-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Difference Between Piles, Fissures, and Fistula
Updated on 7 November 2023

Table of Content
- What is Piles Disease?
- Is Piles Dangerous?
- Causes of Piles
- Are Piles Curable?
- What are Fissures?
- How to Know if you have Anal Fissures?
- What Can Cause Anal Fissures?
- What are Fistulas?
- What are Anal Fistulas Caused by?
- How to Identify Anal Fistulas?
- Difference Between Piles, Fissure, And Fistula
- Conclusion
Piles and fissures are anal pathologies which cause certain common symptoms like passing bloody stools or having trouble passing stools, itchy and irritable anal cavity, and discomfort when sitting for a long time, among other such symptoms.
The anus is the end orifice of the digestive tract through which excreta (stools) are expelled from the body. Piles and fissures are two of the common disorders concerning the anal region. Almost 20% of the Indian population suffers from piles and fissures. However, since both these disorders have very similar symptoms, it is important to understand the piles and fissures difference.
What is Piles Disease?
Piles, also known as haemorrhoids, is a condition of the anus in which the veins in the terminal part of the anus get swollen. Piles primarily affect the population over 50 but are common in pregnant women. In most cases, piles may begin to heal on their own before the symptoms appear.
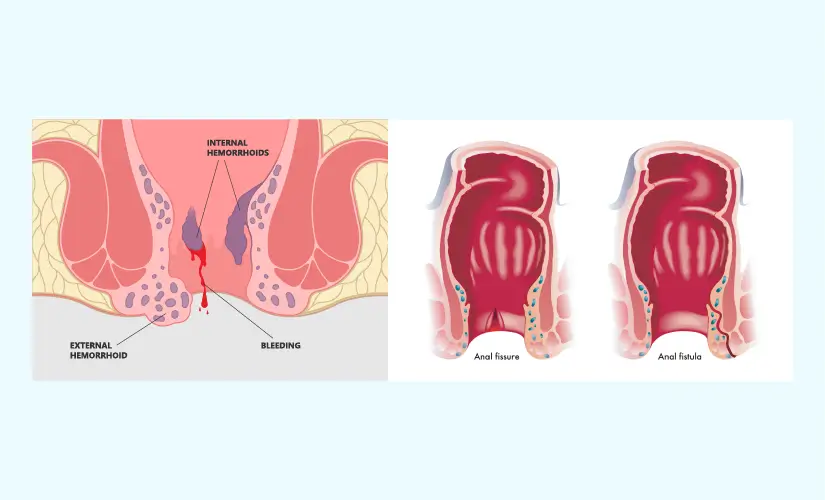
Piles can be broadly classified into three categories:
- Internal Piles: This type of haemorrhoid occurs as hard lumps in the back passage of the anal passage. There can be occasional bleeding and/or pain.
- External Piles: When the haemorrhoids occur at the outer end of the anal region, there can be pain and skin infections.
- Thrombosed Piles: When a blood clot obstructs the flow of blood, there can be swelling and pain. Sometimes, these haemorrhoids may burst and start bleeding.
The symptoms of piles may include:
- Bleeding after passing stool
- Passing bloody stools
- Lump or swelling inside the anal cavity
- Irritation, itchiness, and/or pain in the anal region
- Leakage of stools
The symptoms of piles and the treatment would depend upon the type of piles present in the affected individual and their severity.
Is Piles Dangerous?
Most of the time, piles can get better on their own within a few days. There can be occasional itchiness, pain, and passing blood along with stool. However, it can become a serious problem if there is:
- Anal bleeding leading to anaemia
- Anal fistula
- Faecal incontinence
- Blood clot and infection
Causes of Piles
Chronic constipation and difficulty in bowel movements cause piles. There can be other reasons that may lead to piles. These include the following:
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Pregnancy
- Straining when passing stool
- Lifting heavy weights
Are Piles Curable?
Piles tend to get better on their own if they're in their initial stages. Sometimes, it is possible to treat piles with simple lifestyle changes and treatments such as:
- Making dietary changes
- Reducing body weight
- Using medications such as corticosteroids and laxatives
If non-interventional treatment for piles doesn't work, surgical treatments such as banding, infrared coagulation, sclerotherapy, and haemorrhoidectomy may help fix this problem.
What are Fissures?
Fissures are tears in the moist tissue of the anal region, which causes painful spasms and itching in the anal region. The basic difference between anus fissure and piles is that, unlike piles, the pain in the anal region can be present from the beginning of the problem. Fissures can be categorised into two types depending on the severity of the condition:
- Acute fissures: These are new fissures which can be treated easily with medication or at home or may heal on their own.
- Chronic fissures: Fissures lasting for more than 8 to 12 weeks require medical intervention for treatment. Chronic fissures also develop a skin tag and an extra growth of tissues called hypertrophied papillae.
Fissures can be treated by medications or by making dietary changes by adding more fibre to the diet and drinking more water, especially in the morning on an empty stomach, to help empty the bowels more smoothly. If the problem persists for more than a week, it is best to consult a doctor.
How to Know if you have Anal Fissures?
The symptoms of fissures are usually present from the beginning of the problem due to anal tearing with ensuing pain. There can be additional symptoms of fissures, which may include the following:
- Occasional bleeding, particularly during passing stools
- Mucus-like discharge
- Pus-filled boils, usually painful
- Experiencing painful muscle spasms in the anal region
- Lump or skin tag near the anal fissure
What Can Cause Anal Fissures?
Anal tears causing anal fissures may be caused by a variety of reasons which may include the following:
- Chronic diarrhoea
- Straining hard during passing stools
- Passing large and/or hard stools
- Childbirth
- Anal intercourse
Some of the lesser common yet possible causes of anal fissures may include the following:
- HIV
- Syphilis
- Crohn's disease
- Tuberculosis
- Anal cancer
What are Fistulas?
Fistulas are another condition affecting the anal region. The anal glands present in the middle portion of the anus may get infected, leading to an anal abscess. This can cause pus to start oozing out and create a passage, called a fistula, to the infected gland; a fistula has been associated with being overweight and sitting for a prolonged duration of time. There can be pain, swelling, redness, and release of pus.
The difference between piles and fissures and fistula is in the affected region, i.e. in fistulas, the anal glands are affected, but in piles and fissures, any place in the anal region can be affected. Anal fistulas can be treated with antibiotics.
What are Anal Fistulas Caused by?
Anal fistulas are caused by a blockage in the passage of fluids in the fluid glands in the anus leading to the creation of pus-filled abscesses. Such blockage leads to the growth of bacteria that create pockets in the abscesses. If left untreated, these abscesses may grow and push out of the anus to drain the pus. In most cases, these abscesses become fistulas.
Anal fistulas may also be caused due to diseases such as tuberculosis and due to certain sexually transmitted diseases.
How to Identify Anal Fistulas?
Anal fistulas may cause a number of symptoms which may include the following:
- Pain at the bottom
- Redness and swelling around the anus
- Occasional bleeding
- Pain when passing stool
- Fever
It is advisable to visit a doctor if symptoms of fever occur along with pain and bleeding.
Difference Between Piles, Fissure, And Fistula
There are quite a few differences between piles, fissures, and fistulas in their area of occurrence, symptoms, and other features.
|
Piles |
Fissure |
Fistula |
|
|
Area of occurrence |
Above the orifice of the anus (internal piles) or outside the edge of the anus (external piles) |
Lining of the anal canal |
From the upper part of the anal gland inside the anal passage to the anal skin outside |
|
Causes |
|
|
|
|
Symptoms |
|
|
|
|
Treatment |
Non-surgical: Eating high fibre foods, taking pain relieving medications, and topical treatments. Surgical: Sclerotherapy, coagulation technique, and rubber band ligation. |
Non-surgical: High fibre diet, medications, and hydrating frequently. Surgical: Lateral internal sphincterectomy. |
Non-surgical: Medications. Surgical: Fistulotomy (simple fistula surgery) , Seton drain, endorectal advancement flap, LIFT (ligation of intersphincteric fistula tract). |
All three conditions can be significantly improved or even prevented by taking a fiber-rich diet and intake of more fluids. Additionally, fistulas can be prevented by taking care of hygiene.
Conclusion
Anal bleeding and pain, especially when passing stool, is a primary indicator of such problems, particularly in obese people and those over the age of 50. Piles, fissures, and fistulas should not be left untreated, as these may lead to chronic conditions and unexpected complications. While these problems are common, very few people seek help due to embarrassment.
It is important to remember that these can be easily treated with minimal intervention and even without any surgery. So, do not be embarrassed to ask for help. The top gastroenterologists at CARE Hospitals treat such conditions with utmost expertise and confidentiality.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (52)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (32)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (15)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Acid Peptic Disease: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
How to Get Rid of Gallbladder Stones Without Surgery?
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Preterm Birth (Premature Birth): Symptoms, Causes, Treatment and Prevention
13 May 2025
Read More
-

Rotablation Angioplasty: Benefits, Treatments, And Recovery Time
9 May 2025
Read More
-

What Is The Difference Between IUI and IVF?
9 May 2025
Read More
-

Venous Malformations: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Foam Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Radiofrequency (RF) Ablation Treatment for Varicose Veins: Know More
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Sclerotherapy: Treatment, Benefits, and Procedure
30 April 2025
Read More
-

Varicose Vein Endovenous Laser Ablation: Procedure, Benefits, Risks
30 April 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.