-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Blood in Urine (Hematuria): Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment
Updated on 19 January 2024

Blood in urine, medically known as hematuria, refers to the presence of blood in the urine. It occurs when there is bleeding somewhere along the urinary tract - including the kidneys, ureters, bladder or urethra - that allows blood to enter into the urine. The presence of blood in urine, known as hematuria, can be a concerning observation when initially detected.
This article provides an overview of hematuria, including what it is, its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. It also covers when you should see a doctor for blood in urine.
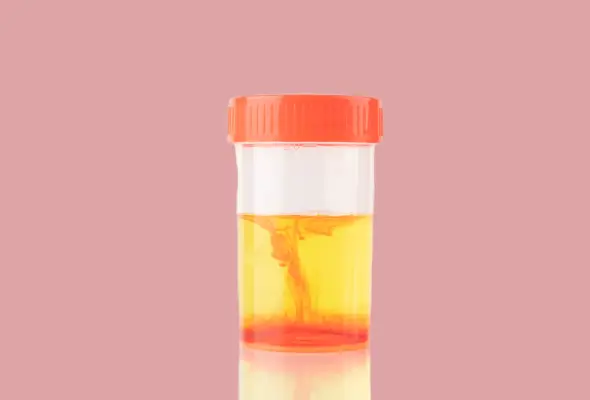
What is Blood in Urine (Hematuria)?
Hematuria is the medical term used to describe blood appearing in urine. It happens when there is damage or inflammation somewhere along the urinary tract that causes bleeding to appear in the urine. The urinary tract includes the kidneys, ureters (tubes connecting kidneys to bladder), bladder, and urethra (tube carrying urine out of the body).
Based on the visibility of blood to the naked eye, hematuria is classified into two types:
- Macroscopic Hematuria: This refers to urine that is visibly red, pink or brownish-red in colour due to the presence of a substantial amount of blood that is visible without a microscope. Patients may notice visible blood in their urine.
- Microscopic Hematuria: This type indicates urine that appears normal in colour but still contains a small amount of blood that can only be detected under a microscope during urinalysis. The blood is essentially invisible or too little to change the colour of the urine.
Even a small leak of blood cells into the urine can cause urine to take on a distinctly red, pink or brownish discolouration. The hematuria itself may or may not be accompanied by any pain symptoms. However, the passing of visible blood clots in urine can cause discomfort.
Symptoms of Blood in Urine
Some common signs and symptoms associated with hematuria include:
- Red, pink, brown, or coca-cola coloured urine
- Painful or burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent urge to urinate
- Passing blood clots through urine
- Fever, chills, nausea or vomiting (possible indicators of infection)
- Pain in the lower back, abdomen, sides or groyne
- Fatigue and weakness
The above symptoms can appear in various combinations, depending on the severity and underlying cause behind the bleeding.
Causes of Blood in Urine
There can be several possible causes behind the occurrence of blood in urine, including:
- Infections:
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Kidney infections (pyelonephritis)
- Inflammation of the prostate gland (prostatitis)
- Structural Issues:
- Development of bladder stones or kidney stones
- Enlarged prostate, which puts pressure on the urethra
- Inherited diseases like sickle cell anaemia or Alport syndrome that damages blood vessels.
- Polycystic kidney disease, which can cause cysts that interfere with urine flow.
- Kidney disorders:
- Glomerulonephritis or inflammation of tiny kidney filters that remove waste from the blood.
- Nephritis, which involves inflammation of kidney tissue, can also cause blood in the urine.
Several types of cancer, including Bladder cancer, Kidney cancer, and Prostate cancer can also cause blood in the urine.
Some other causes include:
- Vigorous exercise or contact sports that may cause trauma to kidneys or bladder.
- Usage of certain medications like penicillin, cyclophosphamide, aspirin, heparin etc.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of hematuria involves:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: This involves asking about symptoms, family history, and risk factors.
- Urine Tests: Urinalysis detects the presence of blood, while urine culture identifies potential infections.
- Imaging Tests: CT scan, ultrasound, cystoscopy are done to visualise the urinary tract.
- Kidney Biopsy: This test involves removing a small sample of kidney tissue for examination.
By thoroughly testing the blood-tinged urine sample and carefully evaluating accompanying symptoms, doctors can determine the likely cause behind bleeding and decide appropriate treatment approaches.
Blood in Urine Treatment
The main aims of treating hematuria are:
- Addressing identifiable underlying causes
- Managing bothersome urinary symptoms
- Preventing recurrence and complications
Blood in urine treatment options include:
- Antibiotic drugs to eliminate urinary tract infection.
- Surgery to remove bladder stones, kidney stones or urinary tract tumours.
- Medications to relieve painful urinary symptoms.
- Lifestyle changes like increased daily fluid intake.
- Avoiding high-risk medications.
- Treating related illnesses like diabetes.
- Follow-up urine tests to monitor condition.
Treatment plans focus on treating the specific cause diagnosed by testing. This helps manage bloody urine and prevent recurrence.
Complications of Blood in Urine
Here are some potential complications associated with blood in urine (hematuria):
- Recurrent UTIs:
- If the underlying cause of hematuria, such as a structural abnormality or prostate enlargement, is not treated, it can lead to repeated episodes of UTIs.
- Recurrent UTIs can cause kidney inflammation and permanent kidney damage over time.
- Kidney Stones:
- Left untreated, some causes of hematuria, like infections and inherited cystic disorders, may result in the formation and growth of kidney stones.
- Large stones can block urine flow from the kidney and also cause recurrent UTIs.
- Kidney Failure:
- Recurring cases of hematuria due to untreated infections, inflammation, or structural defects can progressively impair kidney function if left unaddressed.
- Recurrent bleeding may cause renal scarring over time, which may lead to chronic kidney disease or total kidney failure, requiring dialysis.
- Bladder Scarring:
- In the case of bladder-related causes for hematuria, such as tumours, chronic bleeding and inflammation can cause build up of scar tissue in the bladder walls.
- This scarring reduces bladder capacity and the ability to store urine.
- Sepsis:
- Bacteria causing infections like pyelonephritis can spread from the urinary tract into the bloodstream if persistent hematuria is not treated, resulting in urosepsis.
- This can prove to be life-threatening.
- Anaemia:
- Though rare, exceptionally severe cases of gross hematuria involve very heavy bleeding, leading to unusually high red blood cell loss.
- This rapid loss of RBCs may contribute to a low blood cell count or anaemia.
Prevention
Some lifestyle habits to help prevent hematuria or its recurrence include:
- Drinking plenty of hydrating fluids daily.
- Practising safe sexual contact to avoid STIs.
- Properly managing coexisting chronic illnesses.
- Avoiding unnecessary overuse of certain high-risk medications.
- Preventing injury to kidneys and bladder during contact sports.
When to See a Doctor?
It is crucial to promptly consult a healthcare provider whenever you notice even the slightest presence of blood in urine. Timely medical evaluation and treatment are vital, as they can improve prognosis and prevent recurrence.
You should seek urgent medical care or visit an emergency room if blood in urine occurs along with:
- High fever and chills
- Great difficulty or inability to pass urine
- Debilitating back, side or abdominal pain
- Passing many large visible blood clots
Such symptoms can indicate possibly serious underlying conditions requiring immediate treatment.
Conclusion
The occurrence of blood in urine or hematuria can result from multiple causes, ranging from harmless issues like UTIs to grave illnesses like cancer. Macroscopic hematuria, where blood visibly changes urine colour, is more concerning than microscopic hematuria. While this urinary bleeding seems undeniably alarming, proper evaluation and timely treatment often resolve many cases effectively, especially when addressed early.
However, no matter how insignificant it may appear, you should always consult a doctor promptly when you first notice blood in urine in order to get appropriate diagnostic testing and therapeutic management.
FAQs
1. Is blood in urine serious?
While it can be, hematuria generally occurs due to minor, treatable conditions like UTIs. Evaluating the cause is important to determine severity.
2. How common is blood in urine?
About 1-2% of people exhibit visible hematuria during their lifetime. Microscopic hematuria is more common in the general population.
3. Can drinking water stop blood in urine?
Increased fluid intake may help flush out minor bleeding from the urinary tract but does not treat the underlying cause. Seeking medical care is still necessary.
4. Can blood in urine resolve on its own?
Sometimes, as with strenuous exercise-induced hematuria. However, recurrent or persistent hematuria warrants medical evaluation as it likely indicates an underlying disorder.
5. What does blood in urine signify?
Hematuria signifies abnormal bleeding somewhere along the urinary tract- kidney, ureters, bladder, or urethra. Identifying the source of bleeding is key for accurate diagnosis and treatment.

ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (51)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (30)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (10)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Overactive Bladder: Symptoms, Cures and Natural Treatments
How to Increase Sperm Count: 12 Ways To Do
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Direct Anterior Approach in Total Hip Replacement: Advantages and Challenges
10 April 2025
Read More
-

Zinc Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
9 April 2025
Read More
-

Chest Pain When Coughing: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
9 April 2025
Read More
-

12 Health Benefits of Eating Mushrooms
8 April 2025
Read More
-

7 Health Benefits of Blood Donation You Should Know About
8 April 2025
Read More
-

Implantation Bleeding Vs Periods: Know the Difference
28 February 2025
Read More
-

Bloating During Ovulation: Symptoms, Causes and Remedies
28 February 2025
Read More
-

Itching During Dengue: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
18 February 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.