications that increase your body's eosinophil count.
- Eat a balanced diet that emphasises fruits, vegetables, and whole grains while avoiding acidic foods
Conclusion
Your immune system relies on eosinophils to protect your body from external intruders. If your doctor believes your eosinophils are more than usual, they will use a blood test to monitor the health of your cells. A low eosinophil count frequently does not represent a danger to your general health since other cells will step in to assist your body function in the absence of the eosinophils.
CARE Hospital is one of India's top eosinophilia treatment centres. For the treatment of eosinophilia, we provide unmatched patient care and hospital experiences. We house excellent doctors and cutting-edge technologies under one roof, guaranteeing that patients get high-quality care.
FAQs
1. Is there any permanent cure for Eosinophilia?
Eosinophilia is a persistent, chronic illness for which there is no acknowledged cure. The goal of current treatments and medicines is to control the eosinophilia-related symptoms.
2. How to reduce Eosinophil count by food?
Avoid eating meals that are too acidic, such as fried foods, garlic, tomatoes, chocolate, onions, and coffee. Try to consume low-fat foods, such as lean meats, whole grains, and whole-grain products.
3. Can exercise reduce Eosinophils?
Regular exercise can improve immunological function as well as general health. Even though physical activity may not directly lower eosinophil levels, it can support a strong immune system and general well-being.
4. What are the symptoms of Eosinophilia?
Weight loss, coughing, fevers, rashes, exhaustion, chest pain, swelling, stomachaches, soreness, weakness, and disorientation are some of the symptoms of eosinophilia.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Fruits Good For Diabetes
Many Are Not Aware of Adult Vaccines
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Preterm Birth (Premature Birth): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
13 May 2025
Read More
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
9 May 2025
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
9 May 2025
Read More
-

Venous Malformations: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Foam Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation Treatment for Varicose Veins: Know More
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Endovenous Laser Ablation: Procedure, Benefits, Risks
30 April 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.