-
Doctors
-
Specialities & Treatments
Centre of Excellence
Specialties
Treatments and Procedures
Hospitals & Directions HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet
HyderabadCARE Hospitals, Banjara Hills CARE Outpatient Centre, Banjara Hills CARE Hospitals, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Nampally Gurunanak CARE Hospitals, Musheerabad CARE Hospitals Outpatient Centre, HITEC City CARE Hospitals, Malakpet Raipur
Raipur
 Bhubaneswar
Bhubaneswar Visakhapatnam
Visakhapatnam
 Nagpur
Nagpur
 Indore
Indore
 Chh. Sambhajinagar
Chh. SambhajinagarClinics & Medical Centers
Book an AppointmentContact Us
Online Lab Reports
Book an Appointment
Consult Super-Specialist Doctors at CARE Hospitals
Blood Clot in Brain: Types, Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
Updated on 25 September 2024

Table of Content
- Types of Blood Clots in the Brain
- Causes of Blood Clot in the Brain
- Possible Risks
- Symptoms of Blood Clot in the Brain
- Diagnosis of Blood Clots in the Brain
- Treatment of Blood Clot in the Brain
- Complications of Blood Clot in the Brain
- When to See a Doctor
- Is it Possible to Prevent Blood Clots in the brain?
- Conclusion
- FAQ's
A blood clot, if present inside the brain, is a serious medical condition that may call for immediate attention. This potentially life-threatening issue occurs when a blood vessel in the brain becomes blocked, disrupting the flow of oxygen and nutrients to vital brain tissue.
An in-depth knowledge of the symptoms of a blood clot in the brain can translate into early detection and prompt treatment. This article explores the causes, signs, and treatment options for blood clots in the brain, helping readers identify when they should seek medical help and what to expect during diagnosis and care.
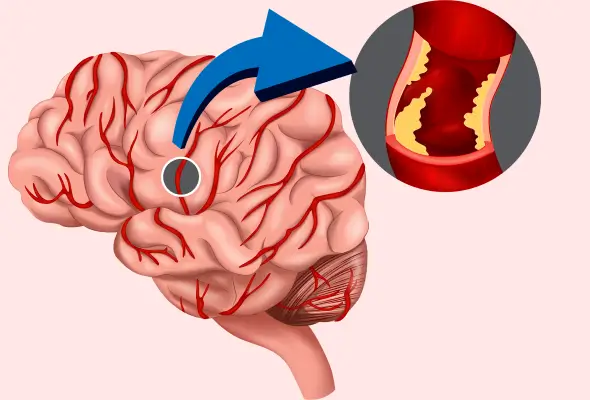
Types of Blood Clots in the Brain
Blood clots in the brain can be of two main types: ischaemic and hemorrhagic. These types differ in their formation and effects on the brain.
- Ischaemic blood clots occur when an artery supplying blood to the brain becomes blocked. This type accounts for approximately 87% of all strokes. Ischaemic clots can be further divided into two subtypes:
- Thrombosis: A stationary clot forms within a damaged blood vessel.
- Embolism: A clot or foreign object moves from its original location to block an artery in the brain.
- Hemorrhagic blood clots result from a ruptured blood vessel leaking into the brain tissue. Although less common, hemorrhagic clots are often more severe and life-threatening. They cause nearby tissues to stop functioning and can lead to brain swelling, exerting pressure on surrounding areas.
Both types of blood clots can cause a stroke, also known as a brain attack, by disrupting the brain's vital blood supply.
Causes of Blood Clot in the Brain
Some of the blood clots in brain reasons are:
- High blood pressure causes impairment of blood vessels, increasing the risk of clots.
- Smoking and uncontrolled diabetes also harm blood vessels, contributing to clot formation.
- Atrial fibrillation, an irregular heartbeat, causes blood to pool in the heart, potentially forming clots that travel to the brain.
- High cholesterol levels and obesity are additional risk factors.
- Genetic predisposition plays a role, as a family history of stroke or blood clots raises an individual's risk.
- Age is another factor, with the likelihood of brain clots increasing as people get older.
Possible Risks
Some factors can make a person susceptible to developing a blood clot in the brain.
- Age and gender play a role, with older individuals and men at higher risk.
- Choices such as smoking & a sedentary lifestyle contribute significantly.
- Medical conditions like high blood pressure, obesity, uncontrolled diabetes, and high cholesterol also raise the likelihood.
- Atherosclerosis (fatty deposit buildup in the arteries) narrows blood vessels and increases clot risk.
- Certain medications, including hormonal contraceptives & hormone replacement therapy, may also elevate the risk.
Symptoms of Blood Clot in the Brain
Recognizing signs and symptoms of blood clots in the brain is crucial for seeking timely medical help. Common symptoms include:
- Sudden severe headaches, accompanied by neck pain and stiffness
- Individuals may experience weakness or numbness, particularly on one side of the body, affecting the face, arm, or leg.
- Speech difficulties, such as slurred speech or trouble understanding others
- Vision problems, including blurred or darkened eyesight
- Loss of balance, coordination issues, and dizziness
- In some cases, people might face acute paralysis, making it challenging to move affected limbs.
- Confusion, tremors, and even seizures can develop as the condition progresses.
Diagnosis of Blood Clots in the Brain
Doctors use various tests to diagnose blood clots in the brain, including:
- Blood tests help determine clotting rates and blood sugar levels.
- Imaging techniques:
- CT scans provide detailed information about the brain, revealing bleeding or injury.
- MRI tests can detect brain cell damage
- Cerebral angiograms offer a complete view of brain and neck arteries.
- Ultrasound scans check the brain's size and shape, potentially locating the clot's origin.
- Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) identifies blood vessel abnormalities and examines blood flow.
- V/Q scans measure oxygen levels in the blood, showing any blockages.
- In some cases, doctors may order a carotid ultrasound to check if a clot fragment from the neck has travelled to the brain.
Treatment of Blood Clot in the Brain
Doctors employ various methods for blood clot in the brain treatment, aiming to restore normal blood flow and minimise brain damage. The approach depends on the clot's size, location, and cause.
- Medications: Anticoagulant medications or blood thinners prevent new clot formation and prevent existing ones from growing. In emergency cases, thrombolytics (clot-busting drugs) rapidly dissolve clots. These are most effective when administered within hours of symptom onset.
- Surgery: For severe cases, mechanical thrombectomy may be necessary. This surgical procedure involves removing the clot from the brain's main artery using a mesh-equipped device.
In some instances, doctors might recommend burr hole drainage or craniotomy to remove blood clots and relieve pressure.
Additionally, stents can be placed in brain blood vessels to maintain proper flow, while vena cava philtres catch clots before they reach vital organs.
Complications of Blood Clot in the Brain
Blood clots in the brain can cause severe complications, impacting various bodily functions:
- One of the most serious consequences is the formation of a pulmonary embolism, where a clot travels to the lungs, potentially causing life-threatening breathing difficulties.
- Kidney damage is another possible complication, which can result in renal failure if left untreated.
- Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) may also develop, particularly in the legs or arms.
- Pregnant women face an increased risk of clot formation in the pelvic or lower limb veins.
- These complications can cause permanent brain damage, loss of specific abilities, and, in severe cases, death. Timely medical intervention is crucial to minimise the risk of these life-altering complications.
When to See a Doctor
Seeking immediate medical attention is crucial when experiencing symptoms suggestive of a blood clot in the brain. These symptoms include:
- Sudden severe headaches
- Difficulty speaking or understanding speech
- Numbness or weakness on one side of the body
- Sudden vision problems
- Seizures
- Dizziness and confusion, or loss of consciousness
Delaying medical attention can lead to severe brain damage, disability, or even death. A neurologist should evaluate the patient quickly for accurate diagnosis and timely treatment.
Is it Possible to Prevent Blood Clots in the Brain?
Preventing blood clots in the brain is possible through lifestyle changes and medical management.
- Staying physically active helps promote healthy blood circulation, reducing the risk of clot formation.
- Maintaining a healthy weight & quitting smoking are crucial steps.
- Controlling blood pressure and diabetes also plays a vital role.
- Staying hydrated and taking breaks during long periods of immobility can help prevent clots.
- Compression stockings may be beneficial for some individuals.
- It's essential to limit the intake of unhealthy foods and salt, as well as alcoholic consumption.
- Treating the root cause of potential clots and managing medical concerns are key strategies in prevention.
- Discussing medications with doctors is also essential for comprehensive prevention.
Conclusion
Blood clots in the brain pose a serious health risk, demanding immediate attention and swift action. By understanding the warning indicators and risk factors, individuals can better protect themselves & seek timely medical help when needed. The importance of lifestyle changes and proper management of underlying health conditions cannot be overstated in preventing brain clots.
Advancements in medical and clinical technology have improved the diagnosis & treatment of brain clots, offering hope to those affected. However, prevention remains the best approach. By staying informed, managing chronic diseases, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and addressing risk factors, we can lower the likelihood of experiencing this dangerous condition.
FAQ's
1. Can blood clots on the brain be treated?
Yes, blood clots in the brain are treatable. Treatment options include anticoagulants, thrombolytics, and mechanical thrombectomy. Early detection & prompt treatment significantly improve outcomes. Rehabilitation may be necessary for patients who have suffered brain damage.
2. Are Brain Clots Curable?
Brain clots are curable, but outcomes vary based on the clot's cause, type, size, location, and the patient's overall health. Early identification of the condition and timely intervention are crucial for successful recovery.
3. Can a blood clot in the brain dissolve on its own?
While the body has natural processes to break down clots, blood clots in the brain often require medical intervention. Anticoagulants can prevent new clots from forming and allow the body time to dissolve existing ones.
4. What food should be avoided for a blood clot?
To reduce blood clot risk, avoid processed foods, sugary drinks, trans fats, and red and processed meats. Limit salt intake and alcohol consumption, as excessive amounts can increase clot risk.
5. Can stress induce blood clots in the brain?
Yes, severe or chronic stress can indirectly contribute to blood clot formation in the brain. Stress can result in unhealthy lifestyle habits that increase the risk of conditions associated with blood clots.
ENQUIRY FORM
SELECT CATEGORIES
-
Neurosciences (16)
-
Neurology (37)
-
Neurosurgery (14)
-
Orthopaedics (48)
-
Oncology (33)
-
Obstetrics and gynecology (51)
-
Pulmonology (23)
-
Urology (20)
-
Nephrology (13)
-
Psychiatry (7)
-
Dietetics and Nutrition (111)
-
General Medicine (63)
-
Cardiac Sciences (30)
-
Vascular & Endovascular Surgery and Interventional Radiology (10)
-
Gastroenterology (46)
-
Endocrinology (23)
-
Plastic Surgery (10)
-
Critical Care Medicine (5)
-
COVID-19 (16)
-
Dermatology (16)
-
Emergency Care (1)
-
Ophthalmology (4)
-
Pediatrics (14)
-
Laparoscopic and Bariatric Surgery (8)
-
ENT (15)
-
Kidney Transplant (1)
-
Liver Transplantation and Hepatobiliary Surgery (5)
-
General Surgery (3)
-
Internal Medicine (5)
-
Medicine Information
Traumatic Brain Injury: Types, Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
YOU MAY ALSO LIKE
RECENT BLOGS
-

Direct Anterior Approach in Total Hip Replacement: Advantages and Challenges
10 April 2025
Read More
-

Zinc Deficiency: Signs and Symptoms, Causes, Treatment
9 April 2025
Read More
-

Chest Pain When Coughing: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
9 April 2025
Read More
-

12 Health Benefits of Eating Mushrooms
8 April 2025
Read More
-

7 Health Benefits of Blood Donation You Should Know About
8 April 2025
Read More
-

Implantation Bleeding Vs Periods: Know the Difference
28 February 2025
Read More
-

Bloating During Ovulation: Symptoms, Causes and Remedies
28 February 2025
Read More
-

Itching During Dengue: Causes, Treatment and Home Remedies
18 February 2025
Read More
Have a Question?
If you cannot find answers to your queries, please fill out the enquiry form or call the number below. We will contact you shortly.